中国科学技术大学:《Muon物理》课程教学讲稿(技术及其应用)第二讲 慢正Muon束的产生 Low energy positive muons beam

Low energy positive muons beam Bangjiao Ye Science of Science University of Science and technology of China
Low energy positive muons beam

Cryogenic moderator Laser lonization method
Cryogenic moderator Laser Ionization method

Slow muon beam Slow muons muons which are (re-)accelerated from the muons which are almost at a rest. Beam energy is tunable,and its spread is very small. The range in the material is tunable down to sub um. Emittance is very small. Small sample can be used. polarized muons ideal as a microscopic magnetic probe to solid state physics(uSR technique) ● Depolarization of the muon spin due to local magnetic fields can be monitored through decay positrons which are emitted preferentially along the spin direction
Slow muon beam l Slow muons : muons which are (re-)accelerated from the muons which are almost at a rest. l Beam energy is tunable, and its spread is very small. a The range in the material is tunable down to sub mm. – Emittance is very small. aSmall sample can be used. lpolarized muons ideal as a microscopic magnetic probe to solid state physics (mSR technique) l Depolarization of the muon spin due to local magnetic fields can be monitored through decay positrons which are emitted preferentially along the spin direction
Study of Surface Interfaces ▣thin films ▣nanomaterials multi-layered compounds ▣small size samples ▣Atomic Physics. Surface Chemistry-Catalysis
Study of Surface & Interfaces pthin films pnanomaterials pmulti-layered compounds psmall size samples pAtomic Physics. pSurface Chemistry-Catalysis
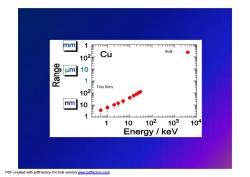
mm 1 Cu Bulk 102 m 101 Thin films 02 nm 1 ◆ 1 7 o L 1 10 102 103 104 Energy keV
Thin films Bulk

Muon cooling methods 1keV range Methods capable of muon cooling below keV within the lifetime of 2.2us: Relatively efficient,problems with muonium 1keV Frictional cooling in gasses formation,loss LE muons in extraction from gas cell Uses layer of solid rare gas as a moderator for controlled slowing down emission process. Ideal are perfect insulators with wide band-gap 10eV Cold moderator method (epithermal muons) energy (11-22 eV) Good quality beam with small emittance BUT: Laser ionization of Only pulsed operation<30 Hz rep <leV muonium complex laser required (ultraslow muons)
Muon cooling methods < 1keV range Methods capable of muon cooling below keV within the lifetime of 2.2 ms: 1 keV Frictional cooling in gasses m + m - Relatively efficient , problems with muonium formation, loss LE muons in extraction from gas cell 10 eV Cold moderator method (epithermal muons) m + Uses layer of solid rare gas as a moderator for controlled slowing down emission process. Ideal are perfect insulators with wide band-gap energy (11-22 eV) <1 eV Laser ionization of muonium (ultraslow muons) m + Good quality beam with small emittance BUT: Only pulsed operation < 30 Hz rep & complex laser required

Two methods to generate slow muon beam Cryogenic moderator method Use a layer of solid rare gas as a moderator. Initial energy is 10-100eV,and its spread is around 10eV. Time structure is determined by initial beam. slow muon muon beam solid rare-gas film
Two methods to generate slow muon beam • Cryogenic moderator method – Use a layer of solid rare gas as a moderator. – Initial energy is 10-100eV, and its spread is around 10eV. – Time structure is determined by initial beam
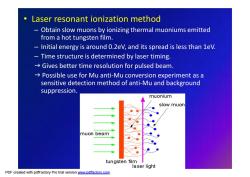
● Laser resonant ionization method Obtain slow muons by ionizing thermal muoniums emitted from a hot tungsten film. 一 Initial energy is around 0.2eV,and its spread is less than 1eV. Time structure is determined by laser timing. Gives better time resolution for pulsed beam. Possible use for Mu anti-Mu conversion experiment as a sensitive detection method of anti-Mu and background suppression. muonium slow muon muon beam tungsten film laser light
• Laser resonant ionization method – Obtain slow muons by ionizing thermal muoniums emitted from a hot tungsten film. – Initial energy is around 0.2eV, and its spread is less than 1eV. – Time structure is determined by laser timing. g Gives better time resolution for pulsed beam. g Possible use for Mu anti-Mu conversion experiment as a sensitive detection method of anti-Mu and background suppression

Cryogenic moderator PSI slow muon beam line ISIS EC slow muon beam line oCryogenic moderator method Applied cryogenic moderator method to Efficiency close to 10-4 a pulsed muon source. Initial beam energy spread is ● Yielded about 1 u/sec (*2) about 10eV ●Pulsed source ● Yielded about 700 u/sec (1) ● DC source Time-of-flight showed time resolution was about 90nsec(FWHM),according to A timing counter needs to be ISIS beam pulse width. inserted in the transport line for uSR study Better energy resolution than PSI thanks to absence of a trigger counter. Successful operation since 1993 ●Currently defunct
Cryogenic moderator PSI slow muon beam line l Cryogenic moderator method n Efficiency close to 10-4 n Initial beam energy spread is about 10eV l Yielded about 700 m/sec (*1) l DC source n A timing counter needs to be inserted in the transport line for mSR study l Successful operation since 1993 ISIS EC slow muon beam line l Applied cryogenic moderator method to a pulsed muon source. l Yielded about 1 m/sec (*2) l Pulsed source n Time-of-flight showed time resolution was about 90nsec (FWHM), according to ISIS beam pulse width. n Better energy resolution than PSI thanks to absence of a trigger counter. l Currently defunct

PSI slow muon beam line Surface u beam E~4 Mev MCP1 ■D Mirror Spin Einzel lens Einzel lens (LN:cooled) Moderator Trigger Detector (C-foil) ☒ ☒ Einzel lens Low Energy u beam (LN:cooled) 0-30 kev Gate Valye Conical Helmholtz Coils lens Sample or MCP Sample Cryostat
PSI slow muon beam line
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 中国科学技术大学:《Muon物理》课程教学讲稿(技术及其应用)第一讲 Muon的基本慨况(主讲:陈祥磊)μ(muon)子简介.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(科普报告)医学物理的发展与展望(我国医学物理发展的思考).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(科普报告)正电子在材料科学中的应用.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(科普报告)反物质探索.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《物理学》课程教学资源(科普报告)核物理与核技术的发展与应用(主讲:叶邦角).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)巨磁电阻效应及应用(主讲:李晓光).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)表面分析中的电与磁(主讲:张增明).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)只是应用于iPOD的GMR——漫谈2007诺贝尔物理奖(主讲:朱弘).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)单原子分子测控(主讲:徐春凯).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)Using Multi-gap Resistive Plate Chamber as TOF.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)物质的磁性及其应用(主讲:张泰永).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)加速器与同步辐射(主讲:戚伯云).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)铁电物理研究新进展 New Progress in Ferroelectrics(主讲:王忆).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)反物质探索(主讲:叶邦角).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)等离子体物理及应用.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《电磁学》课程教学资源(专题报告)超导电性与磁性.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)MIT-ID Interference and Diffraction.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)麦克斯韦方程和规范理论的观念起源(杨振宁)maxwell-y.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)Exam and Solutions Exam 2 Practice Problems Part 1 Solutions.pdf
- 《电磁学》课程教学资源(拓展资料)Exam and Solutions Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)01 正电子概况(1/2,主讲:叶邦角).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)02 正电子概况(2/2).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)03 正电子技术及其发展(1/2).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)04 正电子技术及其发展(2/2).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)正电子技术在材料科学中的应用(Low-k材料)Low-k materials.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)12 正电子技术在材料科学中的应用(Positron for Nano-particles).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)13 Positronium Bose-Einstein Condensation.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)14 正电子技术及其发展 Pulsed positron beam and its application.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)05 正电子技术及其发展(其它正电子技术).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)06 正电子技术及其发展(正电子技术的发展).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)07 正电子技术在材料科学中的应用.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)08 正电子技术在材料科学中的应用(半导体).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《正电子物理》课程教学讲稿(正电子在材料科学中的应用)09 正电子技术在材料科学中的应用(介孔材料).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《科学与社会》课程教学资源(研讨讲稿)反物质研究.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《科学与社会》课程教学资源(研讨讲稿)反物质的若干问题.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《科学与社会》课程教学资源(研讨讲稿)狄拉克是如何预言反物质的.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《科学与社会》课程教学资源(研讨讲稿)正电子科学与技术.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《科学与社会》课程教学资源(参考资料)CDB-1 Momentum Distribution Techniques.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《科学与社会》课程教学资源(参考资料)CDB-2 实验原理.docx
- 中国科学技术大学:《固体物理》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 晶体结构 Crystal Structure 1.1 晶体结构的周期性、晶体点阵.pdf
