内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第7章 输入输出流

第7章输入输出流
第7章 输入输出流

7.1文件类File 7.2文件输入输出 7.3二进制l/o 7.4 FilelnputStream类和FileOutputStream 7.5 FilterlnputStream FilterOutputStream 7.6 DatalnputStream类和DataOutputStream 7.7 BufferedlnputStream BufferedOutputStream 7.8 ObjectlnputStreamObjectOutputStream
7.1 文件类File 7.2 文件输入输出 7.3 二进制I/O 7.4 FileInputStream类和FileOutputStream 7.5 FilterInputStream类和FilterOutputStream 7.6 DataInputStream类和DataOutputStream 7.7 BufferedInputStream类和BufferedOutputStream 7.8 ObjectInputStream类和ObjectOutputStream

7.1文件类Fle 为了能够永久地保存程序中创建的数据,需 要将它们存储到文件中。 本节介绍如何使用文件File类获取文件的属 性以及删除和重命名文件
5 7.1 文件类File 为了能够永久地保存程序中创建的数据,需 要将它们存储到文件中。 本节介绍如何使用文件File类获取文件的属 性以及删除和重命名文件

7.1文件类Fle 在文件系统中,每个文件都存放在一个目录下。 文件名是一个字符串。 绝对文件名(absolute file name)是由文件名和 它的完整路径以及驱动器字母组成。例如: c:\book\Welcome.java c.book\Welcome.java是Velcome.java在 Vindows操作系统上的绝对文件名
6 在文件系统中,每个文件都存放在一个目录下。 文件名是一个字符串。 绝对文件名(absolute file name)是由文件名和 它的完整路径以及驱动器字母组成。例如: c:\book\Welcome.java 是Welcome.java在 Windows操作系统上的绝对文件名。 c:\book\Welcome.java 7.1 文件类File

7.1文件类Fle File类是文件名及其目录路径的一个包装类。 n构造一个File类的对象: Windows目录的分隔符是反斜杠l,这 里的“是“的转义字符, File file1=new File("d:\la.mp3"); File file2=new File("image/a.txt"); 斜杠/是Java的目录分隔符 注意:构造一个File类的对象,并不会在机器 上创建一个文件
File类是文件名及其目录路径的一个包装类。 ◼ 构造一个File类的对象: ◼ 注意:构造一个File类的对象,并不会在机器 上创建一个文件。 File file1 = new File("d:\\a.mp3"); File file2 = new File("image/a.txt"); Windows目录的分隔符是反斜杠\,这 里的“\\”是“\”的转义字符, 斜杠/是Java的目录分隔符 7.1 文件类File

java.io.File 根据给定路径名创建一个新File对象。这里的路 +File(pathname:String) 径名可以是一个目录,也可以是一个文件。 +File(parent:String,child:String) 为目录parent下的child创建一个File对象。这个child 可以是一个文件名,也可以是一个子目录。 +File(parent:File,child:String) +exists():boolean- 测试此路径名表示的文件或目录是否存在。存在时, +canRead():boolean 返回true;否则返回false。 +canWrite():boolean Returns true if the file represented by the File object exists and can be written. +isDirectory():boolean Returns true if the File object represents a directory. +isFileO:boolean Returns true if the File object represents a file. +isAbsolute():boolean Retums true if the File object is created using an absolute path name. +isHidden():boolean Returns true if the file represented in the File object is hidden.The exact definition of hidden is system-dependent.On Windows,you can mark a file hidden in the File Properties dialog box.On Unix systems,a file is hidden if its name begins with a period character'.'. +getAbsolutePath():String Returns the complete absolute file or directory name represented by the File object. +getCanonicalPath():String Returns the same as getAbsolutePath()except that it removes redundant 返回文件名。如:new +getName():String File(“c.:llbooklltest.dat.getName()返▣test.dat 返回文件的完整路径名和文件名。如:new +getPath():String File(“c:lbooklltest.dat).getPath(0返▣c:\bookltest.dat +getParent():String 返回文件的上级目录。如:new File("c:\\booklltest.dat").getParent()c:\book +lastModified():long Returns the time that the file was last modified. +delete():boolean Deletes this file.The method returns true if the deletion succeeds. +renameTo(dest:File):boolean Renames this file.The method returns true if the operation succeeds
8 java.io.File +File(pathname: String) +File(parent: String, child: String) +File(parent: File, child: String) +exists(): boolean +canRead(): boolean +canWrite(): boolean +isDirectory(): boolean +isFile(): boolean +isAbsolute(): boolean +isHidden(): boolean +getAbsolutePath(): String +getCanonicalPath(): String +getName(): String +getPath(): String +getParent(): String +lastModified(): long +delete(): boolean +renameTo(dest: File): boolean Creates a File object for the specified pathname. The pathname may be a directory or a file. Creates a File object for the child under the directory parent. child may be a filename or a subdirectory. Creates a File object for the child under the directory parent. parent is a File object. In the preceding constructor, the parent is a string. Returns true if the file or the directory represented by the File object exists. Returns true if the file represented by the File object exists and can be read. Returns true if the file represented by the File object exists and can be written. Returns true if the File object represents a directory. Returns true if the File object represents a file. Returns true if the File object is created using an absolute path name. Returns true if the file represented in the File object is hidden. The exact definition of hidden is system-dependent. On Windows, you can mark a file hidden in the File Properties dialog box. On Unix systems, a file is hidden if its name begins with a period character '.'. Returns the complete absolute file or directory name represented by the File object. Returns the same as getAbsolutePath() except that it removes redundant names, such as "." and ".", from the pathname, resolves symbolic links (on Unix platforms), and converts drive letters to standard uppercase (on Win32 platforms). Returns the last name of the complete directory and file name represented by the File object. For example, new File("c:\\book\\test.dat").getName() returns test.dat. Returns the complete directory and file name represented by the File object. For example, new File("c:\\book\\test.dat").getPath() returns c:\book\test.dat. Returns the complete parent directory of the current directory or the file represented by the File object. For example, new File("c:\\book\\test.dat").getParent() returns c:\book. Returns the time that the file was last modified. Deletes this file. The method returns true if the deletion succeeds. Renames this file. The method returns true if the operation succeeds. 根据给定路径名创建一个新 File对象。这里的路 径名可以是一个目录,也可以是一个文件。 测试此路径名表示的文件或目录是否存在。存在时, 返回 true;否则返回 false。 为目录parent下的child创建一个File对象。这个child 可以是一个文件名,也可以是一个子目录。 返回文件名。如:new File(“c:\\book\\test.dat”).getName()返回test.dat 返回文件的完整路径名和文件名。如:new File(“c:\\book\\test.dat”).getPath()返回c:\book\test.dat 返回文件的上级目录。如:new File(“c:\\book\\test.dat”).getParent()返回c:\book

DTestFileClass.java 1 import java.io.File; 2 public class TestFileclass 4 public static void main(String[]args)( 5 File file1 new File("d:\\a.mp3"); 6 File file2 new File("image/a.txt"); System.out.println("Is filel absolute?"file1.isAbsolute()); 8 System.out.println("Is file2 absolute?"file2.isAbsolute()); 9 10 11 曰Console☒ TestFileClass [Java Applicat: Is file1 absolute?true Is file2 absolute?false
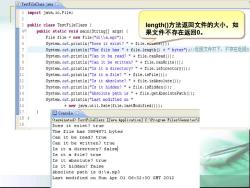
JTestFileClass.java 1 import java.io.File; 2 3 public class TestFileClass length(0方法返回文件的大小,如 % public static void main(String[]args)( 果文件不存在返回0。 5 Filefile new File("d:\\a.mp3"); 6 System.out.println("Does it exist?"file.exasts()); 7 y3tem.out.printin("The file has3"+file.length()+"bytes"):l/返回文件打下,不存在返回o 8 System.out.println("Can it be read?"file.canRead()); 9 System.out.println("Can it be written?"file.canWrite()); 10 System.out.println("Is it a directory?"file.isDirectory()); 11 System.out.println("Is it a file?"+file.isFile()); System.out.println("Is it absolute?"file.isAbsolute()) 13 System.out.println("Is it hidden?"file.isHidden()) 14 System.out.println("Absolute path is "file.getAbsolutePath()); 15 System.out.println("Last modified on 16 +new java.util.Date(file.lastModified() 旦Console3 18 TestFileClass [Java Application]C:\Program Files\Genuitec\C 19 Doe3 it exis3t?true The file has 3894871 bytes Can it be read?true Can it be written?true Is it a directory?false I31taf11e?true Is it absolute?true Is it hidden?false Absolute path is d:\a.mp3 Last modified on Sun Apr 01 06:32:30 GMT 2012
length()方法返回文件的大小,如 果文件不存在返回0
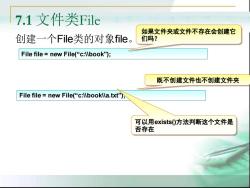
7.1文件类File 如果文件夹或文件不存在会创建它 创建一个File类的对象file。 们吗? File file new File("c:\Ibook"); 既不创建文件也不创建文件夹 File file new File("c:\lbooklla.txt"), 可以用exists(0方法判断这个文件是 否存在
File file = new File(“c:\\book"); 创建一个File类的对象file。 既不创建文件也不创建文件夹 File file = new File(“c:\\book\\a.txt"); 如果文件夹或文件不存在会创建它 们吗? 可以用exists()方法判断这个文件是 否存在 7.1 文件类File
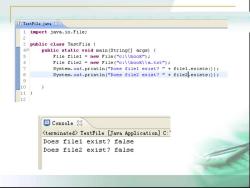
JTestFile.jawa☒ 1 import java.io.File; 2 3 public class TestFile( 4e public static void main(String[]args) File file1 new File("c:\\book"); 6 File file2 new File("c:\\book\\a.txt"); 7 System.out.println("Does file1 exist?"file1.exists()); 8 System.out.println("Does file2 exist?"file2.exists()); 9 10 11 貝Console TestFile [Java Application]C: Does file1 exist?false Does file2 exist?false
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第10章 数据库连接.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第8章 图形用户界面.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第9章 多线程.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第11章 网络编程.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第1章 JSP简介(主讲:张晓琳).ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第3章 JSP内置对象.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第2章 JSP语法.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第5章 在JSP中使用数据库.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第4章 JavaBean.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第6章 JavaServlet技术.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验一 安装与配置JSP环境.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验二 JSP语法指令标记.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验四 JSP内置对象.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验三 JSP语法指令标记.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验六 JavaBean.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验五 JSP内置对象.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验八 连接数据库.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验七 JSP与Javabean结合.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验十 分页显示记录.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《JSP编程》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验九 数据库编程技术.doc
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第5章 接口与Java API基础.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第6章 异常处理.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第4章 类与对象.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第3章 数组与字符串.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第2章 Java程序设计基础.ppt
- 内蒙古科技大学:《Java编程》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第1章 Java入门(任课教师:褚燕华).ppt
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学资源(书籍文献)数据结构与算法分析.pdf
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 图.ppt
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第六章 树与二叉树.ppt
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 数组与广义表.ppt
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 串.ppt
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 栈和队列.ppt
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 线性表.ppt
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 java描述.ppt
- 《数据结构与算法分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)前言(JAVA).ppt
- 山东理工大学:《计算机算法设计与分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第六章 分支限界法 Branch-and-Bound Algorithm.ppt
- 山东理工大学:《计算机算法设计与分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 回溯算法 Backtrack Algorithm.ppt
- 山东理工大学:《计算机算法设计与分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 贪心算法 Greedy Algorithm.ppt
- 山东理工大学:《计算机算法设计与分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 动态规划 Dynamic Programming.ppt
- 山东理工大学:《计算机算法设计与分析》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 分治与递归.ppt
