上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)let them die

Let Them Die By Kenan Malik From Prospect,November 2000
Let Them Die By Kenan Malik From Prospect, November 2000

Words and Structure expressing the extinction of language When she dies,so will her language. ·Die 。Take.to the grave ·Kill off ·Pass away 。Disappear
Words and Structure expressing the extinction of language • When she dies, so will her language. • Die • Take…to the grave • Kill off • Pass away • Disappear

Para.1:When does a language die? Common sense-when the last speaker dies:Some endangered languages are listed. Language Interaction Produces Bilingual Speakers. Bilingual Individuals:"Drop"Language if not economically useful people stop speaking a language and start speaking another-language shift Most frequently-all speakers shift to other languages -Australia and Americas If every speaker shifts and the original language is no longer spoken anywhere-language death
Para. 1: When does a language die? • Common sense – when the last speaker dies: Some endangered languages are listed. • Language Interaction Produces Bilingual Speakers. • Bilingual Individuals: “Drop” Language if not economically useful • people stop speaking a language and start speaking another – language shift • Most frequently – all speakers shift to other languages – Australia and Americas • If every speaker shifts and the original language is no longer spoken anywhere – language death
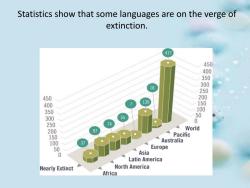
Statistics show that some languages are on the verge of extinction. 417 450 0汤 18 250 450 139 400 8 350 100 300 55 5 250 74 87 World Pacific 1 37 Australia 5 Europe 0 Asia Latin America Nearly Extinct North America Africa
Statistics show that some languages are on the verge of extinction

How do languages become extinct? Languages become extinct when a community finds itself under pressure to integrate with a larger or more powerful group. The community is pressured to give up its language and even its ethnic and cultural identity--ethnic Kurds in Turkey,are forbidden by law to print or formally teach their language.Younger speakers of Native American languages,as recently as the 1960s,were punished for speaking their native languages at boarding schools. Outright genocide--When European invaders exterminated the Tasmanians in the early 19th century, an unknown number of languages died
How do languages become extinct? • Languages become extinct when a community finds itself under pressure to integrate with a larger or more powerful group. • The community is pressured to give up its language and even its ethnic and cultural identity -- ethnic Kurds in Turkey, are forbidden by law to print or formally teach their language. Younger speakers of Native American languages, as recently as the 1960s, were punished for speaking their native languages at boarding schools. • Outright genocide -- When European invaders exterminated the Tasmanians in the early 19th century, an unknown number of languages died

Why do languages die out? official language policies:Occasionally by force- boarding school policy for American Indians from 1890s Sometimes disease(Tasmania),flood, earthquakes,AlDS in Africa Acceleration with rise of modern empires- French,English,Russian--and migration Socio-economic competition:Spread of an imperial language ---colonization,globalization
Why do languages die out? • official language policies: Occasionally by force – boarding school policy for American Indians from 1890s • Sometimes disease (Tasmania), flood, earthquakes, AIDS in Africa • Acceleration with rise of modern empires – French, English, Russian -- and migration • Socio-economic competition: Spread of an imperial language ---colonization, globalization
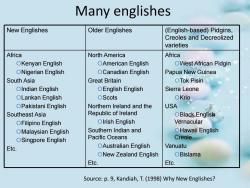
Many englishes New Englishes Older Englishes (English-based)Pidgins, Creoles and Decreolized varieties Africa North America Africa OKenyan English OAmerican English OWest African Pidgin ONigerian English OCanadian English Papua New Guinea South Asia Great Britain OTok Pisin OIndian English OEnglish English Sierra Leone OLankan English OScots OKrio OPakistani English Northern Ireland and the USA Southeast Asia Republic of Ireland OBlack English OFilipino English OIrish English Vernacular OMalaysian English Southern Indian and OHawaii English OSingpore English Pacific Oceans Creole Etc. OAustralian English Vanuatu ONew Zealand English OBislama Etc. Etc. Source:p.9,Kandiah,T.(1998)Why New Englishes?
Many englishes New Englishes Older Englishes (English-based) Pidgins, Creoles and Decreolized varieties Africa ¡Kenyan English ¡Nigerian English South Asia ¡Indian English ¡Lankan English ¡Pakistani English Southeast Asia ¡Filipino English ¡Malaysian English ¡Singpore English Etc. North America ¡American English ¡Canadian English Great Britain ¡English English ¡Scots Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland ¡Irish English Southern Indian and Pacific Oceans ¡Australian English ¡New Zealand English Etc. Africa ¡West African Pidgin Papua New Guinea ¡Tok Pisin Sierra Leone ¡Krio USA ¡Black English Vernacular ¡Hawaii English Creole Vanuatu ¡Bislama Etc. Source: p. 9, Kandiah, T. (1998) Why New Englishes?

Reasons for many varieties of English Development of language in"new and unfamiliar contexts" - Contexts marked by different ecological,cultural, linguistic,social,etc.characteristics
Reasons for many varieties of English – Development of language in “new and unfamiliar contexts” – Contexts marked by different ecological, cultural, linguistic, social, etc. characteristics

Para.2-4:campaign to preserve linguistic diversity . Consequences of language death: --language death results in the loss of unique biological and ecological knowledge. -Reduces knowledge about human language and mind Death of unique cultures
Para.2-4:campaign to preserve linguistic diversity • Consequences of language death: --language death results in the loss of unique biological and ecological knowledge. – Reduces knowledge about human language and mind – Death of unique cultures

Can dying languages be maintained? Serious attempts from mid-20th century in US,Australia,Europe Subjects in school,media,education Success is limited economic and cultural factors
Can dying languages be maintained? • Serious attempts from mid-20th century in US, Australia, Europe • Subjects in school, media, education • Success is limited – economic and cultural factors
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)language.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)language and thought.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)Glorious Messiness of English.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)Generation X.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)Does America Still Exist.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)Canadians.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)beauty of Britain.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源_语苑荟萃_上海高校开展语言文字工作评估成效选编-市语委办市教育评估院-学林出版社-2017-3.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)试读几片甲骨.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)甲骨及甲骨学.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)汉字造字方法.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)汉字规范.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)汉字文化 课程说明.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)汉字文化 绪论.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)汉字与文字游戏.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)汉字与书法(新版本).pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)汉字与中国传统文学.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)春秋战国文字.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)6今文字简述.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汉字文化》教学资源(PPT讲义)4青铜器及金文.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)on seeing England for the first time.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)on various means.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)political correctness.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)rhetoric.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《英语读写》课程教学资源(PPT)why the rich are getting richer.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Antony and Cleopatra_Antony and Cleopatra.docx
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Antony and Cleopatra_Antony&Cleopatra-student.docx
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Antony and Cleopatra_安东尼与克莉奥佩特拉.docx
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Hamlet_Hamlet全文(英).doc
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Hamlet_哈姆雷特.doc
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_KingLear_KingLear-class.docx
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_KingLear_KingLear.docx
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_KingLear_李尔王.docx
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Macbeth_Macbeth(in-class).doc
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Macbeth_Macbeth.doc
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Macbeth_麦克白.doc
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Merchant of V_Merchant of Venice.doc
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Merchant of V_威尼斯商人 students.doc
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Merchant of V_威尼斯商人.doc
- 上海交通大学:《莎士比亚戏剧赏析》课程教学资源_Midsummer N D_MidsummerNightDream(节选).doc
