上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 2 Kinematic Fundamentals
ea+口 LECTURE 2 Kinematic Fundamentals -Fun with MECHANISMS Covered Cha2-in Design of Machinery 漫 OUTLINE Basic concepts and definitions Configuration of MECHANISMS How does a MECHANISM work? The kinematic diagram DOF-Degree of Freedom A simple equation-Gruebler Criterion Exceptions to Gruebler's Equation Design Catalogue of MECHANISMS ME357 Design Manufacturing ll 1
1 Kinematic Fundamentals -Fun with MECHANISMS LECTURE 2 Covered Cha2- in Design of Machinery ME357 Design & Manufacturing II OUTLINE Basic concepts and definitions Configuration of MECHANISMS How does a MECHANISM work? The kinematic diagram DOF-Degree of Freedom A simple equation-Gruebler Criterion Exceptions to Gruebler’s Equation Design Catalogue of MECHANISMS

Basic concepts and definitions Needle mechanism 到布机构 10 8 8品o Basic concepts and definitions Mechanism(机构):a kinematic chain in which at lease one link has been"grounded",or attached,to the frame of reference(which itself may be in motion);the links in the kinematic chain move upon each other with definite relative motion. Kinematic Chain(运a动链):an assembly of links and joints.(Interconnected in a way to provide a controlled output motion in response to a supplied input motion.)? ME357 Design Manufacturing ll 2
2 8 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 11 12 10 P 1 4 2 3 1 2 3 Basic concepts and definitions Take-up mechanism 挑线机构 Needle mechanism 刺布机构 ME357 Design & Manufacturing II Mechanism(机构): a kinematic chain in which at lease one link has been “grounded”, or attached, to the frame of reference(which itself may be in motion); the links in the kinematic chain move upon each other with definite relative motion. Kinematic Chain(运动链): an assembly of links and joints. (Interconnected in a way to provide a controlled output motion in response to a supplied input motion.) ? Basic concepts and definitions
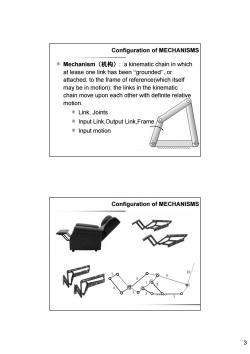
Configuration of MECHANISMS ⑧Mechanism(机构):a kinematic chain in which at lease one link has been"grounded",or attached,to the frame of reference(which itself may be in motion);the links in the kinematic chain move upon each other with definite relative motion. ©Link,Joints Input Link,Output Link,Frame Input motion Configuration of MECHANISMS 10 3
3 Mechanism(机构): a kinematic chain in which at lease one link has been “grounded”, or attached, to the frame of reference(which itself may be in motion); the links in the kinematic chain move upon each other with definite relative motion. Link, Joints Input Link,Output Link,Frame Input motion Configuration of MECHANISMS Configuration of MECHANISMS
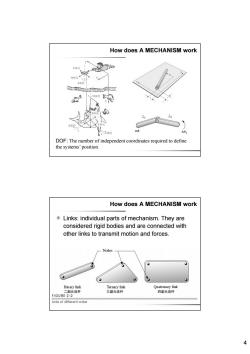
How does A MECHANISM work Y移动 x移动“ Z旋转1 地皮中 X旋转 Y旋转 △02 DOF:The number of independent coordinates required to define the systems'position. How does A MECHANISM work Links:individual parts of mechanism.They are considered rigid bodies and are connected with other links to transmit motion and forces. Nodes 0 0 Binary link Ternary link Quatemary link 二副元连杆 三副元连杆 四副元连杆 FIGURE 2-2 Links of different order 4
4 How does A MECHANISM work DOF: The number of independent coordinates required to define the systems’ position. Links: individual parts of mechanism. They are considered rigid bodies and are connected with other links to transmit motion and forces. How does A MECHANISM work 二副元连杆 三副元连杆 四副元连杆
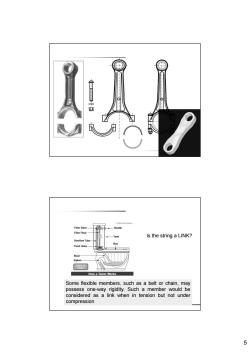
Filler Valve Handle Filler Float -Tank Is the string a LINK? Overflow Tube Flush Valve Bowl Siphon How a Toilet Works Some flexible members,such as a belt or chain,may possess one-way rigidity.Such a member would be considered as a link when in tension but not under compression 5
5 Is the string a LINK? Some flexible members, such as a belt or chain, may possess one-way rigidity. Such a member would be considered as a link when in tension but not under compression

How does A MECHANISM work Kinematic pairs 运动副 三守告 May roll afike.oe rollalie.depsmnditz on Sictioe iint-1or2Dor GURI 3-3 ME357 Design Manufacturing Il How does A MECHANISM work ©A joint is a movable connection between two or more links (at their nodes),which allows some motions,or potential motions between the connected links. Higher pairs高副 Lower pairs低副 GURE 3-3 6
6 ME357 Design & Manufacturing II How does A MECHANISM work Kinematic pairs 运动副 How does A MECHANISM work A joint is a movable connection between two or more links (at their nodes), which allows some motions, or potential motions between the connected links. Higher pairs 高副 Lower pairs 低副
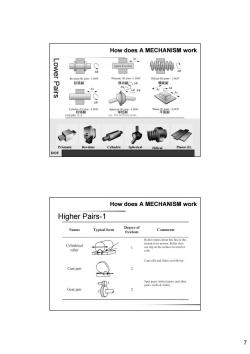
How does A MECHANISM work Lower Pairs square X-section Revolute (R)joint-1 DOF Prismatic (P)joint-1 DOF Helical (H)joint-1 DOF 铰链副 移动副△9 螺旋副 Ar △y +40 Cylindric (C)joint-2 DOF Spherical (S)joint-3 DOF 柱销副 球铰副 %"罩省3pof FIGURE 2-3 (a)The six lower pairs Prismatic Revolute Cylindric Spherical Helical Planar(F) DOF How does A MECHANISM work Higher Pairs-1 Names Typical form Degree of Comments freedom Roller rotates about this line at this Cylindrical instant in its motion.Roller does not slip on the surface on which it roller rolls. Cam rolls and slides on follower. Cam pair Spur gears.helical gears.and other gears.(rolls slides) Gear pair 7
7 Prismatic Revolute Cylindric Spherical Helical Planar (F) DOF 1 1 2 3 1 3 Lower Pairs How does A MECHANISM work 铰链副 移动副 螺旋副 柱销副 球铰副 平面副 Higher Pairs-1 How does A MECHANISM work
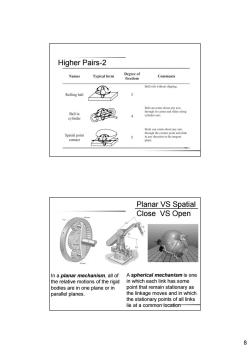
Higher Pairs-2 Names Typical form Degree of Comments freedom Ball rolls without slipping. Rolling ball Ball can rotate about any axis Ball in through its center and slides along cylinder axis. cylinder Body can rotate about any axis Spatial point through the contact point and slide in any direction in the tangent contact plane. Planar VS Spatial Close VS Open In a planar mechanism,all of A spherical mechanism is one the relative motions of the rigid in which each link has some bodies are in one plane or in point that remain stationary as parallel planes. the linkage moves and in which the stationary points of all links lie at a common location 8
8 Higher Pairs-2 Planar VS Spatial Close VS Open In a planar mechanism, all of the relative motions of the rigid bodies are in one plane or in parallel planes. A spherical mechanism is one in which each link has some point that remain stationary as the linkage moves and in which the stationary points of all links lie at a common location
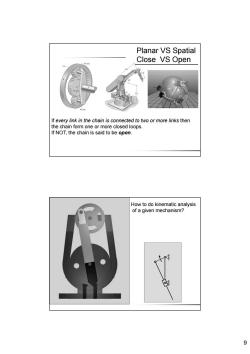
Planar VS Spatial Close VS Open mm If every link in the chain is connected to two or more links then the chain form one or more closed loops. If NOT,the chain is said to be open. How to do kinematic analysis of a given mechanism? 9
9 Planar VS Spatial Close VS Open If every link in the chain is connected to two or more links then the chain form one or more closed loops. If NOT, the chain is said to be open. How to do kinematic analysis of a given mechanism?
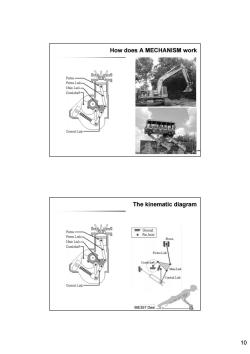
How does A MECHANISM work Piston- Piston Link- Main Link Crankshaf- Control Link- The kinematic diagram g Piston- m示 Ground Piston Link. Pin Joint Piston Main Link- Crankshaft- Piston Link 事 Min Link Contol Link Control Link ME357 Desi 10
10 How does A MECHANISM work ME357 Design & Manufacturing II The kinematic diagram
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 2 kinematic diagram representing method.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 12 gear design.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 1 introduction to engineering design_Lecture-1 Introduction to Design 2in1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 1 introduction to engineering design_conversion factors in mechanical design.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 0 Course Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)07_Homework cam.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)07_Homework cam solutions.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)06_Homework Power Screw.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)06 power screw solution.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)05 solutions Homework.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)05 Homework.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)04_Homework 4bar linkage.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)04_Homework 4bar linkage solutions.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)03_Homework+Motor.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)03 motor solution.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)02_homework.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)02_homework solutions.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)01_Homework.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(作业)01_Homework - solutions.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物与机器人学》课程教学资源_Rehabilitation and Health Care Robotics.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 2 实现基本运动功能的机构目录.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 3 Electric Motors.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 4 Planar Linkages.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 5 Hrones and Nelson Atlas.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 5 Graphical Linkage Synthesis.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 6 Vector fundamentals for kinematic analysis.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 7 Kinematic Analysis of Mechanisms.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture 9 CAM.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture10 gears.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture11 gear train.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(讲义)Lecture8 Transmission Power_screws.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(学生项目)DAG14518-交大-自动台球机的摆球装置-发明-可定稿.doc
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(学生项目)Lab-2 Project Management.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(学生项目)Lab3.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(学生项目)Manufacturing and assembling process-sample.doc
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(学生项目)样图-装配图 02-02-01-00.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(学生项目)样图-零件图 02-02-01-02.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(参考文献)Design of Machinery-ch8 cam design.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(参考文献)Design of Machinery-ch9 gear trains.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Design and Manufacturing》课程教学资源(参考文献)Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design ch1 Introduction to mechanical engineering design.pdf
