同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)固体废物1 Solid Waste Management(2)landfilling

Environmental Science-- Solid Waste Management(2)landfilling Niu Dongjie @tongji.edu.cn
Environmental Science--- Solid Waste Management (2) landfilling Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn

Table of contents o Definitions o Structure of Landfill o Landfilling operation o Siting o Landfill stibilization o leachate collection and treatment
Table of contents Definitions Structure of Landfill Landfilling operation Siting Landfill stibilization leachate • collection and treatment

Definitions of Terms oLandfil:facility disposal of waste in to soils. OSanitary landfiIl: Engineered facility for the disposal of MSW designed and operated to minimize public health and environmental impacts. o secure landfill-hazardous waste oLandfilling The process:monitoring of the stream,placement and compaction, installation of landfill environmental monitoring and control facility
Definitions of Terms Landfill: facility disposal of waste in to soils. Sanitary landfill: • Engineered facility for the disposal of MSW designed and operated to minimize public health and environmental impacts. secure landfill—hazardous waste Landfilling • The process: monitoring of the stream, placement and compaction, installation of landfill environmental monitoring and control facility

Dumping
Dumping
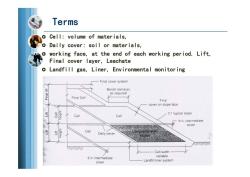
Terms o Cell:volume of materials, Daily cover:soil or materials, working face,at the end of each working period.Lift, Final cover layer,Leachate o Landfill gas,Liner,Environmental monitoring Final cover system Bench(terrace】 as required Final Cell Final cover on slope face Cell 3:1 typical siope Cell 6 in intermediate cover Cell Daily cover 汲 Cell-width 6 in intermediate varable cover Landfill liner system
Terms Cell: volume of materials, Daily cover: soil or materials, working face, at the end of each working period. Lift, Final cover layer, Leachate Landfill gas, Liner, Environmental monitoring

Sanitary Landfills Engineering principles used to: confine waste to smallest practical area reduce waste to smallest practical volume cover waste with layer of compacted soil (or tarps)each day(finishing cover is ~50 cm or more of compacted clay-rich soil) NOTE:Compaction and subsidence will continue after site is closed;any further development must be able to accommodate these potential problems. S.Hughes 2000
S. Hughes 2000 Sanitary Landfills Engineering principles used to: • confine waste to smallest practical area • reduce waste to smallest practical volume • cover waste with layer of compacted soil (or tarps) each day (finishing cover is ~50 cm or more of compacted clay-rich soil) NOTE: Compaction and subsidence will continue after site is closed; any further development must be able to accommodate these potential problems

USEFUL DEFINITIONS LEACHATE-Leachate is a combination of infiltrated precipitation and any liquids squeezed from the waste as it naturally compacts. Leachate will percolate to the base of land disposal sites due to the influence of gravity.Leachate can carry particulate matter, pollutants,biological contaminants and other constituents with it. Leachate will travel through the subsurface following the same flow direction as groundwater.All land based disposal facilities must incorporate a leachate collection and disposal system into their designs.Liners and covers must be added so as to minimize infiltration into the waste site thereby minimizing leachate production or escape LINER-Generally there are several layers of liners at the base of a land disposal site.Layers consist of compacted clay alternating with plastic.The purpose of the liner is to prevent leachate from escaping into the subsurface. CAP/COVER-Caps and covers are constructed(starting at the waste and working outward)of compacted,low permeability clay. This is followed by a flexible plastic liner(theoretically impermeable).Next comes a drainage layer designed to transport surface water away from the waste disposal site.Finally,this is followed by a layer of earth and then some type of vegetative cover
USEFUL DEFINITIONS LEACHATE - Leachate is a combination of infiltrated precipitation and any liquids squeezed from the waste as it naturally compacts. Leachate will percolate to the base of land disposal sites due to the influence of gravity. Leachate can carry particulate matter, pollutants, biological contaminants and other constituents with it. Leachate will travel through the subsurface following the same flow direction as groundwater. All land based disposal facilities must incorporate a leachate collection and disposal system into their designs. Liners and covers must be added so as to minimize infiltration into the waste site thereby minimizing leachate production or escape. LINER - Generally there are several layers of liners at the base of a land disposal site. Layers consist of compacted clay alternating with plastic. The purpose of the liner is to prevent leachate from escaping into the subsurface. CAP/COVER - Caps and covers are constructed (starting at the waste and working outward) of compacted, low permeability clay. This is followed by a flexible plastic liner (theoretically impermeable). Next comes a drainage layer designed to transport surface water away from the waste disposal site. Finally, this is followed by a layer of earth and then some type of vegetative cover

Structure of landfill oLiner system ODrainage system (leachate col lection,underground water protection system) oCover(Daily cover,intermidit cover) OGas col lection system
Structure of landfill Liner system Drainage system (leachate collection, underground water protection system) Cover(Daily cover, intermidit cover) Gas collection system
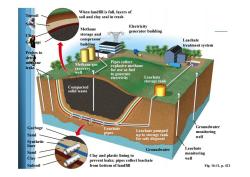
When landfill is full,layers of soil and clay seal in trash Electricity Methane generator building storage and compressor Leachate building treatment system Pipes collect Methane gas explosive methane recovery for use as fuel well to generate electricity Leachate storage tank Compacted solid waste Garbage Leachate Groundwater Leachate pumped pipes monitoring up to storage tank well for safe disposal nthetic Groundwater Leachate Clay and plastic lining to monitoring prevent leaks;pipes collect leachate well Subsoil from bottom of landfill Fig.16-11,p.421
Fig. 16-11, p. 421 When landfill is full, layers of soil and clay seal in trash Topsoil Sand Electricity generator building Clay Garbage Methane storage and compressor building Leachate treatment system Probes to detect methane leaks Pipes collect explosive methane for use as fuel to generate electricity Methane gas recovery well Leachate storage tank Compacted solid waste Garbage Leachate pipes Leachate pumped up to storage tank for safe disposal Groundwater monitoring well Synthetic liner Leachate monitoring well Sand Groundwater Clay Clay and plastic lining to prevent leaks; pipes collect leachate Subsoil from bottom of landfill Sand
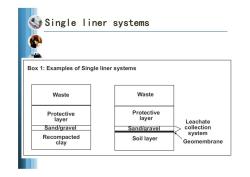
Single liner systems Box 1:Examples of Single liner systems Waste Waste Protective Protective layer layer Leachate Sand/gravel Sand/gravel collection Recompacted system Soil layer clay Geomembrane
Single liner systems
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)Part 2 Water Resources and Treatment Topic 1 Water resources 水资源.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)来自水的挑战 Water Challenges in China.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)概论 Environmental Science(负责人:李风亭).pdf
- 《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(文献资料)UNEP and UN-HABITAT——GREEN HILLS, BLUE CITIES AN ECOSYSTEMS APPROACH TO WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT FOR AFRICAN CITIES.pdf
- 《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(文献资料)Growing greenhouse gas emissions due to meat production.pdf
- 《水污染控制工程》课程教学资源(书籍资料)水污染治理先进技术汇编(科学技术部,2011年8月).pdf
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《遥感与地理信息系统》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《生产布局原理》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《环境质量评价》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《环境生物学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《环境工程学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《环境土壤学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《测量学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《水土保持学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《植物营养学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《房地产开发与经营管理》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《房地产市场学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《房地产估价》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《应用测量学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《地质学基础》课程教学大纲.doc
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)Part 2 Water Resources and Treatment Topic 3 Water and wastewater treatment 水处理.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)Part 2 Water Resources and Treatment Topic 2 Water pollution 水污染.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)固体废物2 Solid Waste Management(3)Incineration.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)固体废物3 Solid waste management(4)composting.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)大气 Fundamentals of Air Pollution Meteorology.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)大气污染 Air and Air Pollution.pdf
- 中国人民大学:《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Analysis of Environment Administration system.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)2011-2015年我国31个省能源使用情况数据统计.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)2012-2015年我国31个省用水情况数据统计.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)我们怎样喝到好水?.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)环境保护相关法律汇编.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)2011-2015年全国31个省SO2和COD排放数据(课程使用).pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)生态文明体制改革总体方案.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)新形势下改革和加强中国环境保护管理体制的思考.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)基于GDP的中国资源环境基尼系数分析.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)论绿色发展理念下环境执法垂直管理体制的改革与构建.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)中国环境管理体制改革的回顾与反思.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)美国环境管理体制对中国的启示 Enlightenment of US environmental management system to China.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)我国环境管理体制改革思路探析.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)全国生态保护“十三五”规划纲要(2016年10月).pdf
