同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)固体废物2 Solid Waste Management(3)Incineration

UNEP Environmental Science--- Solid Waste Management(3)Incineration Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn
Environmental Science--- Solid Waste Management (3) Incineration Niu Dongjie niudongjie@tongji.edu.cn

Table of content o Heat Value of Refuse o Materials and Thermal Balance o Combustion Hardware Used for MSW o Undesirable Effects of Combustion UNEP
Table of content Heat Value of Refuse Materials and Thermal Balance Combustion Hardware Used for MSW Undesirable Effects of Combustion
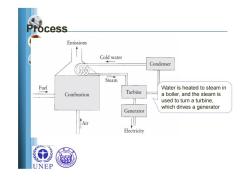
cess Emissions Cold water Condenser Steam Fuel Water is heated to steam in Combustion Turbine a boiler,and the steam is used to turn a turbine, which drives a generator Generator Air Electricity UNEP
Process Water is heated to steam in a boiler, and the steam is used to turn a turbine, which drives a generator

Heat Value of Refuse ●ultimate analysis compositional analysis o proximate analysis ●calorimetry UNEP
Heat Value of Refuse ultimate analysis compositional analysis proximate analysis calorimetry

Heat Value of Refuse Ultimate analysis Using the chemical makeup of the fuel to approximate its heat value Bib=145c+620H-0)+40s Bu/1b=144C+672H+6.20+41.4S-10.8N where C,H,O,S,and N are the weight percentages(dry basis)of carbon,hydrogen,oxygen,sulfur,and nitrogen,respectively UNEP
Heat Value of Refuse Ultimate analysis Using the chemical makeup of the fuel to approximate its heat value where C, H, O, S, and N are the weight percentages (dry basis) of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and nitrogen, respectively

Heat Value of Refuse Compositional analyses Bu/b=49R+22.5G+P)-3.3W Using regression analysis and comparing the results to actual measurements of heat value Bu/l=1238+15.6R+4.4P+2.7G-20.7W R-plastics,percent by weight,on dry basis P- paper,percent by weight,on dry basis G food wastes,percent by weight,on dry basis water,percent by weight,on dry basis UNEP
Heat Value of Refuse Compositional analyses Using regression analysis and comparing the results to actual measurements of heat value R= plastics, percent by weight, on dry basis P= paper, percent by weight, on dry basis G= food wastes, percent by weight, on dry basis W= water, percent by weight, on dry basis
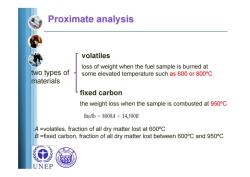
Proximate analysis volatiles loss of weight when the fuel sample is burned at two types of some elevated temperature such as 600 or 800C materials fixed carbon the weight loss when the sample is combusted at 950C B/l=8000A+14,500B A =volatiles,fraction of all dry matter lost at 600C B =fixed carbon,fraction of all dry matter lost between 600C and 950C UNEP
Proximate analysis volatiles fixed carbon loss of weight when the fuel sample is burned at some elevated temperature such as 600 or 800ºC the weight loss when the sample is combusted at 950ºC two types of materials A =volatiles, fraction of all dry matter lost at 600ºC B =fixed carbon, fraction of all dry matter lost between 600ºC and 950ºC
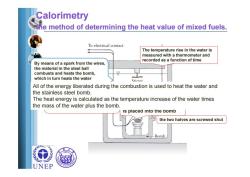
Calorimetry the method of determining the heat value of mixed fuels. To electrical contact The temperature rise in the water is measured with a thermometer and recorded as a function of time By means of a spark from the wires, the material in the steel ball combusts and heats the bomb, which in turn heats the water Stirrer All of the energy liberated during the combustion is used to heat the water and the stainless steel bomb The heat energy is calculated as the temperature increase of the water times the mass of the water plus the bomb is placed into the bomb the two halves are screwed shut -Bomb UNEP
Calorimetry the method of determining the heat value of mixed fuels. A sample of known weight is placed into the bomb the two halves are screwed shut By means of a spark from the wires, the material in the steel ball combusts and heats the bomb, which in turn heats the water Oxygen under high pressure the bomb is placed in an adiabatic is then injected into the bomb water bath with wires leading from the bomb to a source of electrical current The temperature rise in the water is measured with a thermometer and recorded as a function of time All of the energy liberated during the combustion is used to heat the water and the stainless steel bomb. The heat energy is calculated as the temperature increase of the water times the mass of the water plus the bomb

An important aspect of calorimetric heat values higher heating value (HHV) the net calorific energy The HHV is calculated by including the contribution due to the distinction this latent heat of vaporization(the heat required to produce steam from water) lower heating value(LHV) the gross calorific energy The LHV is then the HHV minus the latent heat of vaporization that has occurred in the bomb calorimeter UNEP
the gross calorific energy the net calorific energy the distinction higher heating value(HHV) lower heating value(LHV) The HHV is calculated by including the contribution due to this latent heat of vaporization (the heat required to produce steam from water) The LHV is then the HHV minus the latent heat of vaporization that has occurred in the bomb calorimeter An important aspect of calorimetric heat values

why the HHV number overestimates the actual heat value 1. the presence of metals temperature maybe not sufficiently high to force the reaction, like the oxidation of aluminum 2. the incomplete combustion of organics while all organic material will oxidize in a calorimeter,this will not occur in a full-scale combustor. The amount of unburned organics can vary from 2 to 25%, depending on the effectiveness of the operation Q龙 UNEP
1. the presence of metals 2. the incomplete combustion of organics temperature maybe not sufficiently high to force the reaction, like the oxidation of aluminum while all organic material will oxidize in a calorimeter, this will not occur in a full-scale combustor. The amount of unburned organics can vary from 2 to 25%, depending on the effectiveness of the operation why the HHV number overestimates the actual heat value
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)Part 2 Water Resources and Treatment Topic 2 Water pollution 水污染.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)Part 2 Water Resources and Treatment Topic 3 Water and wastewater treatment 水处理.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)固体废物1 Solid Waste Management(2)landfilling.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)Part 2 Water Resources and Treatment Topic 1 Water resources 水资源.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)来自水的挑战 Water Challenges in China.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)概论 Environmental Science(负责人:李风亭).pdf
- 《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(文献资料)UNEP and UN-HABITAT——GREEN HILLS, BLUE CITIES AN ECOSYSTEMS APPROACH TO WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT FOR AFRICAN CITIES.pdf
- 《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(文献资料)Growing greenhouse gas emissions due to meat production.pdf
- 《水污染控制工程》课程教学资源(书籍资料)水污染治理先进技术汇编(科学技术部,2011年8月).pdf
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《遥感与地理信息系统》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《生产布局原理》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《环境质量评价》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《环境生物学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《环境工程学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《环境土壤学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《测量学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《水土保持学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《植物营养学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《房地产开发与经营管理》课程教学大纲.doc
- 广东海洋大学:环境资源系《房地产市场学》课程教学大纲.doc
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)固体废物3 Solid waste management(4)composting.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)大气 Fundamentals of Air Pollution Meteorology.pdf
- 同济大学:《环境科学概论》课程教学资源(教案课件)大气污染 Air and Air Pollution.pdf
- 中国人民大学:《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Analysis of Environment Administration system.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)2011-2015年我国31个省能源使用情况数据统计.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)2012-2015年我国31个省用水情况数据统计.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)我们怎样喝到好水?.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)环境保护相关法律汇编.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)2011-2015年全国31个省SO2和COD排放数据(课程使用).pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)生态文明体制改革总体方案.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)新形势下改革和加强中国环境保护管理体制的思考.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)基于GDP的中国资源环境基尼系数分析.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)论绿色发展理念下环境执法垂直管理体制的改革与构建.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)中国环境管理体制改革的回顾与反思.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)美国环境管理体制对中国的启示 Enlightenment of US environmental management system to China.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)我国环境管理体制改革思路探析.pdf
- 《环境管理体制分析》课程教学资源(文献资料)全国生态保护“十三五”规划纲要(2016年10月).pdf
- 山西师范大学:《生态学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《环境工程学》课程教学大纲 Environmental Engineering.pdf
- 北方工业大学:环境设计《公共空间设计》课程教学大纲.pdf
