厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 05 The structure of polyatomic molecules

Chapter 5 Stucture of polyatomic molecules (A) 5.1 Theory of hybrid orbital and atomic orbital hybridization 1.Theory of hybrid orbital Two Theories of Bonding MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY valence electrons are delocalized valence electrons spread over entire molecule. VALENCE BOND THEORY 。 valence electrons are localized between atoms (or are lone pairs). half-filled atomic orbitals overlap to form bonds
Chapter 5 Stucture of polyatomic molecules (A) MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY • valence electrons are valence electrons are delocalized delocalized • valence electrons spread over entire molecule. valence electrons spread over entire molecule. Two Theories of Bonding Two Theories of Bonding VALENCE BOND THEORY VALENCE BOND THEORY • valence electrons are valence electrons are localized localized between atoms (or are between atoms (or are lone pairs). lone pairs). • half-filled atomic filled atomic orbitals orbitals overlap to form bonds. overlap to form bonds. §5.1 Theory of hybrid orbital and atomic orbital hybridization 1. Theory of hybrid orbital
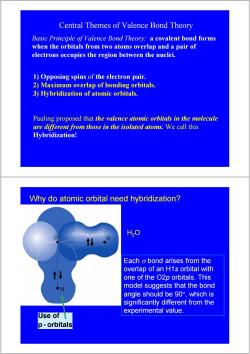
Central Themes of Valence Bond Theory Basic Principle of Valence Bond Theory:a covalent bond forms when the orbitals from two atoms overlap and a pair of electrons occupies the region between the nuclei. 1)Opposing spins of the electron pair. 2)Maximum overlap of bonding orbitals. 3)Hybridization of atomic orbitals. Pauling proposed that the valence atomic orbitals in the molecule are different from those in the isolated atoms.We call this Hybridization! Why do atomic orbital need hybridization? H20 Each o bond arises from the overlap of an H1s orbital with one of the O2p orbitals.This ●H model suggests that the bond angle should be9o°,which is significantly different from the experimental value. Use of p-orbitals
Central Themes of Valence Bond Theory 1) Opposing spins of the electron pair. 2) Maximum overlap of bonding orbitals. 3) Hybridization of atomic orbitals. Pauling proposed that the valence atomic orbitals in the molecule are different from those in the isolated atoms. We call this Hybridization! Basic Principle of Valence Bond Theory: a covalent bond forms when the orbitals from two atoms overlap and a pair of electrons occupies the region between the nuclei. Use of p - orbitals H2O Why do atomic orbital need hybridization? Each σ bond arises from the overlap of an H1s orbital with one of the O2p orbitals. This model suggests that the bond angle should be 90°, which is significantly different from the experimental value
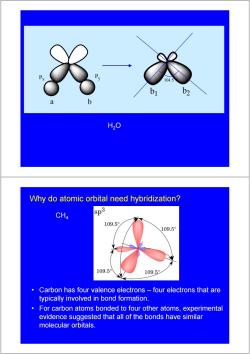
P 104.5 b1 b2 H2O Why do atomic orbital need hybridization? CH4 sp3 109.5 109.5° 109.5 109.5 Carbon has four valence electrons four electrons that are typically involved in bond formation. For carbon atoms bonded to four other atoms,experimental evidence suggested that all of the bonds have similar molecular orbitals
Px Py a b 104.5 b1 b2 H2O • Carbon has four valence electrons – four electrons that are typically involved in bond formation. • For carbon atoms bonded to four other atoms, experimental evidence suggested that all of the bonds have similar molecular orbitals. CH4 Why do atomic orbital need hybridization?

b.How do atomic orbital hybridize? 中n=C中,+C22m+C3中2py+C4中2pr If we begin with n AO's,we must end up with n orbitals after hybridization. All n hybrids are equivalent except for directionality same energy. 2.Construction of hybrid orbitals
b. How do atomic orbital hybridize? h s px py pz c c c c φ = 1 φ2 + 2φ2 + 3 φ2 + 4φ2 If we begin with n AO’s, we must end up with n orbitals after hybridization. All n hybrids are equivalent except for directionality Æ same energy. 2. Construction of hybrid orbitals
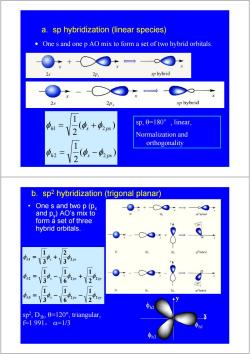
a.sp hybridization (linear species) One s and one p AO mix to form a set of two hybrid orbitals. 2s sp hybrid 2Px sp hybrid -+ sp,0=l80°,linear, Normalization and orthogonality 0h2 1V2 s b.sp2 hybridization (trigonal planar) One s and two p(Px and py)AO's mix to form a set of three 30 hybrid orbitals. 1 2 <30! 1 25 h2 sp2,Dh,0=l20°,triangular, f=1.991,=1/3 h
a. sp hybridization (linear species) • One s and one p AO mix to form a set of two hybrid orbitals. ( ) 2 1 ( ) 2 1 2 2 1 2 h s px h s px φ φ φ φ φ φ = − = + sp, θ=180°, linear, Normalization and orthogonality h s px py h s px py h s px 3 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 6 1 3 1 2 1 6 1 3 1 3 2 3 1 φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ = − − = − + = + • One s and two p (px and py) AO’s mix to form a set of three hybrid orbitals. b. sp2 hybridization (trigonal planar) sp2, D3h, θ=120°, triangular, f=1.991, α=1/3 φh1 φh2 φh3 x y

=a,,+b,中2x+C,02pmy For equivalent hybridization:the weighting of s orbital in each hybrid orbital is 1/3,and therefore a,=V1/3 中i=V1/34,+b,42m+C,中2py Supposed is parallel to the x-axis and is perpendicular to the y-axis 中n1=V1/30,+b,2m Normalization 中a1=V1/30,+V2/30 中1=V1/30+√21342x 中n=V1/30,+b,2x+C,py Normalization and orthogonality a,2+b2+c,2=1 2 1/3+b,2+c,2-1 a1a2+b,b2+cc2=0 1/3+√2/3b2+0c2=0 b2=-1/6 C2=±V1/2 h2 =V1/3。-1/642x+1/24p =V1/30,-V1/64m-V1/24m
hi i s i px i py a b c φ = φ + φ2 + φ2 For equivalent hybridization: the weighting of s orbital in each hybrid orbital is 1/3, and therefore = 1/ 3 i a Supposed φh1 is parallel to the x-axis and is perpendicular to the y-axis. h s px h s i px b 1 2 1 2 1/ 3 2 / 3 1/ 3 φ φ φ φ φ φ = + = + Normalization hi s i px i py b c 2 2 φ = 1/ 3φ + φ + φ hi s i px i py b c 2 2 φ = 1/ 3φ + φ + φ h1 s 3 2 px φ = 1/ 3φ + 2 / φ Normalization and orthogonality 1/ 3 2 / 3 0 0 1/ 3 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 + + ⋅ = + + = b c b c 0 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 + + = + + = a a b b c c a b c b2 = − 1/ 6 c2 = ± 1/ 2 h2 s 2 px 2 py φ = 1/ 3φ − 1/ 6φ + 1/ 2φ h3 s 2 px 2 py φ = 1/ 3φ − 1/ 6φ − 1/ 2φ
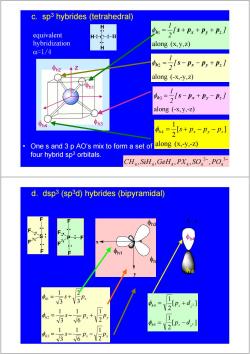
c.sp3 hybrides (tetrahedral) equivalent 1= 2+px+p,+P:] -H hybridization H along (x,y,z) c=1/4 2 22s-n-p,+:/ along (-x,-y,Z) 1 :=2s-Px+P,-P:] along (-x,y,-Z) h4 中n3 s+px -Py-p: 2 One s and 3 p AO's mix to form a set of along (x,-y,-Z) four hybrid sp3 orbitals. CH,SiH,GeHa,PX,SO,PO d.dsp3(sp3d)hybrides (bipyramidal) n3 1 m= 1 =V2Ip.+d:] 0h2= 12 Vlp:-d:] 1 1 S- 3 6 Px 2
H C H H H φh1 φh2 φh4 φh3 z along (-x,-y,z) 2 [ ] 2 1 h px py pz φ = s − − + along (x, y,z) 1 [ ] 2 1 h x y z φ = s + p + p + p along (x,-y,-z) [ ] 2 1 h 4 x y z φ = s + p − p − p along (-x,y,-z) 3 [ ] 2 1 h px py pz φ = s − + − • One s and 3 p AO’s mix to form a set of four hybrid sp3 orbitals. equivalent hybridization α=1/4 c. sp3 hybrides (tetrahedral) − 3− 4 2 4 4 4 4 4 CH , SiH ,GeH , PX , SO , PO P F F F F F h x y h x y h x s p p s p p s p 2 1 6 1 3 1 2 1 6 1 3 1 3 2 3 1 3 2 1 = − − = − + = + φ φ φ φh1 φh2 x y φh3 [ ] 2 1 [ ] 2 1 2 2 5 4 z h z z h z p d p d = − = + φ φ φh4 φh5 z S F F F F d. dsp3 (sp3d) hybrides (bipyramidal)
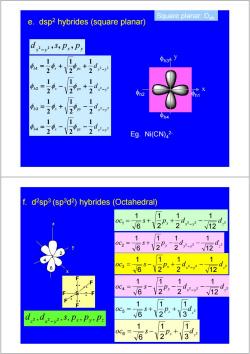
Square planar:D4h e.dsp2 hybrides (square planar) 中1= 9 d: φn2 h2 中n31 2 2 2 Eg.Ni(CN)2- f.d2sp3 (sp3d2)hybrides (Octahedral) 1 1 0G6+22.+24 V12 11 1 oc=65+12P, d2- 2V12 11 6-2+ -dz 1 11 oc=16-V2P,-2d2 1 0C5 =S十 d2 dd5,PxPyP= √ 1 1 0C6 √6 2P+3
Square planar: D4h 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 4 3 2 1 h s py x y py x y h s px x y h s px x y h s d d d d − − − − = − − = + − = − + = + + φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ φ x y x y d 2 2 ,s, p , p − φh1 x y φh3 φh2 φh4 Eg. Ni(CN)4 2- e. dsp2 hybrides (square planar) 5 1 2 3 4 6 x y z 2 3 1 2 1 6 1 5 z z oc = s + p + d 2 2 2 12 1 2 1 2 1 6 1 1 x y z oc = s + px + d − d − 2 2 2 12 1 2 1 2 1 6 1 2 x y z oc = s + py − d − d − 2 2 2 12 1 2 1 2 1 6 1 3 x y z oc = s − px + d − d − 2 2 2 12 1 2 1 2 1 6 1 4 x y z oc = s − py − d − d − 2 3 1 2 1 6 1 6 z z oc = s − p + d x y z z x y d 2 ,d 2 2 ,s, p , p , p − f. d2sp3 (sp3d2) hybrides (Octahedral) F S F F F F F
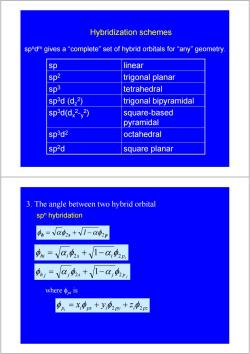
Hybridization schemes spndm gives a“complete'”set of hybrid orbitals for“any”geometry. sp linear sp2 trigonal planar sp3 tetrahedral sp3d (d,2) trigonal bipyramidal sp3d(d,2-y2) square-based pyramidal sp3d2 octahedral sp2d square planar 3.The angle between two hybrid orbital spn hybridation 4n=Va02、+V1-a42p 中m=Va功,+V1-a,2n ,=Va中,+V1-a,4p whereφnmis 中p=X,中x+y,02py+2,02p
Hybridization schemes spndm gives a “complete” set of hybrid orbitals for “any” geometry. sp octahedral 3d2 sp trigonal bipyramidal 3d (dz 2) square-based pyramidal sp3d(dx 2-y 2) sp square planar 2d sp tetrahedral 3 sp trigonal planar 2 sp linear 3. The angle between two hybrid orbital spn hybridation h 2s 2 p φ = αφ + 1−αφ p j φh j = α j φ2s + 1−α j φ2 pi hi i 2s i 2 φ = α φ + 1−α φ p i px i py i pz x y z i φ = φ + φ2 + φ2 where φpi is
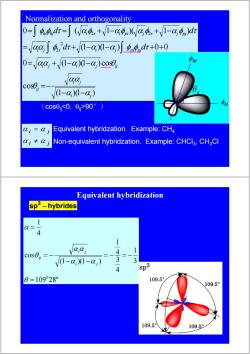
Normalization and orthogonality 0=∫44,dr=∫(Va4+V1-g)(Wa4,+V1-cgn)dr -aaSdr+(1-@)-@)o.dr+0+0 O-aa,+/(1-a)(-@,)cose aa V1-a)0-a) (c0s00,0>90°) Equivalent hybridzation.Example:CH4 i≠0j Non-equivalent hybridzation.Example:CHCl3,CHaCl Equivalent hybridization sp3-hybrides 1 Q= 4 1 aaj 4 1 V1-a,1-a) 3 4 sp3 0=10928" 109.5 109.5° 109.59 109.5
(1 )(1 ) cos 0 (1 )(1 ) cos (1 )(1 ) 0 0 0 ( 1 )( 1 ) 2 2 2 2 i j i j ij i j i j ij i j s i j pi pj hi hj i s i pi j s j pj d d d d α α αα θ αα α α θ αα φ τ α α φ φ τ φ φ τ αφ αφ α φ α φ τ − − =− = + − − = + − − + + = = + − + − ∫ ∫ ∫ ∫ Equivalent hybridzation. Example: CH4 Non-equivalent hybridzation. Example: CHCl3, CH3Cl i j i j α α α α ≠ = (cosθij90°) φ hi φ hj θ ij Normalization and orthogonality sp3 − hybrides 109 28" 3 1 4 3 4 1 (1 )(1 ) cos 4 1 0 = = − = − − − = − = θ α α α α θ α i j i j ij Equivalent hybridization
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 04 The structure of diatomic molecules.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 03 Molecular symmetry and symmetry point group.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 02 The structure and properties of atoms.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 01 The basic knowledge of quantum mechanics.pdf
- Chemcal Reviews:Classical Valence Bond Approach by Modern Methods.pdf
- Nature Chemistry:Quadruple bonding in C2 and analogous eight-valence electron species.pdf
- 化学品毒性鉴定技术规范(2005年6月).pdf
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第八章 吸光光度法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第七章 重量分析法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第六章 沉淀滴定法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第四章 络合滴定法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第五章 氧化还原滴定(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第三章 酸碱滴定法(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第二章 分析化学中的误差与数据处理(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(课后习题)第一章 绪论(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末试题(试卷)C(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末试题(试卷)B(含答案).docx
- 运城学院:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末试题(试卷)A(含答案).docx
- 西北大学:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(考研真题)2022年分析化学考研真题.pdf
- 西北大学:《分析化学 Analytical Chemistry》课程教学资源(考研真题)2021年分析化学考研真题.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 06 The polyatomic molecules.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 07 Introduction to Crystallography.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 08 The structures and properties of metals and alloys.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(电子教案)Chapter 09 Structural chemistry of ionic compounds.pdf
- 《生命的化学》:混合学习在基础生物化学应用中的效果分析(甘肃农业大学:唐勋,张宁,周香艳,吴兵,王旺田,王翠玲,杨德龙).pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十二章 蛋白质的生物合成 Protein Synthesis.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 核酸 nucleic acids(主讲:张宁).pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七章 生物氧化与氧化磷酸化 Biological Oxidation & Oxidative Phosphorylation.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 蛋白质的酶促降解和氨基酸代谢 Degradation of protein and metabolism of amino acid.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《基础生物化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 绪论 Fundamental Biochemistry(主讲:张宁).pdf
- 湖南大学:《基础无机化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Inorganic Chemistry Experiment.doc
- 湖南大学:《基础物理化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2018教学大纲基础物理化学实验(A)Physical Chemistry Experiment(化工).doc
- 湖南大学:《基础物理化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2018教学大纲基础物理化学实验(1)Physical Chemistry Experiment(化学、应化).doc
- 湖南大学:《基础物理化学实验》课程教学资源(教学大纲)2018教学大纲基础物理化学实验(2)Physical Chemistry Experiment(化学、应化).doc
- 湖南大学:《基础化学实验》教课程教学资源(教学大纲)2018基础化学实验教学大纲(环科综合)Basic Chemistry Experiment.doc
- 湖南大学:化学化工学院本科专业(2018 版)课程教学大纲合集汇编4(学门、学类核心课、选修、通识选修).doc
- 湖南大学:化学化工学院本科专业(2018 版)课程教学大纲合集汇编1(学类核心、专业课、选修课).doc
- 湖南大学:化学化工学院本科专业(2018 版)课程教学大纲合集汇编2(应用化学).doc
- 湖南大学:化学化工学院本科专业(2018 版)课程教学大纲合集汇编3(化工).doc
- 湖南大学:《基础有机化学》课程教学资源(实验讲义)有机化学实验Ⅱ.pdf
