山西农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(专题讲座)Olfactory Systems in Insects Morphology and Function of antennal sensilla

Olfactory Systems in Insects: Morphology and Function of antennal sensilla 闫喜中
Olfactory Systems in Insects: Morphology and Function of antennal sensilla 闫喜中

Olfaction plays a key role in guiding the behavior of most animal species Compared with our knowledge on sensory processing in other sensory systems such as visual and auditory systems,however, olfactory coding and perception is far from being understood
▪ Olfaction plays a key role in guiding the behavior of most animal species. ▪ Compared with our knowledge on sensory processing in other sensory systems such as visual and auditory systems, however, olfactory coding and perception is far from being understood

Insects depend widely on olfactory sense to find food sources,mates,and suitable oviposition sites. Their main olfactory organs are paired antennae Olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs)housed in antennal sensilla detect environmental volatiles,convert external chemical signals into electrical information,and transmit them to the insect'brain
▪ Insects depend widely on olfactory sense to find food sources, mates, and suitable oviposition sites. ▪ Their main olfactory organs are paired antennae ▪ Olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) housed in antennal sensilla detect environmental volatiles, convert external chemical signals into electrical information, and transmit them to the insect’ brain

General Morphology of the Antenna The antennae have three segments:scape, pedicel,and flagellum S 孕分食66 Coleoptera:Curculionidae anterior view dorsal posterior scape pedicel proximal distal meriston anterior ventral cockroach 5. 10 15202530 flagellum
General Morphology of the Antenna The antennae have three segments: scape, pedicel, and flagellum Coleoptera: Curculionidae cockroach
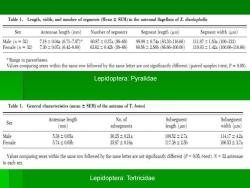
Table 1.Length,width,and number of segments (Mean SEM)in the antennal flagellum of Z.dixolophella Sex Antennae length(mm) Number of segments Segment length(μm)) Segment width (um) Male (n =32) 7.18±0.04a(6.71-7.57)a 60.87±0.37a(58-65 99.99±0.74a(83.33-116.66) 111.97±1.53a(100-133) Female (n 32) 7.30±0.07a(6.42-8.00 63.62±0.42h(59-68》 89.58±2.56(66.66-100.00) 110.93±1.42a(100.00-116.66) Range in parentheses. Values comparing sexes within the same row followed by the same letter are not significantly different (paired samples t-test,P=0.05). Lepidoptera:Pyralidae Table 1.General characteristies (mean SEM)of the antenna of T.batesi Sex Antennae length No.of Subsegment Subsegment (mm) subsegments length(μm) width(μm) Male 5.38±0.05a 36.25±0.21a 109.52±2.7a 11417±4.2a Female 5.74±0.05l 35.87±0.16a 117.38±2.5b 106.53±3.7a Values comparing sexes within the same row followed by the same letter are not significantly different (P=0.05;t-test).N=32 antennae in each sex. Lepidoptera:Tortricidae
Lepidoptera: Tortricidae Lepidoptera: Pyralidae

the types and distribution of antennal sensilla trichodea Sensilla ( chaetia sensilla(剌) basiconica Sensilla ■ Bohm sensilla ( auriculate sensilla (F) ● coeloconic sensilla(腔锥) campaniformia sensilla ( styloconica Sensilla(栓锥 ■ furcatea Sensilla ( placodea Sensilla(板) ■ Sensilla Cavity(腔) squamiformia Sensilla ( styliform complex sensillum ( Terminal sensory pegs (
the types and distribution of antennal sensilla ▪ trichodea Sensilla (毛) ▪ chaetia sensilla (刺) ▪ basiconica Sensilla (锥 ) ▪ Böhm sensilla () ▪ auriculate sensilla (耳) ▪ coeloconic sensilla (腔锥) ▪ campaniformia sensilla (钟) ▪ styloconica Sensilla (栓锥 ) ▪ furcatea Sensilla (叉) ▪ placodea Sensilla (板) ▪ Sensilla Cavity (腔) ▪ squamiformia Sensilla (鳞 ) ▪ styliform complex sensillum () ▪ Terminal sensory pegs ()

1、trichodea Sensilla The sensilla trichodea were the most numerous sensilla on the antennae,being localized and distributed randomly on all subsegments S.trichodea were hair-shaped,angled about 45'to the antennal surface. They can be divided into two subtypes according to their length:Subtype I(82.19um in length)and Subtype II (39.81um in length),which were present in both males and females (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae) Subtype I is mainly present on male antennae Subtype II is mainly present on female antennae
1、trichodea Sensilla ▪ The sensilla trichodea were the most numerous sensilla on the antennae, being localized and distributed randomly on all subsegments ▪ S. trichodea were hair-shaped,angled about 45′to the antennal surface. ▪ They can be divided into two subtypes according to their length:Subtype I(82.19μm in length) and Subtype II (39.81μm in length),which were present in both males and females (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). ▪ Subtype I is mainly present on male antennae . Subtype II is mainly present on female antennae

Function: S.trichodea play a major role in sensing mechanical stimuli and in detecting chemical stimuli in insects S.trichodea have been shown to be the olfactory receptors responsible for detecting sex pheromones (host or mate location
Function: ▪ S. trichodea play a major role in sensing mechanical stimuli and in detecting chemical stimuli in insects ▪ S. trichodea have been shown to be the olfactory receptors responsible for detecting sex pheromones (host or mate location)
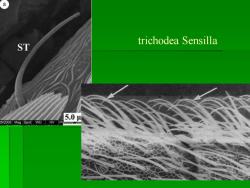
a trichodea Sensilla ST 5.04 8/2008 Mag Spot WD HV圆P
trichodea Sensilla

2、chaetia sensilla Sensilla chaetica were straight,wide at the base,and blunt (rounded)at the distal end and arose from a distinctive round collar--like socket(自状窝) Sensilla chaetica present on each fagellar segment in both sexes,angle to the antennal surface is larger than S. trichodea about 60'-90
2、chaetia sensilla ▪ Sensilla chaetica were straight, wide at the base, and blunt (rounded) at the distal end and arose from a distinctive round collar-like socket (臼状窝). ▪ Sensilla chaetica present on each fagellar segment in both sexes,angle to the antennal surface is larger than S. trichodea ,about 60′-90′
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 山西农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(实验指导,共二十一个实验).pdf
- 山西农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(作业,共六篇,含解答).pdf
- 山西农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(重点与难点指导,共六篇).pdf
- 山西农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(电子教案,共六篇,授课教师:郝赤、马瑞燕).pdf
- 山西农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(教学大纲,负责人:郝赤)Syllabus of General Entomology.pdf
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试题库及答案.pdf
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(拓展资料)案例库(二).docx
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(拓展资料)案例库(一).docx
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 昆虫群落生态学.ppt
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 数理统计预测法.ppt
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 生态系统生态学.ppt
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 昆虫种群生态学.ppt
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 绪论(主讲:李生才).ppt
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 生物多样性及其保护.ppt
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 害虫预测预报的方法.ppt
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 昆虫个体生态学.ppt
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(教案讲义,共八章).docx
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验五 群落物种多样性分析.pdf
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验四 群落组成及优势种群数量调查.pdf
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(实验指导)实验三 昆虫种群生命表的组建和应用.pdf
- 山西农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(试题库,含参考答案,共十套).docx
- 山西农业大学:《农业昆虫学》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:杨友兰).doc
- 山西农业大学:《害虫综合防治》课程教学资源(电子教案).doc
- 山西农业大学:《计算机在农业中的应用》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:李生才、李锐).doc
- 山西农业大学:《检疫除害处理》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:姚艳平).doc
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫毒理学》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:韩巨才).doc
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫生态及预测预报》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:李生才、李锐).doc
- 山西农业大学:《农田鼠害》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:刘素琪).doc
- 山西农业大学:《昆虫研究法》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:马瑞燕).doc
- 山西农业大学:《农田杂草及防除》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:刘慧平).doc
- 山西农业大学:《农业植物病理学》课程教学资源(电子教案,共九章).doc
- 山西农业大学:《植物显微技术》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:李贵全).doc
- 山西农业大学:《植病研究方法》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:王美琴).doc
- 山西农业大学:《植物保护技术》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:曹挥).doc
- 山西农业大学:《植物病害检疫》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:曹挥).doc
- 山西农业大学:《普通昆虫学》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:郝赤).doc
- 山西农业大学:《资源昆虫学》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:李锐).doc
- 山西农业大学:《普通植物病理学》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:张作刚).doc
- 山西农业大学:《植物生理学》课程教学资源(电子教案,授课教师:贺润喜).doc
- 仪器资料——Proteinsimple FluorChem_HD2 凝胶成像系统说明书 FluorChem HD2 and FC2 User Guide.pdf
