北京大学:《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(PPT课件)分布式文件系统 Distributed File systems

DFS@wikipedia(1/2) In computing,a distributed file system or network file system is any file system that allows access to files from multiple hosts sharing via a computer network.[1 This makes it possible for multiple users on multiple machines to share files and storage resources. The client nodes do not have direct access to the underlying block storage but interact over the network using a protocol.This makes it possible to restrict access to the file system depending on access lists or capabilities on both the servers and the clients, depending on how the protocol is designed
DFS@wikipedia (1/2) • In computing, a distributed file system or network file system is any file system that allows access to files from multiple hosts sharing via a computer network. [1] This makes it possible for multiple users on multiple machines to share files and storage resources. • The client nodes do not have direct access to the underlying block storage but interact over the network using a protocol. This makes it possible to restrict access to the file system depending on access lists or capabilities on both the servers and the clients, depending on how the protocol is designed

DFS@wikipedia(2/2) In contrast,in a shared disk file system all nodes have equal access to the block storage where the file system is located.On these systems the access control must reside on the client. Distributed file systems may include facilities for transparent replication and fault tolerance.That is,when a limited number of nodes in a file system go offline,the system continues to work without any data loss. The difference between a distributed file system and a distributed data store can be vague,but DFSes are generally geared towards use on local area networks
DFS@wikipedia (2/2) • In contrast, in a shared disk file system all nodes have equal access to the block storage where the file system is located. On these systems the access control must reside on the client. • Distributed file systems may include facilities for transparent replication and fault tolerance. That is, when a limited number of nodes in a file system go offline, the system continues to work without any data loss. • The difference between a distributed file system and a distributed data store can be vague, but DFSes are generally geared towards use on local area networks

Outline File systems overview NFS AFS (Andrew File System) ·Google File System
Outline • File systems overview • NFS & AFS (Andrew File System) • Google File System

File Systems Overview System that permanently stores data Usually layered on top of a lower-level physical storage medium ·Divided into logical units called“files” -Addressable by a filename ("foo.txt") -Usually supports hierarchical nesting (directories)
File Systems Overview • System that permanently stores data • Usually layered on top of a lower-level physical storage medium • Divided into logical units called “files” – Addressable by a filename (“foo.txt”) – Usually supports hierarchical nesting (directories)

File Paths A file path joins file directory names into a relative or absolute address to identify a file -Absolute:/home/aaron/foo.txt -Relative:docs/someFile.doc The shortest absolute path to a file is called its canonical path The set of all canonical paths establishes the namespace for the file system
File Paths • A file path joins file & directory names into a relative or absolute address to identify a file – Absolute: /home/aaron/foo.txt – Relative: docs/someFile.doc • The shortest absolute path to a file is called its canonical path • The set of all canonical paths establishes the namespace for the file system

What Gets Stored User data itself is the bulk of the file system's contents Also includes meta-data on a drive-wide and per-file basis: Drive-wide: Per-file: available space name formatting info owner character set modification date physical layout
What Gets Stored • User data itself is the bulk of the file system's contents • Also includes meta-data on a drive-wide and per-file basis: Drive-wide: available space formatting info character set ... Per-file: name owner modification date physical layout

High-Level Organization ·Files are organized in a"tree”structure made of nested directories ·One directory acts as the“root'" ·links”(symlinks,shortcuts,etc)provide simple means of providing multiple access paths to one file ·Other file systems can be“mounted"and dropped in as sub-hierarchies (other drives, network shares)
High-Level Organization • Files are organized in a “tree” structure made of nested directories • One directory acts as the “root” • “links” (symlinks, shortcuts, etc) provide simple means of providing multiple access paths to one file • Other file systems can be “mounted” and dropped in as sub-hierarchies (other drives, network shares)

Low-Level Organization (1/2) File data and meta-data stored separately File descriptors meta-data stored in inodes Large tree or table at designated location on disk Tells how to look up file contents Meta-data may be replicated to increase system reliability
Low-Level Organization (1/2) • File data and meta-data stored separately • File descriptors + meta-data stored in inodes – Large tree or table at designated location on disk – Tells how to look up file contents • Meta-data may be replicated to increase system reliability

Low-Level Organization(2/2) ·“Standard"”read-write medium is a hard drive (other media:CDROM,tape,... Viewed as a sequential array of blocks Must address ~1 KB chunk at a time ·Tree structure is“flattened"into blocks Overlapping reads/writes/deletes can cause fragmentation:files are often not stored with a linear layout -inodes store all block ids related to file
Low-Level Organization (2/2) • “Standard” read-write medium is a hard drive (other media: CDROM, tape, ...) • Viewed as a sequential array of blocks • Must address ~1 KB chunk at a time • Tree structure is “flattened” into blocks • Overlapping reads/writes/deletes can cause fragmentation: files are often not stored with a linear layout – inodes store all block ids related to file
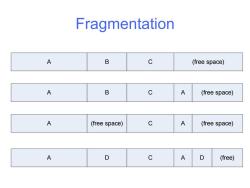
Fragmentation A B C (free space) A B C A (free space) A (free space) C A (free space) A D C A D (free)
Fragmentation A B C (free space) A B C A (free space) A (free space) C A (free space) A D C A D (free)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京大学:《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(PPT课件)并行与分布式系统基础 Introduction to Distributed Systems.ppt
- 北京大学:《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Clustering问题 Clustering.ppt
- 北京大学:《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(PPT课件)MapReduce系统设计与实现 Web Search on MapReduce.ppt
- 北京大学:《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(PPT课件)MapReduce算法设计 Basic MapReduce Algorithm Design.ppt
- 北京大学:《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(PPT课件)MapReduce原理 MapReduce Theory and Practice.ppt
- 北京大学:《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(PPT课件)课程介绍 Introduction to Cloud Computing(主讲:彭波).ppt
- 《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Data-Intensive Text Processing(MapReduce book 20100307).pdf
- 《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(阅读材料)MapReduce——Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters.pdf
- 《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(阅读材料)The Google File System(GFS).pdf
- 《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(阅读材料)k-means++——The Advantages of Careful Seeding.pdf
- 《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Efficient Clustering of High-Dimensional Data Sets with Application to Reference Matching.pdf
- 《大规模数据处理——云计算 Mass Data Processing Cloud Computing》课程教学资源(阅读材料)The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine.pdf
- 上海中医药大学:课程教学大纲汇编合集——教学大纲(计算机中心、图书信息中心).pdf
- 北京中医药大学:《计算机基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第8章 模块.ppt
- 北京中医药大学:《计算机基础》课程PPT教学课件(Access 数据库程序设计)包装应用系统.ppt
- 北京中医药大学:《计算机基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第7章 宏.ppt
- 北京中医药大学:《计算机基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第5章 报表.ppt
- 北京中医药大学:《计算机基础》课程教学资源(教学大纲,Ⅱ).doc
- 北京中医药大学:《计算机基础》课程教学资源(电子教材)《Access 数据库程序设计》第5章 报表.doc
- 北京中医药大学:《计算机基础》课程教学资源(电子教材)《Access 数据库程序设计》第4章 窗体.doc
- 北京大学:《移动计算与无线网络》课程教学资源(学生PPT)课程实验——WLAN性能实证(802.11 Wlan无线通讯实验).ppt
- 北京大学:《移动计算与无线网络》课程教学资源(学生PPT)揭秘WLAN无线链路的丢包规律.ppt
- 北京大学:《移动计算与无线网络》课程教学资源(学生PPT)无线实验——距离障碍物等因素之影响.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《信息系统安全》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一章 绪论(主讲教师:董庆宽).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代密码学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三章 分组密码.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《现代密码学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第五章 消息认证算法.pptx
- 郑州大学:《计算机网络》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第1章 概述.pdf
- 郑州大学:《计算机网络》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第2章 物理层.pdf
- 郑州大学:《计算机网络》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第3章 数据链路层.pdf
- 郑州大学:《计算机网络》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第4章 网络层.pdf
- 郑州大学:《计算机网络》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第5章 运输层.pdf
- 郑州大学:《计算机网络》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第6章 应用层.pdf
- 唐山广播电视大学:Premiere Pro CC视频编辑——期末复习题及答案.doc
- 四川开放大学:《跨境电商》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末考试试题一(试题).doc
- 四川开放大学:《跨境电商》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末考试试题一(答案).doc
- 四川开放大学:《跨境电商》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末考试试题三(试题).doc
- 四川开放大学:《跨境电商》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末考试试题三(答案).doc
- 四川开放大学:《跨境电商》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末考试试题二(试题).doc
- 四川开放大学:《跨境电商》课程教学资源(试卷习题)期末考试试题二(答案).doc
- 四川开放大学:《跨境电商》课程教学资源(试卷习题)章节练习题及答案.docx
