厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 07 Introduction to Crystallography

Chapter 7 Introduction to Crystallography Diamonds
Chapter 7 Chapter 7 Introduction to Introduction to Crystallography Crystallography Diamonds

7.1 periodicity and lattices of crystal structure 7.1.1 The characteristics of crystal structure 1.A few definitions: Solids can be divided into to primary categories, crystalline and amorphous. Crystalline Solids that are built from atoms or molecules arranged in a periodic manner in space. Amorphous Solids posses short range order only. They are not related through symmetry. Short Range Order:Fixed bond lengths and angles Long Range Order:Associated with a lattice point Crystals: Crystals are solids that are built from atoms or molecules arranged in a periodic manner in space. Crystalline vs.Amorphous of SiO2 Quartz:(Crystalline) Glass:(Amorphous) Both Short and Long Range Order Short Range Order Only Oxygen Silicon
7.1 periodicity and lattices of crystal structure 7.1.1 The characteristics of crystal structure 1. A few definitions: • Solids can be divided into to primary categories, crystalline and amorphous. • Crystalline Solids that are built from atoms or molecules arranged in a periodic manner in space. • Amorphous Solids posses short range order only. They are not related through symmetry. • Short Range Order: Fixed bond lengths and angles • Long Range Order: Associated with a lattice point Crystals: Crystals: Crystals are solids that are built from atoms or Crystals are solids that are built from atoms or molecules arranged in a periodic manner in space. molecules arranged in a periodic manner in space
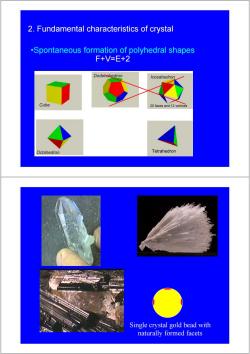
2.Fundamental characteristics of crystal .Spontaneous formation of polyhedral shapes F+V=E+2 Dodecahedron Icosahedron Cube 20 faces and 12 vertices Octahedron Tetrahedron Single crystal gold bead with naturally formed facets
2. Fundamental characteristics of crystal •Spontaneous formation of polyhedral shapes F+V=E+2 Single crystal gold bead with naturally formed facets
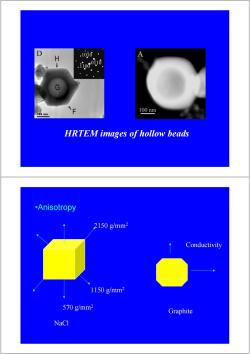
H 1010· .rooind 100nm 100nm HRTEM images of hollow beads •Anisotropy 2150g/mm2 Conductivity 1150g/mm2 570g/mm2 Graphite NaCl
HRTEM images of hollow beads •Anisotropy NaCl 570 g/mm2 1150 g/mm2 2150 g/mm2 Graphite Conductivity

.Definite sharp melting points ·Symmetry -X-ray diffraction by crystals 7.1.2 The lattice and unit cell ·Lattice: A periodic pattern of points in space,such that each lattice point has identical surroundings. 。 Can be reproduced by translational motion along the vector between any two points
• Symmetry •Definite sharp melting points •X-ray diffraction by crystals t T 7.1.2 The lattice and unit cell • Lattice: • A periodic pattern of points in space, such that each lattice point has identical surroundings. • Can be reproduced by translational motion along the vector between any two points

a.The lattice and its unit in 1D: T=ma(m=0,±1,±2,.…) 5 )⊙⊙ ⊙ ,· ● Figure 1.13 A one-dimensional lattice. unit cell and its choice for one-dimensional lattice One dimensional lattice
a. The lattice and its unit in 1D: T = ma (m = 0, ±1, ± 2,…) unit cell and its choice for one-dimensional lattice One dimensional lattice
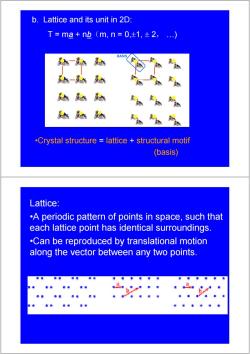
b.Lattice and its unit in 2D: T=ma+nb(m,n=0,±1,±2,.…) BASIS .Crystal structure lattice structural motif (basis) Lattice: .A periodic pattern of points in space,such that each lattice point has identical surroundings. .Can be reproduced by translational motion along the vector between any two points
b. Lattice and its unit in 2D: T = ma + nb(m, n = 0,±1, ± 2, …) •Crystal structure = lattice + structural motif (basis) Lattice: •A periodic pattern of points in space, such that each lattice point has identical surroundings. •Can be reproduced by translational motion along the vector between any two points
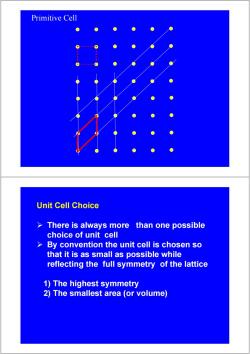
Primitive Cell Unit Cell Choice There is always more than one possible choice of unit cell > By convention the unit cell is chosen so that it is as small as possible while reflecting the full symmetry of the lattice 1)The highest symmetry 2)The smallest area (or volume)
Primitive Cell Unit Cell Choice ¾ There is always more than one possible choice of unit cell ¾ By convention the unit cell is chosen so that it is as small as possible while reflecting the full symmetry of the lattice 1) The highest symmetry 2) The smallest area (or volume)
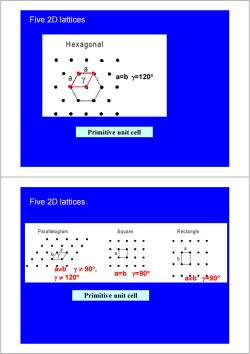
Five 2D lattices Hexagonal a=by=120° Primitive unit cell Five 2D lattices Parallelogram Square Rectangle a a≠bY≠90°, Y≠120° a=by=90° ◆ab”y-90° Primitive unit cell
Five 2D lattices a=b γ=120° Primitive unit cell Five 2D lattices a=b γ=90° a≠b γ=90° a≠b γ ≠ 90° , γ ≠ 120° Primitive unit cell
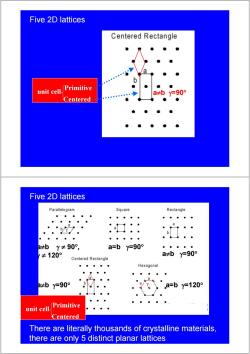
Five 2D lattices Centered Rectangle unit cell. Primitive a≠by=90° Centered Five 2D lattices Parallelogram Square Rectangle a b 日≠bY≠90°, a=by=90° ≠120° a≠by=90° Centered Rectangle Hexagonal a 2≠by=90° a=by=120° unit cell. Primitive Centered There are literally thousands of crystalline materials, there are only 5 distinct planar lattices
Five 2D lattices unit cell a≠b γ=90° Centered Primitive Five 2D lattices a=b γ=90° a≠b γ=90° a≠b γ=90° a=b γ=120° a≠b γ ≠ 90° , γ ≠ 120° unit cell Centered Primitive There are literally thousands of crystalline materials, there are only 5 distinct planar lattices
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 06 The polyatomic molecules.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 05 The structure of polyatomic molecules.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 04 The structure of diatomic molecules.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 03 Molecular symmetry and symmetry point group.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 02 The structure and properties of atoms.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 01 The basic knowledge of quantum mechanics.pdf
- Chemcal Reviews:Classical Valence Bond Approach by Modern Methods.pdf
- Nature Chemistry:Quadruple bonding in C2 and analogous eight-valence electron species.pdf
- 化学品毒性鉴定技术规范(2005年6月).pdf
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第八章 吸光光度法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第七章 重量分析法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第六章 沉淀滴定法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第四章 络合滴定法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第五章 氧化还原滴定(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第三章 酸碱滴定法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第二章 分析化学中的误差与数据处理(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第一章 绪论(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末试题(试卷)C(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末试题(试卷)B(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末试题(试卷)A(含答案).docx
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 08 The structures and properties of metals and alloys.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 09 Structural chemistry of ionic compounds.pdf
- 《生命的化学》:混合学习在基础生物化学应用中的效果分析(甘肃农业大学:唐勋,张宁,周香艳,吴兵,王旺田,王翠玲,杨德龙).pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十二章 蛋白质的生物合成 Protein Synthesis.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 核酸 nucleic acids(主讲:张宁).pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 生物氧化与氧化磷酸化 Biological Oxidation & Oxidative Phosphorylation.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 蛋白质的酶促降解和氨基酸代谢 Degradation of protein and metabolism of amino acid.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《基础生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 绪论 Fundamental Biochemistry(主讲:张宁).pdf
- 湖南大学:《基础无机化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Inorganic Chemistry Experiment.doc
- 湖南大学:《基础物理化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2018教学大纲基础物理化学实验(A)Physical Chemistry Experiment(化工).doc
- 湖南大学:《基础物理化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2018教学大纲基础物理化学实验(1)Physical Chemistry Experiment(化学、应化).doc
- 湖南大学:《基础物理化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2018教学大纲基础物理化学实验(2)Physical Chemistry Experiment(化学、应化).doc
- 湖南大学:《基础化学实验》教课程教学资源(教学大纲)2018基础化学实验教学大纲(环科综合)Basic Chemistry Experiment.doc
- 湖南大学:化学化工学院本科专业(2018 版)课程教学大纲合集汇编4(学门、学类核心课、选修、通识选修).doc
- 湖南大学:化学化工学院本科专业(2018 版)课程教学大纲合集汇编1(学类核心、专业课、选修课).doc
- 湖南大学:化学化工学院本科专业(2018 版)课程教学大纲合集汇编2(应用化学).doc
- 湖南大学:化学化工学院本科专业(2018 版)课程教学大纲合集汇编3(化工).doc
- 湖南大学:《基础有机化学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)有机化学实验Ⅱ.pdf
- 湖南大学:《基础无机化学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)基础无机化学实验.doc
- 湖南大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)物理化学实验教材(共22个实验).doc
