南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)搜索树

计算机问题求解 -论题2-13 树及搜索树 2020年05月21日
计算机问题求解 – 论题2-13 - 树及搜索树 2020年05月21日
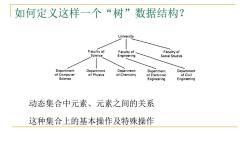
如何定义这样一个“树”数据结构? University Faculty of Faculty of Faculty of Science Engineering Social Studies Department Department Department Department Department of Computer of Physics of Chemistry of Electronic of Civil Science Engineering Engineering 动态集合中元素、元素之间的关系 这种集合上的基本操作及特殊操作
如何定义这样一个“树”数据结构? 动态集合中元素、元素之间的关系 这种集合上的基本操作及特殊操作

树中元素及元素之间的关系 A tree is a recursive abstract data type which is a collection of zero or more nodes each containing an element of type elemtype with the following hierarchi- cal structure: either (a)The empty structure(with no nodes) or (b)A node N containing element E with a finite number (zero or more)of associated disjoint tree structures (that is,they have no common nodes).These trees are known as subtrees of N.N is called the root of the tree. 你如何理解这两个概念:层次结构、递归ADT?
树中元素及元素之间的关系 你如何理解这两个概念:层次结构、递归ADT?

树中元素上应该有哪些操作?基本操作B)?特 殊操作(S)? B B S B S
树中元素上应该有哪些操作?基本操作(B)?特 殊操作(S)? B B B S S

function left_most_child (N node):node; (This function returns the left-most child of the node N. S If there are no children,a null node will be returned * function right_sibling (N:node):node; (If node N has a sibling node,it will be retured as the value of this S function.Otherwise,a null node will be returned * function null_node (N:node):boolean; (This function returns a true value if and only if N is a null node * B/S function cons_treen (E:elemtype;T1,T2,...,Tn:tree):tree; (This function constructs a tree with a node N as its root containing element E and the trees T1,T2,...,Tn as its children,in that order. B/S The trees T1,T2,...,Tn should not be used again after this operation to construct other trees.If copies of these subtrees are required,they can be constructed using the assign(T,T)operation.This is meant for space-efficiency so that this function need not copy these subtrees in order to make a new tree *
S S B/S B/S

procedure insert_child (P:node;E:elemtype); (This procedure is defined for constructing trees in a top-down manner. B A node containing element E will be created and it will be made the right-most child of node P*) procedure delete (var T:tree); B (This procedure deletes all the nodes of the tree T,and T will be made an empty tree.The tree T should not be a subtree of another tree * procedure assign(T1 tree;var T2:tree); (This procedure copies the entire tree T1 and asigns it to T2 * S/B 你能够从你的判断中得到一个一般 性的规律吗: 当你定义一个数据结构时,哪些操 作是必须的,哪些操作是特定的?
B B S/B 你能够从你的判断中得到一个一般 性的规律吗: 当你定义一个数据结构时,哪些操 作是必须的,哪些操作是特定的?

你有没有感觉到,在树这样的数据结构中,递 归如呼吸般自然? ways.These are known as tree walkings or tree traversals.In a tree with the root N and subtrees T1,T2,...,Tn we define: pre-order traversal:visit the root node N,then visit all the nodes in T in pre-order,then visit all the nodes in T2 in pre-order, and so on until all the nodes in Tn are visited in pre-order. post-order traversal:visit the nodes of T1,T2,...,Tn in post-order (in that order);then visit the root node
你有没有感觉到,在树这样的数据结构中,递 归如呼吸般自然?
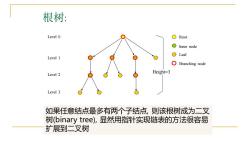
根树: Level 0 Root Inner node O Leaf Level 1 O Branching node Level 2 Height=3 Level 3 如果任意结点最多有两个子结点,则该根树成为二叉 树binary tree),显然用指针实现链表的方法很容易 扩展到二叉树
根树: Root Inner node Branching node Leaf Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Height=3 如果任意结点最多有两个子结点, 则该根树成为二叉 树(binary tree), 显然用指针实现链表的方法很容易 扩展到二叉树
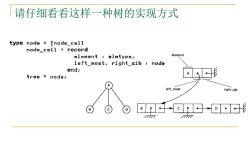
请仔细看看这样一种树的实现方式 type node÷1node_cei1 node_cel】=record element elmtype, element left_most,right_sib node end; tree node; □形 A left_most right_sib B ©□-o形 7777 777
请仔细看看这样一种树的实现方式
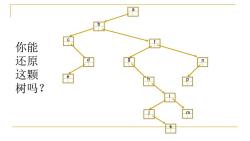
a C f 你能 还原 d 9 这颗 e h D 树吗? m
a b c d e g f h i j k mp n 你能 还原 这颗 树吗?
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Hashing方法.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)B树.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)堆的结构、实现以及算法应用 Heap & HeapSort.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)基本数据结构.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)排序与选择算法 sorting and selection(简版).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)排序与选择算法 sorting and selection.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)离散概率基础.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)概率分析与随机算法.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)算法方法.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)递归及其数学基础 linear-recurrences(简版).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)递归及其数学基础 linear-recurrences.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)递归及其数学基础(part-1).pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)组合与计数 Counting(简版).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)组合与计数 Counting.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)算法的正确性.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法的效率 Efficiency(简版).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)算法的效率 Efficiency.pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)分治法与递归.pptx
- 《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(参考书籍)Proofs from THE BOOK(Fifth Edition,Martin Aigner · Günter M. Ziegler).pdf
- 《计算机问题求解》课程参考书籍资料:《Mathematics for Computer Science》PDF电子书(revised Wednesday 6th June, 2018,Eric Lehman、F Thomson Leighton、Albert R Meyer).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)红黑树.pptx
- 《计算机问题求解》课程参考书籍教材:《Introduction to Algorithms》PDF电子版(Third Edition,Thomas H. Cormen、Charles E. Leiserson、Ronald L. Rivest、Clifford Stein).pdf
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)动态规划.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)红黑树.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)图的基本概念.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)摊还分析.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)贪心算法.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)树.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)用于动态等价关系的数据结构.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)单源最短路径算法.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)图的计算机表示以及遍历.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)多源最短路径算法.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)图中的匹配与覆盖.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)图的连通度.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)旅行问题.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)最大流算法(一).pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)平面图与图着色.pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)最大流算法(二).pptx
- 南京大学:《计算机问题求解》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)矩阵计算.pptx
- 《计算机问题求解》课程参考书籍教材:Abstract Algebra - Theory and Applications(Thomas W. Judson).pdf
