上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_Diffraction intensity

Key points in X-ray properties and diffraction geometry Distinguish between continuous and characteristic radiation .of K&Ke radiation and ik Good aspects/uses of absorption:X-ray filters Bad aspects/uses of absorption:X-ray fluorescence ·Bragg'slaW ·Ewald sphere method 1
Key points in X-ray properties and diffraction geometry • Distinguish between continuous and characteristic radiation • of K & K radiation and K • Good aspects/uses of absorption: X-ray filters • Bad aspects/uses of absorption: X-ray fluorescence • Bragg’s law • Ewald sphere method 1

Intensity of diffraction Leyun Wang eyunwang@sjtu.edu.cn
Intensity of diffraction Leyun Wang leyunwang@sjtu.edu.cn 2
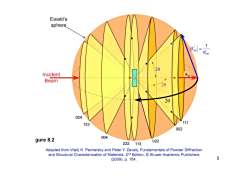
Ewald's sphere. 20 Incident Beam 20 20 024 133 111 002 gure 8.2 004 222113 022 Adapted from Vitalij K.Pecharsky and Peter Y.Zavalij,Fundamentals of Powder Diffraction and Structural Characterization of Materials,2nd Edition,Kluwer Academic Publishers (2009),p.154. 3
3
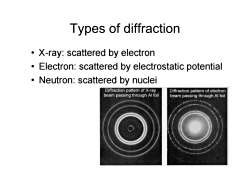
Types of diffraction X-ray:scattered by electron Electron:scattered by electrostatic potential Neutron:scattered by nuclei Diffraction pattern of X-ray Diffraction pattern of electron beam passing through Al foil beam passing through Al foil
Types of diffraction • X-ray: scattered by electron • Electron: scattered by electrostatic potential • Neutron: scattered by nuclei 4

Scattering of X-rays by atoms X-rays are scattered by electrons Electron positions are determined by atom positions 。Therefore: Size and shape of unit cell determine position of diffracted beam and Atom position determines the intensity of the diffracted beam 5
Scattering of X-rays by atoms • X-rays are scattered by electrons • Electron positions are determined by atom positions • Therefore: – Size and shape of unit cell determine position of diffracted beam and – Atom position determines the intensity of the diffracted beam 5

Intensity of diffraction • Scattering by a unit cell Atomic scattering factor Structure factor Interpretation of diffracted intensities The Lorentz polarization factor The structure factor The multiplicity of the reflecting planes The sampling geometry Absorption effects -Temperature ●Software 6
Intensity of diffraction • Scattering by a unit cell – Atomic scattering factor – Structure factor • Interpretation of diffracted intensities – The Lorentz polarization factor – The structure factor – The multiplicity of the reflecting planes – The sampling geometry – Absorption effects – Temperature • Software 6
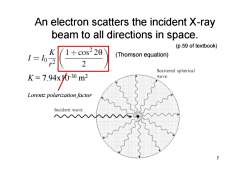
An electron scatters the incident X-ray beam to all directions in space. (p.59 of textbook) (Thomson equation) 2 Scattered spherical K=7.94x0-30m2 wave Lorentz polarization factor Incident wave 7
An electron scatters the incident X-ray beam to all directions in space. 7 K = 7.94x10-30 m 2 (Thomson equation) Lorentz polarization factor (p.59 of textbook)
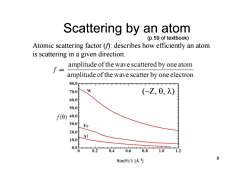
Scattering by an atom (p.59 of textbook) Atomic scattering factor ()describes how efficiently an atom is scattering in a given direction. I= amplitude of the wave scattered by one atom amplitude of the wave scatter by one electron 80.0 70.0E (Z,0,) 60.0E 50.0f f0) 40.0F 30.0f Fe 20.0 Al 10.0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 Sin()/A-] 8
8 Scattering by an atom Atomic scattering factor (f): describes how efficiently an atom is scattering in a given direction. (p.59 of textbook) (~Z, , )
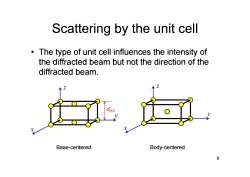
Scattering by the unit cell The type of unit cell influences the intensity of the diffracted beam but not the direction of the diffracted beam. Base-centered Body-centered 9
Scattering by the unit cell • The type of unit cell influences the intensity of the diffracted beam but not the direction of the diffracted beam. 9 Base-centered Body-centered
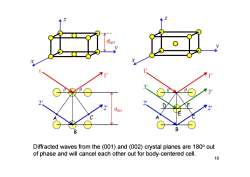
doo1 B Diffracted waves from the(001)and(002)crystal planes are 180 out of phase and will cancel each other out for body-centered cell. 10
10 Diffracted waves from the (001) and (002) crystal planes are 18 0 o out of phase and will cancel each other out for body-centered cell
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_Diffraction geometry.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_Physics of X-ray radiation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_crystallography.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_OM4 Confocal Microscopy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_OM3 Recap of the previous lectures.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_OM2 Specimen preparation for metallography.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_OM1 Optical principles of light microscopy.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)一种利用蝶翅纳米吸光结构的太阳能电池的设计.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)通识课研究论文汇编.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)耶鲁校长:这才是判断一个人受过教育的铁证.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)纳米技术研究进展讲稿.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)纳米技术最新进展及思考.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)纳米技术进展详述(合集).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)深度解读2016年诺贝尔化学奖.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)大气净化机器人《走进纳米科学》报告书.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)普林斯顿校长:教育的真正意义在于让你能在挫折中成就自己.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)纳米技术在输电线路防冰除冰中的应用.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)开设纳米技术新生研讨课的实践与体会.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)纳米生物陶瓷材料面对骨科应用中的作用及改变.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《走进纳米科学》课程教学资源(文献资料)减轻汽车发动机磨损的两种方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_Powder X-ray diffraction method and applications.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_Precise lattice parameter determination.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_Understand the diffraction peak broadening in XRD.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_EM1.1_Electron optics of transmission electron microscope.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_EM1.2_Specimen preparation for TEM.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_EM2_Diffraction in TEM and its analysis.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_EM3_Image contrast in TEM and its application.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_EM4 phase contrast HREM.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_EM5 X-ray microanalysis.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_homework assignment-tem.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_homework assignment3-19.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_homework assignment4-2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_HW.docx
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_HW.docx
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_HW.doc
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_HW.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_HW.doc
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_HW.docx
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_HW.docx
- 上海交通大学:《Structural and Chemical Characterization of Materi》教学资源_HW.docx
