《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)Antigen Recognition

Lecture 15 Antigen Recognition
Lecture 15 Antigen Recognition

Overview In order to initiate an immune response antigen must be recognized. Antigen recognition depends on detection of antigen by special receptors. Antigen recognition depends on cellular cooperation. Cellular cooperation is controlled by recognition of MHC-encoded receptors
Overview ◼ In order to initiate an immune response antigen must be recognized. ◼ Antigen recognition depends on detection of antigen by special receptors. ◼ Antigen recognition depends on cellular cooperation. ◼ Cellular cooperation is controlled by recognition of MHC-encoded receptors

Clonal Selection Theory (F.Macfarlane Burnet) 0 pre-existence of of many different potential antibody producing cells each cell displays surface receptors for specific antigens antigen encounter selects cells What prevents recognition/destruction of self tissues?
Clonal Selection Theory (F. Macfarlane Burnet) ◼ pre-existence of of many different potential antibody producing cells ◼ each cell displays surface receptors for specific antigens ◼ antigen encounter selects cells ◼ What prevents recognition/destruction of self tissues?

Postulates of the Clonal Selection Hypothesis Each lymphocyte bears a single type of receptor of a unique specificity Interaction between a foreign molecule and a lymphocyte receptor capable of binding that molecule with high affinity leads to lymphocyte activation The differentiated efector cells derived from an activated lymphocyte will bear receptors of identical specificity to those of the parental cell from which that lymphocyte was derived Lymphocytes bearing receptors specific for self molecules are deleted at an early stage in lymphocyte development and are therefore absent from the repertoire
Postulates of the Clonal Selection Hypothesis ◼ Each lymphocyte bears a single type of receptor of a unique specificity ◼ Interaction between a foreign molecule and a lymphocyte receptor capable of binding that molecule with high affinity leads to lymphocyte activation ◼ The differentiated effector cells derived from an activated lymphocyte will bear receptors of identical specificity to those of the parental cell from which that lymphocyte was derived ◼ Lymphocytes bearing receptors specific for self molecules are deleted at an early stage in lymphocyte development and are therefore absent from the repertoire

Diversity of Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors Variable region of antigen receptor encoded by sets of gene segments During lymphocyte development somatic gene rearrangement create unique combinations of gene segments Once recombinant events have occurred,further rearrangement is prohibited Receptor specificity of a lymphocyte cannot change Each lymphocyte bears many copies of the unique receptor At least 108 different lymphocytes in an individual
Diversity of Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors ◼ Variable region of antigen receptor encoded by sets of gene segments ◼ During lymphocyte development somatic gene rearrangement create unique combinations of gene segments ◼ Once recombinant events have occurred, further rearrangement is prohibited ◼ Receptor specificity of a lymphocyte cannot change ◼ Each lymphocyte bears many copies of the unique receptor ◼ At least 108 different lymphocytes in an individual

Genomic Organization of heavy-and light-chain segments λlight chain L1 V1 22 K light chain L1 Vk1 L2 Vk2 L3 V3 L V-40 Jx1-5 ■H==; Heavy chain L11L2M2L33 H451 Dm1-27 JH1-6 H:t0一00 1997 Current Biology Ltd./Garland Publishing.Inc
Genomic Organization of heavy- and light-chain segments

Development of the Antibody Repertoire The antibody repertoire is generated during B cell development by DNA rearrangements that combine and assemble variable-region gene segments (somatic diversification theory) Diversity is enhanced by hypermutation in mature B cells (germline theory)
Development of the Antibody Repertoire ◼ The antibody repertoire is generated during B cell development by DNA rearrangements that combine and assemble variable-region gene segments (somatic diversification theory) ◼ Diversity is enhanced by hypermutation in mature B cells (germline theory)

Some Comments on Cluster of Differentiation/Designation(CD)Antigens _What are they? Differentiation antigens Expressed by cells at distinct stages of differentiation Expressed by cells having different functions How are they detected?
Some Comments on Cluster of Differentiation/Designation (CD) Antigens ◼ What are they? ◼ Differentiation antigens ◼ Expressed by cells at distinct stages of differentiation ◼ Expressed by cells having different functions ◼ How are they detected?
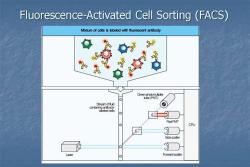
Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) Mixture of cells is labeled with fluorescent antibody Q¥ 68 tbe (PMT) Streamof fud labeled oeis RedPMT CPU Side scatter Laser Forward scatter
Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)

Lymphocyte Populations B lymphocytes Plasma cells T lymphocytes Helper/Inducer (CD4) ·Suppressor(CD8)
Lymphocyte Populations ◼ B lymphocytes ◼ Plasma cells ◼ T lymphocytes ◼ Helper/Inducer (CD4) ◼ Suppressor (CD8)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)Antibody-Antigen Reactions.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体 Complement(英文)1.pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体 Complement(英文)2.pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体调节蛋白(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体缺陷性疾病(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体的检测法(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的经典途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的末端途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体激活的旁路途径(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)补体受体(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗微生物蛋白和肽(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原递呈给淋巴细胞(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原被淋巴细胞识别(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原抗体结合(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗原处理过程(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)抗体(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)免疫系统的细胞(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)免疫应答(英文).pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)STUDY OF DISEASE AND PHYSIOLOGY IN THE 1979 HOMING STUDY HATCHERY STOCKS——A SUPPLEMENT TO - IMPRINTING SALMON AND STEELHEAD TROUT FOR HOMING, 1979 BY SLATICK, GILBREATH, AND WALCH.pdf
- 《动物免疫学》课程教学资源(文献资料)T and B cells 2.doc
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)B细胞对抗原的识别和应答.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)B细胞的生物学(Biology of the B Lymphocyte).ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)细胞因子 Cytokines.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)IL-8生物活性的检测.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)Cellular Cooperation and Antigen Recognition.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)T淋巴细胞与特异性细胞免疫.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)主要的补体系统缺乏(Primary deficiencies of the complement system).ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)主要组织相容性复合体及其编码分子.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)主要组织相容性抗原系统(histicompatibility antigen).ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)传染与免疫(病原体对机体的感染、机体对感染的预防和治疗).ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)体液免疫反应 Humoral Immune Response.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫学发展简史及展望.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫学概论.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫应答概述(Immune response).ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫标记技术及应用.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫球蛋白(Immunoglobulin, Ig).ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫系统(The Immune System).ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫系统的遗传学(Genetics of the Immune system).ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫耐受 Immunological Tolerance.ppt
- 《动物免疫学》课程PPT教学课件(讲稿)免疫自动化仪器分析.ppt
