同济大学:《软件测试》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 05 Test Management

Testing is part of quality assurance. Software Testing Chapter 5: Test Management 同海大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Software Testing Testing is part of quality assurance. Chapter 5: Test Management

Outline ·Test organization Test planning and estimation Test progress monitoring and control Configuration management ·Risk and testing ·Incident management 同将大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Software Testing 15/6/82
Software Testing Outline • Test organization • Test planning and estimation • Test progress monitoring and control • Configuration management • Risk and testing • Incident management 15/6/8 2

Test Organization Understand the importance of independent testing Explain the benefits and drawbacks of independent testing Recognize different team members to be considered for the organization of a test team Realize tasks of typical test leader and tester 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/5/18 3
Software Testing 15/5/18 3 • Understand the importance of independent testing • Explain the benefits and drawbacks of independent testing • Recognize different team members to be considered for the organization of a test team • Realize tasks of typical test leader and tester Test Organization

Independent Testing Spectrum of independence: -No independent testers,developers test their own code -Independent testers within the development teams -Independent test team or group within the organization, reporting to project management or executive management -Independent testers from the business organization or user community -Independent test specialists for specific test targets such as usability testers,security testers or certification testers -Independent testers outsources or external to the organization 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Software Testing 15/6/84
Software Testing Independent Testing 15/6/8 4 Spectrum of independence: – No independent testers, developers test their own code – Independent testers within the development teams – Independent test team or group within the organization, reporting to project management or executive management – Independent testers from the business organization or user community – Independent test specialists for specific test targets such as usability testers, security testers or certification testers – Independent testers outsources or external to the organization

Why independence? For a complex or safety critical projects: -Multiple levels of testing -Some or all of the levels done by independent testers Development staff may -Participate in testing,especially at lower levels -Limit their effectiveness since lack of objectivity Independent tester should have clear direction -Have the authority to require and define test processes and rules -Take on such process-related roles 同濟大学 SoftwareTesting 15/6/8 5 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Software Testing Why independence? 15/6/8 5 For a complex or safety critical projects: – Multiple levels of testing – Some or all of the levels done by independent testers Development staff may – Participate in testing, especially at lower levels – Limit their effectiveness since lack of objectivity Independent tester should have clear direction – Have the authority to require and define test processes and rules – Take on such process-related roles
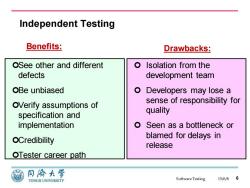
Independent Testing Benefits: Drawbacks: OSee other and different Isolation from the defects development team OBe unbiased Developers may lose a OVerify assumptions of sense of responsibility for specification and quality implementation o Seen as a bottleneck or OCredibility blamed for delays in release OTester career path 同海大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/6/86
Software Testing Independent Testing 15/6/8 6 Benefits: See other and different defects Be unbiased Verify assumptions of specification and implementation Credibility Tester career path Isolation from the development team Developers may lose a sense of responsibility for quality Seen as a bottleneck or blamed for delays in release Drawbacks:
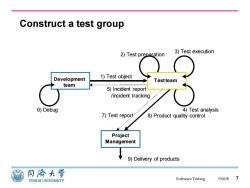
Construct a test group 2)Test preparation 3)Test execution Development 1)Test object Testteam team 5)Incident report /incident tracking 6)Debug 4)Test analysis 7)Test report' 8)Product quality control Project Management 9)Delivery of products 同源大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/6/8
Software Testing Construct a test group 15/6/8 7 Development team Test team Project Management 1) Test object 2) Test preparation 3) Test execution 8) Product quality control 9) Delivery of products 6) Debug 5) Incident report /incident tracking 7) Test report 4) Test analysis
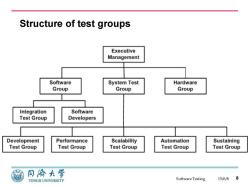
Structure of test groups Executive Management Software System Test Hardware Group Group Group Integration Software Test Group Developers Development Performance Scalability Automation Sustaining Test Group Test Group Test Group Test Group Test Group 同海大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/6/88
Software Testing Structure of test groups 15/6/8 8

Test leader/manager/coordinator Typical tasks: -Devise test strategies,plans -Ensure configuration management of -Write or review test policy testware -Consult on testing for other project activities-Ensure traceability -Test estimation Measure test progress,evaluate the -Test resource acquisition quality of the testing and the product -Lead specification -Plan any test automation -Preparation -Select tools and organize any tester -Implementation and execution of tests training -Monitor and control the test execution -Ensure implementation of the test -Adapt the test plan based on test results environment -Schedule tests -Write test summary reports 同源大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY SoftwareTesting 15/6/89
Software Testing Test leader/manager/coordinator 15/6/8 9 Typical tasks: – Devise test strategies, plans – Write or review test policy – Consult on testing for other project activities – Test estimation – Test resource acquisition – Lead specification – Preparation – Implementation and execution of tests – Monitor and control the test execution – Adapt the test plan based on test results – Ensure configuration management of testware – Ensure traceability – Measure test progress, evaluate the quality of the testing and the product – Plan any test automation – Select tools and organize any tester training – Ensure implementation of the test environment – Schedule tests – Write test summary reports

Testers Typical tasks: -Review and contribute to test plans -Analyze,review and assess user requirements,specifications -Create test suites,cases,data and procedures -Set up the test environment -Implement tests on all test levels -Execute and log the tests -Evaluate results and document problems found -Monitor testing using the appropriate tools -Automate tests -Measure performance of components and systems -Review each others'tests 同海大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY Software Testing 15/6/810
Software Testing Testers 15/6/8 10 Typical tasks: – Review and contribute to test plans – Analyze, review and assess user requirements, specifications – Create test suites, cases, data and procedures – Set up the test environment – Implement tests on all test levels – Execute and log the tests – Evaluate results and document problems found – Monitor testing using the appropriate tools – Automate tests – Measure performance of components and systems – Review each others’ tests
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《软件测试》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 04 Test Design Techniques.pptx
- 同济大学:《软件测试》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 03 Static Techniques.pptx
- 同济大学:《软件测试》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 02 Testing throughout the Software Lifecycle.pptx
- 同济大学:《软件测试》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 01 Soft Testing - Fundamentals of Testing.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 10 Multimedia.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 9 Service and Broadcast Receiver.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 8 Multi-threading.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 7 Data Persistence.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 6 List View and Custom View.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 5 Intent.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 4 Activity, Intent and UI.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 3 File structure and Layout.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 2 Introduction to Java and Object Oriented Programming.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《网络计算》课程PPT教学课件(Android Programming)Lecture 1 Introduction to Network Computing(主讲:栾浩).pptx
- 《算法基础》课程教学资源(学习笔记)算法基础 课堂笔记.pdf
- 长沙理工大学:《微机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(大纲教案)微机原理与应用授课教案(负责人:叶青,打印版).pdf
- 同济大学:《逻辑网络》课程电子教案(PPT课件)数字设计中的基本电路 Introduction to the circuits in digital design.ppt
- 同济大学:《逻辑网络》课程电子教案(PPT课件)异步时序电路分析与设计 Introduction to asynchronous circuits design.ppt
- 同济大学:《逻辑网络》课程电子教案(PPT课件)寄存器与计数器 register and counters.ppt
- 同济大学:《逻辑网络》课程电子教案(PPT课件)同步时序电路设计中的问题 Advanced design issue.ppt
- 同济大学:《软件测试》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 06 Tool Support for Testing.pptx
- 同济大学:《软件测试》课程电子教案(PPT课件)How To Do High Quality Research, Write Acceptable Papers, and Make Effective Presentations?.ppt
- 《软件测试》课程电子教案(参考资料)Standard glossary of terms used in Software Testing(Version 2.0).pdf
- 《软件测试》课程电子教案(参考资料)Certified Tester Foundation Level Syllabus Released(Version 2011).pdf
- 《软件测试》课程电子教案(参考资料)Certified Tester Foundation Level Syllabus Released(Version 2011).pdf
- 河南科技大学:信息工程学院教育技术学专业本科课程教学大纲(汇编).pdf
- 吉林大学:《人工智能》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 绪论 Artificial Intelligence(AI).ppt
- 吉林大学:《人工智能》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第七章 机器学习.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人工智能》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 知识与知识表示.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人工智能》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 人工智能的数学基础.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人工智能》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 搜索策略.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人工智能》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 智能决策支持系统.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人工智能》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 专家系统.ppt
- 吉林大学:《人工智能》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第四章 经典逻辑推理.ppt
- 吉林大学:《微机原理及汇编语言》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第10章 80X86的最新技术发展.ppt
- 吉林大学:《微机原理及汇编语言》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第1章 绪论(主讲人:赵宏伟).ppt
- 吉林大学:《微机原理及汇编语言》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第2章 8088指令系统.ppt
- 吉林大学:《微机原理及汇编语言》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第3章 汇编语言程序设计.ppt
- 吉林大学:《微机原理及汇编语言》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第4章 8088的总线操作和时序.ppt
- 吉林大学:《微机原理及汇编语言》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第5章 半导体存储器.ppt
