重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学大纲 Basic Form of the Teaching Outline for Overseas Student of CQMU(2009)

Basic Form of the Teaching Outline for Foreign Student A Teaching Outline of Histology and Embryology Deportment of Histology and Embryology Chongqing medical university 2009.5.21
1 Basic Form of the Teaching Outline for Foreign Student A Teaching Outline of Histology and Embryology Deportment of Histology and Embryology Chongqing medical university 2009.5.21

1.Course Title:Histology and Embryology 2.Course General Description: Histology and Embryology are two courses.They are different but closely correlated Histology (Microanatomy)is a science which studies the normal microstructure of the human body and the relationship between the microstructure and its functions.Cell is the basic structural and functional units ofhuman body.Cells and extracellular matrix form the tissue. Tissue can be divided into 4 kinds of primary tissue,they are Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue,Muscle tissue and Nervous tissue.Organs are formed by four types of tissue,have their special structure and functions.For example:the skin is consisted of epithelium and connective tissue,covered outside of body. The skin can receive the stimulation of environment;secreting metabolite: regulating body temperature,at so on. Several organs which have correlated functions form system.For example digestive system is consisted of mouth,esophagus,stomach,intestine and anus. Under microscope,most of them have 4 layers;perform the function of digestive and absorption cooperatively. Embryology is a science which studies the processes ofnormal development and congenital malformation ofa human being in the maternal uterus.A sperm combine with a ovum,to form a zygote.The zygote becomes a 2
2 1. Course Title : Histology and Embryology 2. Course General Description: Histology and Embryology are two courses. They are different but closely correlated. Histology (Microanatomy) is a science which studies the normal microstructure of the human body and the relationship between the microstructure and its functions. Cell is the basic structural and functional units of human body. Cells and extra cellular matrix form the tissue. Tissue can be divided into 4 kinds of primary tissue, they are Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue, Muscle tissue and Nervous tissue. Organs are formed by four types of tissue, have their special structure and functions. For example: the skin is consisted of epithelium and connective tissue,covered outside of body. The skin can receive the stimulation of environment; secreting metabolite; regulating body temperature, at so on. Several organs which have correlated functions form system. For example: digestive system is consisted of mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestine and anus. Under microscope, most of them have 4 layers; perform the function of digestive and absorption cooperatively. Embryology is a science which studies the processes of normal development and congenital malformation of a human being in the maternal uterus. Asperm combine with a ovum, to form a zygote. The zygote becomes a
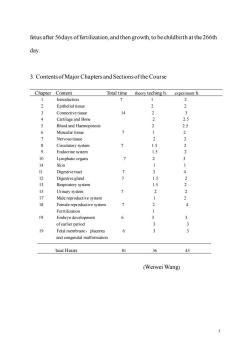
fetus after 56days offertilization,and then growth,to be childbirth at the 266th day. 3.Contents ofMajor Chapters and Sectionsofthe Course Chapter Content Total time theory teching h.experiment h. Introduction 7 2 2 Epithelial tisse 2 34 Connective tissue 14 2 Cartilage and Bone 2 Blood and Haemopoiesis 2 35 6 Muscular tissue 1 2 1 15 1.5 2 10 Lymphatic organs 2 14 Skin 1 11 Digestive tract 7 3 4 12 egland Kespiratory system 15 Urinary system 7 2 22 17 Male reproductive system 18 Female reproductivesystem > 2 4 Ferrtilization 19 Embryo development 6 3 of earlier period 3 19 Fetal membrane,placenta 6 3 and congenital malformation Total Hours 81 36 (Weiwei Wang)
3 fetus after 56days of fertilization, and then growth, to be childbirth at the 266th day. 3. Contents of Major Chapters and Sections of the Course Chapter Content Total time theory teching h. experiment h. 1 Introduction 7 1 2 2 Epithelial tissue 2 2 3 Connective tissue 14 2 3 4 Cartilage and Bone 2 2.5 5 Blood and Haemopoiesis 2 2.5 6 Muscular tissue 7 1 2 7 Nervous tissue 2 2 8 Circulatory system 7 1.5 2 9 Endocrine system 1.5 2 10 Lymphatic organs 7 2 3 14 Skin 1 1 11 Digestive tract 7 3 4 12 Digestive gland 7 1.5 2 13 Respiratory system 1.5 2 15 Urinary system 7 2 2 17 Male reproductive system 1 2 18 Female reproductive system 7 2 4 Ferrtilization 1 19 Embryo development 6 3 3 of earlier period 3 3 19 Fetal membrane,placenta 6 3 3 and congenital malformation Total Hours 81 36 45 (Weiwei Wang)

Chapter1.Introduction [Teaching aim and requirements] 1.Understanding:what are histology and Embryology. 2.Mastering:what is tissue?what is paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3.Understanding:electron microscopy and other study methods. [Teaching conte What are ogy and Embryology?Why medical students should study Hand E? 2.Histological Methods: (1)The paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin for LM (2)Other methods for LM(frozen section et al (3)The Ultra-thin sections for the Transmission Electron Microscope (Comparison between LM and EM) Scanning Electron Microscope (4)Histochemistry and cytochemistry (5)Immunocytochemistry (6)Tissue and cell culture Focaland Difficult points] Focal points The paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin Difficult points Histochemistrv and Cytochemistry. Immunocytochemistry Teaching methods Cass Teaching [Teaching hours]1 hour (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 2.Epithelial Tissue [Teaching aim and requirements] 1.Mastering:the general features and classification of epithelial tissue 2.Mastering:the structural features,distribution,classification,functions of covering Epithelium Mastering:the structural features,functions of microvilli and cilia 4.Understanding the ultrastructure and function ofcell junction 5.Understanding the structure and function of basement membrane 6.Having the conception of glandular epithelium and glands,structural features of endocrine gland and exocrine [Teaching contents] 1.General description Composition,distribution,classification,functions of the epithelium 2.Covering Epithelium
4 Chapter1. Introduction [Teaching aim and requirements] 1. Understanding: what are histology and Embryology. 2. Mastering: what is tissue? what is paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3. Understanding: electron microscopy and other study methods. [Teaching contents] 1. What are histology and Embryology? Why medical students should study H and E? 2. Histological Methods: (1) The paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin for LM (2) Other methods for LM ( frozen section et al ) (3) The Ultra-thin sections for the Transmission Electron Microscope (Comparison between LM and EM) Scanning Electron Microscope (4) Histochemistry and cytochemistry (5) Immunocytochemistry (6) Tissue and cell culture [Focal and Difficult points] Focal points The paraffin sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin Difficult points Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, Immunocytochemistry. [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching hours] 1 hour (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 2. Epithelial Tissue [Teaching aim and requirements] 1. Mastering: the general features and classification of epithelial tissue 2. Mastering: the structural features, distribution, classification, functions of covering Epithelium 3. Mastering: the structural features, functions of microvilli and cilia 4. Understanding the ultrastructure and function of cell junction 5. Understanding the structure and function of basement membrane 6. Having the conception of glandular epithelium and glands, structural features of endocrine gland and exocrine. [Teaching contents] 1. General description: Composition, distribution, classification, functions of the epithelium 2.Covering Epithelium

(1)Structural Features of covering Epithelium (2)Classification-rule (3)The common types of covering epithelium (structure,location and functions) Simple squamous epithelium Simple columnar epithelium Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium ous epithelium Transitional epithelium 4.Epithelial specialisations (1)Free surface:microvilli and cilia (2)Lateral surface: cell junctions Tight junction,Desmosome.Gap junction,Junctional complex (3)B surface basement membrane 5.Glandular epithelium and glands Focal and Difficult points] Focal points Cell junctions [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching hours]2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter3.Connective Tissue proper Teaching aim and requirements 1.Mastering:the characteristic and classification of connective tissue 2.Mastering:the structural features.functions of cells in loose connective tissue Understanding the structural features.functions of fibers and the composition of grand substance 3.Understanding the structural features,functions of dense connective tissue,adipose tissue and reticula r tissue [Teaching contents] 1 General Concention Classification of c T General characteristics:composition,Origination(mesenchymal cell) Functions part one:Connective Tissue proper 1.Loose Connective Tissue,L.C.T. (1)Structural features (2)Fibres:(structure, Location and functions)
5 (1) Structural Features of covering Epithelium (2) Classification-rule (3) The common types of covering epithelium ( structure, location and functions) Simple squamous epithelium Simple columnar epithelium Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium Stratified squamous epithelium Transitional epithelium 4. Epithelial specialisations (1) Free surface: microvilli and cilia (2) Lateral surface: cell junctions Tight junction, Desmosome, Gap junction, Junctional complex (3) Basal surface: basement membrane 5. Glandular epithelium and glands [Focal and Difficult points] Focal points The structure, location and functions of covering epithelium Difficult points Cell junctions [Teaching methods] Class Teaching [Teaching hours] 2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 3. Connective Tissue proper Teaching aim and requirements 1.Mastering: the characteristic and classification of connective tissue 2.Mastering: the structural features, functions of cells in loose connective tissue Understanding the structural features, functions of fibers and the composition of grand substance 3.Understanding the structural features, functions of dense connective tissue, adipose tissue and reticular tissue [Teaching contents] 1. General Conception Classification of C.T. General characteristics: composition , Origination(mesenchymal cell) Functions part one : Connective Tissue proper 1. Loose Connective Tissue, L.C.T. (1) Structural features (2) Fibres: (structure , Location and functions)

Collagenous fibers (white fibers) Elastic fibers (yellow fibers) Reticular fibers (3)Ground substance :composition of molecule,functions(Molecular sieve,medium) (4)Cells (structure,Location and functions) Fibroblast. ropha Plas Mast cell Fat cell Undifferentiated mesenchymal cell Wandering cells 2.D (1)Structural characteristic (2)Classification 3)Function 3.Adipose tissue ral cha racteristic and Function Tissue Structural characteristic and Function [Focal and Difficult points] Focal point ture and functions of Fibroblast,Macrophage,Plasma cell,Mast cell Difficult points The Molecular sieve [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching hours]2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter4.cartilage,bone and osteogenesis [Teaching aim and requirements] Mastering:the structural features,functions of Cartilage Understanding:the characterastic and distribution of three kind of cartilage. 2.Mastering:the structural features of osseous tissue,and three kind of bone lamellae. 3.Understanding the osteogenesis,and the growth of bone. ITeaching contentsl Cartilage (1 )The component-characterastic of cartilage:chondrocytes and cartilage matrix The form and function of chondrocytes (2)The classification of cartilage:hyaline cartilage,elastic cartilage fibrocartilage The feature-structure.location.functions of the three kinds of cartilage
6 Collagenous fibers (white fibers) Elastic fibers ( yellow fibers ) Reticular fibers (3) Ground substance :composition of molecule, functions (Molecular sieve, medium) (4) Cells (structure , Location and functions) Fibroblast, Macrophage Plasma cell Mast cell Fat cell Undifferentiated mesenchymal cell Wandering cells 2.Dense Connective tissue, D.C.T. (1) Structural characteristic (2) Classification (3) Function 3. Adipose tissue Structural characteristic and Function 4.Reticular Tissue Structural characteristic and Function [Focal and Difficult points] Focal point Structure and functions of Fibroblast, Macrophage , Plasma cell, Mast cell Difficult points The Molecular sieve [Teaching methods] Class Teaching [Teaching hours] 2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 4. cartilage ,bone and osteogenesis [Teaching aim and requirements] 1.Mastering: the structural features, functions of Cartilage. Understanding: the characterastic and distribution of three kind of cartilage. 2.Mastering: the structural features of osseous tissue, and three kind of bone lamellae. 3.Understanding the osteogenesis , and the growth of bone. . [Teaching contents] 1. Cartilage (1 )The component- characterastic of cartilage: chondrocytes and cartilage matrix The form and function of chondrocytes (2) The classification of cartilage: hyaline cartilage , elastic cartilage fibrocartilage The feature – structure, location, functions of the three kinds of cartilage

(3)Perichodrium and the growth of cartilage 2.bone (1)The component-characterastic ofosseous tissue The component of bone matrix -lamellae The form,function,location of osteocyte,osteoblast,osteoclast,osteoprogenitor cell. (2)Bone architecture Spongy bone: Compact bone: Circumferential lamellae Havensian system (osteons) Interstitial lamellae Periosteum:structure and function (1)E sse ses of ossification (2)Classification of osteogenesis Intramembranous ossification Endochondral ossification Focaland Difficult points] Focal point Characterastic of cartilage and osseous tissue.Bone architecture Difficult points Osteogenesis,formation of the long bone. 2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 5.Blood and Hematopoiesis [Teaching aim and requirements] 1.Mastering:the form.function and normal concentrations of blood cells. 2.Understanding:the structural features and function of red bone marrow,and the hemopoietic inductive microenvironment 3.Mastering:the biological fea of He emopoietic Stem Cell and Hemopoietic progenitor 4.Understanding:the rule of major morphological changes in maturation of blood cells [Teaching contents] 1.General Description:composition of blood 2、Blood Cells normal c centrations Form of LM,features of EM and function (1)Erythrocyte: Form of LM,features of RBC,reticulocyte,clinical significance (2)Leukocytes (Form and main function) >
7 (3) Perichodrium and the growth of cartilage. 2. bone (1) The component- characterastic of osseous tissue The component of bone matrix -lamellae The form ,function , location of osteocyte, osteoblast, osteoclast, osteoprogenitor cell. (2) Bone architecture Spongy bone: Compact bone: Circumferential lamellae Havensian system (osteons) Interstitial lamellae Periosteum:structure and function 3. Osteogenesis and endosteum (1) Essential processes of ossification (2) Classification of osteogenesis Intramembranous ossification Endochondral ossification [Focal and Difficult points] Focal point Characterastic of cartilage and osseous tissue. Bone architecture Difficult points Osteogenesis, formation of the long bone. [Teaching methods] Class Teaching [Teaching hours] 2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 5. Blood and Hematopoiesis [Teaching aim and requirements] 1. Mastering: the form , function and normal concentrations of blood cells. 2. Understanding: the structural features and function of red bone marrow, and the hemopoietic inductive microenvironment 3. Mastering: the biological features of Hemopoietic Stem Cell and Hemopoietic progenitor cell. 4. Understanding: the rule of major morphological changes in maturation of blood cells [Teaching contents] 1、General Description: composition of blood 2、Blood Cells normal concentrations , Form of LM, features of EM and function (1 ) Erythrocyte : Form of LM, features of RBC, reticulocyte, clinical significance (2) Leukocytes :(Form and main function)

general feature and classification granulocytes Neutrophils,Eosinophils,Basophils agranulocytes Monocyte,lymphocyte (3)Blood platelets Form of LM,features of EM and function 3、Hematopoiesis (1)Haemo poietic organs (3) Hemopoiesis Hemopoietic Stem Cell and Hemopoietic progenitor cell. Maturation of blood cells(four stages)in each cell line. The major morphological changes in maturation of blood cells Focal and Difficult points] Focal point The form,function and normal numbers of blood cells Difficult points Hemopo ietic stemcell and Hemopoietic progenitor cell.Hemopoietic inductive microenvironment [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching hours]2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter6.Muscular Tissue Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1)Master the light microscope(LM)structure of 3 types of muscular tissues (2)Master the ulrastructure of skeletal andcardiac mus (3)Master the structure of neurons [Teaching Contents] 1.General characteristics of muscular tissue 1.1 Component of muscle tissu 1.2 A specific terminology in respect of muscle cells 1.3 Classification 2.Histological and ultrastructural features of three types of muscle tissue 2.1 Skeletal muscle 2.1.1 microstructure of skeletal muscle underLM 2.1.2 Ultrastructure of skeletal muscle under EM 2.1.3 Contraction mechanism 2.2 Cardiac muscle
8 general feature and classification granulocytes: Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils agranulocytes: Monocyte, lymphocyte (3) Blood platelets Form of LM, features of EM and function 3、Hematopoiesis (1) Haemopoietic organs (2) Red bone marrow (hemopoietic inductive microenvironment) (3) Hemopoiesis Hemopoietic Stem Cell and Hemopoietic progenitor cell. Maturation of blood cells (four stages) in each cell line. The major morphological changes in maturation of blood cells [Focal and Difficult points] Focal point . The form, function and normal numbers of blood cells Difficult points Hemopoietic stem cell and Hemopoietic progenitor cell. Hemopoietic inductive microenvironment [Teaching methods] Class Teaching [Teaching hours] 2 hours (Weiwei Wang) Chapter 6.Muscular Tissue [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) Master the light microscope (LM) structure of 3 types of muscular tissues (2) Master the ultrastructure of skeletal and cardiac muscles (3) Master the structure of neurons [Teaching Contents] 1. General characteristics of muscular tissue 1.1 Component of muscle tissue 1.2 A specific terminology in respect of muscle cells 1.3 Classification 2. Histological and ultrastructural features of three types of muscle tissue 2.1 Skeletal muscle 2.1.1 microstructure of skeletal muscle under LM 2.1.2 Ultrastructure of skeletal muscle under EM 2.1.3 Contraction mechanism 2.2 Cardiac muscle

2.2.1 microstructure of cardiac muscle under LM 2.2.2 Ultrastructure of cardiac muscle under EM 2.3 Smooth muscle Focaland Difficult points] Focal points: (1)LM structure of3 types ofmusculartissues (2)EM structure of skeletal muscles (3)Structure of neurons Difficult point: EM structure of skeletal muscles [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching Hours]1 hours (Yong Tang) Chapter 7.Nervous Tissue [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1)Master the ultrastructureofsynapses (2)Master the classificationand distribution of neuroglial cells (3)Master the structure ofnerve fibers and nerve endings [Teaching Contents] Nervous Tissue 1.General characteristics 1.1 Component 1.2General function 2.Neurons 2.1 Classification 2.2 Morphology 2 3 Structure 2 3 1 Nucleu 2.3.2 Cytoplasn 2.3.3 Processes 1.Synapse 1.1 Definition of svnapse 1.2 Classification of synapses
9 2.2.1 microstructure of cardiac muscle under LM 2.2.2 Ultrastructure of cardiac muscle under EM 2.3 Smooth muscle [Focal and Difficult points] Focal points: (1) LM structure of 3 types of muscular tissues (2) EM structure of skeletal muscles (3) Structure of neurons Difficult point: EM structure of skeletal muscles [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching Hours] 1 hours (Yong Tang) Chapter 7. Nervous Tissue [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) Master the ultrastructure of synapses (2) Master the classification and distribution of neuroglial cells (3) Master the structure of nerve fibers and nerve endings [Teaching Contents] Nervous Tissue 1. General characteristics 1.1 Component 1.2 General function 2. Neurons 2.1 Classification 2.2 Morphology 2.3 Structure 2.3.1 Nucleus 2.3.2 Cytoplasm 2.3.3 Processes 1. Synapse 1.1 Definition of synapse 1.2 Classification of synapses

1.3 Structural features of every part in the chemical synapse 2.1.Neuroglia in central nervous system 2.1.1.Astrocytes 2.1.2 Oligodendrocytes 2.1.3 Microglia 2.14.Ep ymal cells 2.2.Neuoglia in peripheral nervous system 3.Nerve fibers 3.1.Mvelinated nerve fibers 3.2.Unmyelinated nerve fibers 4.Nerves and nerve endings 4I Nerves Nerve endings 4.21.Afferent endings 4.2.2 Efferent nerve endings [Focaland Difficult points] Focal point Ultrastructure ofsynapses Difficult points Structure of nerve fibers and nerve endings [Teaching methods]Class Teaching Teaching Hours]2hours (Yong Tang) Chapter8.Circulatory System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1)Master LM and EM structures of capillaries (2)Master the structural characteristics oflarge arteries medium-sized arteries and small arteries (3)Master the structure ofheart (4)Be familiar with veins,medium-sized veins and small vens [Teaching Contents] 1.General description 2.Heart
10 1.3 Structural features of every part in the chemical synapse 2. Neuroglia 2.1. Neuroglia in central nervous system 2.1.1. Astrocytes 2.1.2 Oligodendrocytes 2.1.3 Microglia 2.1.4. Ependymal cells 2.2. Neuoglia in peripheral nervous system 3. Nerve fibers 3.1. Myelinated nerve fibers 3.2. Unmyelinated nerve fibers 4. Nerves and nerve endings 4.1 Nerves 4.2. Nerve endings 4.21. Afferent endings 4.2.2 Efferent nerve endings [Focal and Difficult points] Focal point Ultrastructure of synapses Difficult points Structure of nerve fibers and nerve endings [Teaching methods]Class Teaching [Teaching Hours]2 hours (Yong Tang) Chapter 8.Circulatory System [Teaching Aim and Requirements] (1) Master LM and EM structures of capillaries (2) Master the structural characteristics of large arteries, medium-sized arteries and small arteries (3) Master the structure of heart (4) Be familiar with the structural characteristics of large veins, medium-sized veins and small veins [Teaching Contents] 1. General description 2. Heart
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊治指导(COPD,2013年修订版.pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(讲稿)慢性支气管炎——辅助检查.pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(讲稿)慢性支气管炎——诊断与鉴别诊断.pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(讲稿)慢性支气管炎——病因与发病机制.pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(讲稿)慢性支气管炎——治疗.pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(讲稿)慢性支气管炎——临床表现.pdf
- 人民卫生出版社:《医学微生物学》书籍教材PDF电子版(第8版).pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)中国高血压防治指南(第三版全文,2010年修订).pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版).pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)中国心力衰竭治疗指南(2014版).pdf
- 人民卫生出版社:《药理学》书籍教材PDF电子版(第8版).pdf
- 人民卫生出版社:《神经病学》书籍教材PDF电子版(第7版).pdf
- 人民卫生出版社:《传染病学》书籍教材PDF电子版(第8版).pdf
- 人民卫生出版社:《诊断学》书籍教材PDF电子版(第8版).pdf
- 人民卫生出版社:《人体寄生虫学》书籍教材PDF电子版(第8版).pdf
- 人民卫生出版社:《内科学》书籍教材PDF电子版(第9版,彩色).pdf
- 人民卫生出版社:《内科学》书籍教材PDF电子版(第8版).pdf
- 《西医内科学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)支气管哮喘防治指南(2020年版).pdf
- 山东中医药高等专科学校:《西医内科学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 皖南医学院:《生物化学与分子生物学》课程教学大纲(四年制本科).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(讲义)本科实验课教案.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(讲义)本科理论课教案.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学实习指导书.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程综合习题(含参考答案).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)01 绪论(负责人:王亚平).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)02 上皮组织(Epithelial Tissue).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 固有结缔组织(Connective Tissue).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)04 血液和血细胞发生(Blood and Hematopoiesis).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)05 软骨和骨(cartilage and bone).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)06 肌肉组织(Muscle Tissue).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)07 神经组织(Nerve Tissue).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)08 循环系统(Circulatory System).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)09 内分泌系统(Endocrine System).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)10 免疫系统(Immune System).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)11 皮肤(Skin).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)12 消化系统(Digestive System).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)13 呼吸系统(Respiratory System).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)14 泌尿系统(Urinary System).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)15 男性生殖系统(Male Reproductive System).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《组织学与胚胎学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)16 女性生殖系统(Female Reproductive System).ppt
