吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)09 Grammar Patten Drills

Lesson Nine Grammar Patten Drills Text A Exercises
Grammar Patten Drills Text A Exercises

Lesson Nine Part One Grammar---Indirect Speech(1) There are two ways of relating what a person has said:direct and indirect. In direct speech(直接引语)we repeat the original speaker's exact words: He said,"I am writing a letter." Remarks thus repeated are placed between inverted commas(引号),and a comma or colon(冒号)is placed immediately before the remark. In indirect speech(间接引语)we give the exact meaning of a remark or a speech,without necessarily using the speaker's exact words:
Part One Grammar---Indirect Speech(1) There are two ways of relating what a person has said: direct and indirect. In direct speech(直接引语)we repeat the original speaker’s exact words: He said,“I am writing a letter.” Remarks thus repeated are placed between inverted commas(引号), and a comma or colon(冒号) is placed immediately before the remark. In indirect speech(间接引语)we give the exact meaning of a remark or a speech, without necessarily using the speaker’s exact words: Lesson Nine

Grammar He said that he was writing a letter. (He said,"I am writing a letter.") Indirect speech is usually used in reporting conversation, though direct speech is sometimes used here to give a more life-like effect. When we turn direct speech into indirect,some changes are usually necessary.These are most easily studied by considering statements,questions and commands separately 1.Statements in indirect speech I)When the reporting verb(☑引述动词)is in the present,. present perfect,or future tense,there is no change of tense in the word reported
He said that he was writing a letter. (He said,“I am writing a letter.”) Indirect speech is usually used in reporting conversation, though direct speech is sometimes used here to give a more life-like effect. When we turn direct speech into indirect, some changes are usually necessary. These are most easily studied by considering statements, questions and commands separately. 1. Statements in indirect speech 1) When the reporting verb(引述动词) is in the present, present perfect, or future tense, there is no change of tense in the word reported. Grammar

Grammar e.g."I'm tired." She says (that)she is tired. She has just told me (that)she is tired She will tell you (that)she is tired 2)Indirect speech is usually introduced by a verb in the past.Verbs in the direct speech normally go back one tense from what was said originally:
e.g. “I’m tired.” She says (that) she is tired. She has just told me (that) she is tired. She will tell you (that) she is tired. 2) Indirect speech is usually introduced by a verb in the past. Verbs in the direct speech normally go back one tense from what was said originally: Grammar
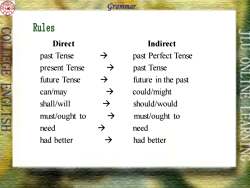
2 Grammar Rules Direct Indirect past Tense past Perfect Tense present Tense → past Tense future Tense future in the past can/may → could/might shall/will → should/would must/ought to must/ought to need need had better had better
Direct Indirect past Tense → past Perfect Tense present Tense → past Tense future Tense → future in the past can/may → could/might shall/will → should/would must/ought to → must/ought to need → need had better → had better Grammar

Grammar e.g. (I)He said,“T'm sorry.” He said he was sorry. (2)She said,"You haven't changed much." She said that I hadn't changed much." (3)He said,"The man came at six." He said that the man had come at six (4)She said,“I will go with you.” She told me that she would go with me. (5)He said,"the man may come." He said that the man might come
(1) He said, “I’m sorry.” He said he was sorry. (2) She said, “You haven’t changed much.” She said that I hadn’t changed much.” (3) He said, “The man came at six.” He said that the man had come at six. (4) She said, “I will go with you.” She told me that she would go with me. (5) He said, “the man may come.” He said that the man might come. Grammar e.g

Grammar 3)Adverbs of time and place and a few other expressions change as follows: Direct Indirect now → then here → there this/these → that/those today that day yesterday the day before tomorrow the next day/ the following day
3) Adverbs of time and place and a few other expressions change as follows: Direct Indirect now → then here → there this/these → that/those today → that day yesterday → the day before tomorrow → the next day/ the following day Grammar

Grammar next week/year the following week/year a year ago > a year before/ the previous year last night → the night before three days ago → three days before e.g.1)"You may have this book for one week."said the librarian. The librarian said that I might have that book for a week. 2)She said,"Now I live in London She said that then she lived in London
next week/year → the following week/year a year ago → a year before/ the previous year last night → the night before three days ago → three days before e.g.1) “You may have this book for one week.”said the librarian. The librarian said that I might have that book for a week. 2) She said, “Now I live in London” She said that then she lived in London. Grammar

Grammar 3)He said,"She arrived here yesterday." He said that she had arrived there the day before. 4)The pronouns also change. e.g.1)Jane said,"I am glad to see you." Jane said that she was glad to see me BUT In some sentences,the pronouns don't have to be changed. 2)He said,"she is tired." He said that she was tired
3) He said, “She arrived here yesterday.” He said that she had arrived there the day before. 4) The pronouns also change. e.g.1) Jane said, “I am glad to see you.” Jane said that she was glad to see me. BUT In some sentences, the pronouns don’t have to be changed. 2) He said, “she is tired.” He said that she was tired. Grammar

Grammar 5)When the sentence expresses a fact that is supposed to be universally true and not merely applicable to the time when the statement was made,the present tense may be used in indirect speech. e.g.1)"The earth moves around the sun,"the teacher told us. The teacher told us that the earth moves around the sun.(客观真理) 2)"The meeting is next Tuesday,"He said. He said that the meeting is next Tuesday. (间接引语所说的情况在说话人说话时仍然存在)
5) When the sentence expresses a fact that is supposed to be universally true and not merely applicable to the time when the statement was made,the present tense may be used in indirect speech. e.g. 1) “The earth moves around the sun,”the teacher told us. The teacher told us that the earth moves around the sun.(客观真理) 2) “The meeting is next Tuesday,” He said. He said that the meeting is next Tuesday. (间接引语所说的情况在说话人说话时仍然存在) Grammar
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)08 Revision(I).ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)07 Using the Sun’s Energy.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)06 Cambridge - the University Town.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)04 Grammar Pattern Drill.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)02(主讲教师:张莘梅).ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit17 At the Hotel 2.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit21 Special English 2.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit16 At the Hotel 1.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit1-unit11(主讲人:董育英、寇晓虹).ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit23 Special English.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit22 Special English.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit20 Special English 1.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit18-19 UNIVERSITY LIFE.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit15 Service and economy.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit14 Transportation.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit13 family.ppt
- 吉林大学:《英语听说》课程电子教案(PPT课件)unit12 communuication..ppt
- 《大学英语语法》课程电子教案(PPT课件)09 替代(substitution)、省略(Ellipsis)、It- 句型(“It” patterns)、直接引语和间接引语(Direct and Indirect Speech).ppt
- 《大学英语语法》课程电子教案(PPT课件)08 否定(Negation)、倒装(Inverted Order)、反意疑问句(tag question).ppt
- 《大学英语语法》课程电子教案(PPT课件)07 介词(preposition)、状语从句(Adverbial Clause)、定于从句(Attributive Clause)、名词性从句(Nominal Clauses)、主谓一致(Subject-verb Concord).ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)10 Grammar Pattern Drills.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)11 Grammar Pattern drills.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)12 Grammar Pattern Drills.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程电子教案(PPT课件,一)13.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 05 Beauty is Truth.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 06 Button, Button.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 07 Twelve Angry Men(Part One)By Reginald Rose.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 08 Twelve Angry Men(Part Two)By Reginald Rose.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 01 Christmas Day in the Morning.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 02 The Nightingale and the Rose.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 03 Clearing in the sky.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 04 Darken your Graying hair, and Hide your Fright.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 09 Pompeii.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 10 The Man in Asbestos(负责人:张而立).ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 11 Diogenes and Alexander(主讲人:郑世华).ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(二)lesson 12 Farewell, My Unlovely.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(三)lesson 13 Mr. Imagination.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(三)lesson 14 The Odour of Cheese.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(三)lesson 15 A Horseman in the Sky.ppt
- 吉林大学:《综合英语精读》课程PPT教学课件(三)lesson 16 The Oyster and the Pearl.ppt
