同济大学:《空气动力学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations

Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Road Map Aerodynamics tools Review of vector relations Basic flow equations Useful concepts for the implementation of the basic flow equations Continuity equation Substantial derivative Momentum equation Streamline Vorticity Energy equation Circulation Stream function Velocity potential
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Road Map Aerodynamics tools Basic flow equations Review of vector relations Continuity equation Substantial derivative Momentum equation Energy equation Circulation Vorticity Streamline Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Useful concepts for the implementation of the basic flow equations Velocity potential Stream function
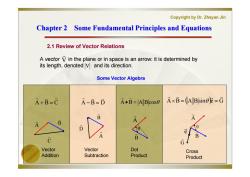
Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations A vector V in the plane or in space is an arrow:it is determined by its length,denoted V and its direction. Some Vector Algebra A+B=C A-B=D A.B=A Blcose A×B=(ABsin0E=G B 6 B G Vector Vector Dot Cross Addition Subtraction Product Product
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin A vector in the plane or in space is an arrow: it is determined by its length, denoted and its direction. Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Some Vector Algebra B A V AB A Bcos A C V A B C A G B B B A D A B D Vector Addition Vector Subtraction A B A Bsin e G θ Dot Product θ e Cross Product

Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Typical Orthogonal Coordinate Systems ---Cartesian coordinate system y P (x,y,Z) f=xi+yj+z求 A=Ai+Ayj+Ak
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Typical Orthogonal Coordinate Systems j Az Ax A A i A j A k x y z i r k r xi yj zk --- Cartesian coordinate system P (x,y,z) y x z j i A k Ay
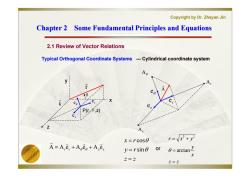
Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Typical Orthogonal Coordinate Systems ---Cylindrical coordinate system A X P(r ,z) x=rcos0 r=x+y A=A,e,+Age。+A,e2 y=rsine or 0=arctan Z=2 =2
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Typical Orthogonal Coordinate Systems Az r e e A r r z z A A e A e A e r k z z y r x r sin cos --- Cylindrical coordinate system P(r,θ,z) y x z A Ar θ z e z e r e e z z x y r x y arctan 2 2 or

Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Typical Orthogonal Coordinate Systems ---Spherical coordinate system e Z P,,0 A=A,e+Aoeo+A e Φ r=Vx2+y2+22 x=rsinecoso 0-arccos==arccos- z y=rsinesin Or x2+y2+2 z=rcos0 X arccos- x2+2
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Typical Orthogonal Coordinate Systems r e e A A e A e A e r r r cos sin sin sin cos z r y r x r --- Spherical coordinate system P(r,Φ,θ) z y x θ e A Ar A A e r e e 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 arccos arccos arccos x y x x y z z r z r x y z or Φ

Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Scalar and Vector Fields: Scalar field:A scalar quantity given as a function of coordinate space and time t. p=p(x,y,z,)=P2(r,0,z,t)=P3(r,0,,) p=p1(x,y2,)=P2(r,0,z,t)=P3(c,0,,) T=T(x,y,2,t)=T(r,0,z,t)=T(,0,p,) Vector field:A vector quantity given as a function of coordinate space and time t. V=Vi+Vj+Vk V.=V.(x,y,zt) V,=V,(x.y,z.t) V.=V.(x,y,zt)
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Scalar and Vector Fields: V V (x, y,z,t) V V (x, y,z,t) V V (x, y,z,t) V V i V j V k z z y y x x x y z ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) ( , , , ) 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 T T x y z t T r z t T r t x y z t r z t r t p p x y z t p r z t p r t Scalar field: A scalar quantity given as a function of coordinate space and time t. Vector field: A vector quantity given as a function of coordinate space and time t

Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Scalar and Vector Products: A=Ai+Ayj+A k B=Bi+Byj+B,k A.B=A,Bs +A,By +A,B Cartesian Coordinates: AxB= Bx BB. A=Ae+Ao+A e B=B.e,+Boeo+Bez A.B=A,B,+AoBo+A,B, Cylindrical Coordinates: e,eo A×B= A:Ao A B,B。 B
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Scalar and Vector Products: x y z x y z x x y y z z x y z x y z B B B A A A i j k A B A B A B A B A B A A i A j A k B B i B j B k Cartesian Coordinates: Cylindrical Coordinates: r z r z r z r r z z r z z r z z B B B A A A e e e A B A B A B A B A B A A e A e A e B B e B e B e r r
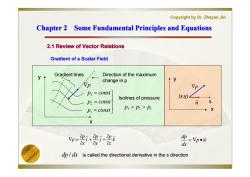
Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Gradient of a Scalar Field Gradient lines Direction of the maximum p change in p ↑y p3 =const Isolines of pressure (xy) P2=const p=const P3>P2>P X X p=2i+2j+史x =Vpn ds p/ds is called the directional derivative in thes direction
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Gradient of a Scalar Field p k z p j y p i x p p p n ds dp n Gradient lines p p const p const p const 1 2 3 Isolines of pressure 3 2 1 p p p Direction of the maximum change in p x y (x,y) s x y dp / ds is called the directional derivative in the s direction 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations

Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Example 1: fΦ=1/r,findV f=xi+y+z求 V= i+0j+2 a x2+y2+z29 Vx2+y2+z2)3 Vx2+y2+z2)9 7中= xi+yi+z求 Vx2+y2+z2)
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Example 1: If Φ=1/r, find k ˆ j z ˆ i y ˆ r x 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 r r x y z ˆ x ˆ y ˆ z x y z ˆ z x y z y ˆ x y z x ˆ ˆ x y z 1 ˆ x y z 1 ˆ x y z 1 x y z 1 r 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) i j k i j k k z j y i x k z j y i x

Copyright by Dr.Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations Example 2:Find directional derivative of=x+4x2 at point(1,-2,1) in the direction of 2-j-2 =x2yz+4xz2 Vo=(2xyz+422,x2=,x2y+8xz) =Vpi d At point(1,-2,1)Vp=(0,l,6) The unit vector for 2-j-2k Directional derivative is
Copyright by Dr. Zheyan Jin Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations Chapter 2 Some Fundamental Principles and Equations 2.1 Review of Vector Relations (0,1,6) k ˆ j 2 ˆ i ˆ 2 Example 2: 3 1 4 3 2 3 1 3 2 (0,1,6)( , , ) in the direction of ( , , ) 3 2 3 1 3 2 2xyz 4 8 ) 4xz 2 2 2 2 2 z x z x y xz x yz ( , , Find directional derivative of 2 2 x yz 4xz k ˆ j 2 ˆ i ˆ 2 at point (1,-2,1) The unit vector for At point (1,-2,1) p n ds dp Directional derivative is is
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《空气动力学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Introduction to Aerodynamics(负责人:金哲岩).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(作业习题,无答案)第六章.docx
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(作业习题,无答案)第五章.docx
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(作业习题,无答案)第四章.docx
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(作业习题,无答案)第三章.docx
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(作业习题,无答案)第二章.docx
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(作业习题,无答案)第一章.doc
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(参考资料)湖南华润电力鲤鱼江有限公司300MW火电机组培训教材《锅炉设备及系统》电子版(共十四章).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(参考资料)湖南华润电力鲤鱼江有限公司300MW火电机组培训教材《燃料运输设备及系统》电子版(共二十二章).pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(参考资料)湖南华润电力鲤鱼江有限公司300MW火电机组培训教材《汽轮机设备及系统》电子版.pdf
- 《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(教案讲义)热力发电厂授课教案教材(共八章).doc
- 华北电力大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(讲稿)原则性热力系统与全面性热力系统.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(参考资料)热力发电厂课程设计.pdf
- 《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(参考资料)热力发电厂常用计算符号表.doc
- 《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(参考资料)热力发电厂常用英语技术词汇.doc
- 《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(参考资料)汽机系统图例集.pdf
- 《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(参考资料)发电站热力系统图.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《热力发电厂》课程教学资源(大纲教案)授课教案 Thermal Power Plant.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《高等传热学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第十章 槽道内层流流动与对流换热.pptx
- 长沙理工大学:《高等传热学》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第九章 紊流强迫对流传热.pptx
- 同济大学:《空气动力学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Fundamentals of Inviscid Inviscid, Incompressible Flow.pdf
- 同济大学:《空气动力学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷 Final.doc
- 上海海洋大学:食品学院能源与动力工程和建筑环境与能源应用工程专业教学大纲汇编(2022年版).pdf
- 《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(文献资料)国家电网公司电力安全工作规程.pdf
- 《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(文献资料)电气规范汇编.doc
- 《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(试卷习题)电力系统继电保护题库(共三部分,含参考答案).doc
- 《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(试卷习题)电力系统继电保护练习题库(含参考答案).pdf
- 《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)继电保护和安全自动装置面临的问题与需要开展的研究(西安交通大学:张保会).ppt
- 华北电力大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)继电保护技术的发展.ppt
- 石河子大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(试卷习题)继电保护各章习题集(打印版,含答案).pdf
- 《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)对数字化保护的认识(西安交通大学:索南加乐).ppt
- 高等学校教材:《电力系统继电保护原理》教学参考书(第三版)电力系统继电保护原理PDF电子版(共八章,天津大学:贺家李、宋从矩).pdf
- 21世纪高等院校教材:《电力系统继电保护原理及新技术》教学教材电子书(共九章,PDF电子版,主编:李佑光、林东).pdf
- 石河子大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(电子教案)电力系统继电保护原理教案(负责人:王洪坤,打印版).pdf
- 石河子大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(实验指导)电力系统继电保护原理实验指导书(共五个实验,含附录,打印版).pdf
- 石河子大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(实验指导)电力系统继电保护原理课程设计指导书(打印版).pdf
- 石河子大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(教案大纲)电力系统综合课程设计 Comprehensuve Course Design of Power System.doc
- 石河子大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(教案大纲)电力系统综合实验教学大纲.doc
- 石河子大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(教案大纲)电力系统继电保护原理 Principle of Protection Relay.pdf
- 石河子大学:《电力系统继电保护原理》课程教学资源(教案大纲)电力系统继电保护原理实验教学大纲.pdf
