香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 9 Online algorithm

CMS57opmtr cince Week 9:Online Algorithms Instructor:Shengyu Zhang 1
Instructor: Shengyu Zhang 1

Secretary hiring problem 2
Secretary hiring problem 2

A motivating problem ■Secretary problem: We want to hire a new office assistant. There are a number of candidates. We can interview one candidate each day,but we have to decide the acceptance/rejection immediately. 3
A motivating problem ◼ Secretary problem: ❑ We want to hire a new office assistant. ❑ There are a number of candidates. ❑ We can interview one candidate each day, but we have to decide the acceptance/rejection immediately. 3

One possible strategy On each day,if candidate A is better than the current secretary B,then fire B and hire A. Each has a score.Assume no tie. Firing and hiring always have overhead. Say:cost c. We'd like to pay this but it'll be good if we could have an estimate first. Question:Assuming that the candidates come in a random order,what's the expected total cost?
One possible strategy ◼ On each day, if candidate 𝐴 is better than the current secretary 𝐵, then fire 𝐵 and hire 𝐴. ❑ Each has a score. Assume no tie. ◼ Firing and hiring always have overhead. ❑ Say: cost 𝑐. ◼ We’d like to pay this but it’ll be good if we could have an estimate first. ◼ Question: Assuming that the candidates come in a random order, what’s the expected total cost? 4

Probability... Define a random variable X X=#of times we hire a new secretary Our question is just to compute E[cX]=c·E[X]. By definition, E[X]=∑x=1x·Pr[X=x]. But this seems complicated to compute. 5
Probability… ◼ Define a random variable 𝑋 𝑋 = # of times we hire a new secretary ◼ Our question is just to compute 𝐄 𝑐𝑋 = 𝑐 ⋅ 𝐄 𝑋 . ◼ By definition, 𝐄 𝑋 = σ𝑥=1 𝑛 𝑥 ⋅ 𝐏𝐫 𝑋 = 𝑥 . ◼ But this seems complicated to compute. 5
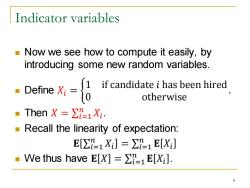
Indicator variables Now we see how to compute it easily,by introducing some new random variables. Define Xi 0 if candidate i has been hired otherwise "Then X=∑1Xi. Recall the linearity of expectation: E[∑1X]=∑1E[X] ·We thus have E[X]=∑1E[x]. 6
Indicator variables ◼ Now we see how to compute it easily, by introducing some new random variables. ◼ Define 𝑋𝑖 = ቊ 1 if candidate 𝑖 has been hired 0 otherwise . ◼ Then 𝑋 = σ𝑖=1 𝑛 𝑋𝑖 . ◼ Recall the linearity of expectation: 𝐄 σ𝑖=1 𝑛 𝑋𝑖 = σ𝑖=1 𝑛 𝐄 𝑋𝑖 ◼ We thus have 𝐄 𝑋 = σ𝑖=1 𝑛 𝐄 𝑋𝑖 . 6

Analysis continued What is EXi? Recall Xi=0 1 if candidate i has been hired otherwise Thus E[Xi]Pr[Xi=1]=1/i. 0( Candidate i was hired iff she is the best among the first i candidates. ■ So E[X]=1E[Xi]=11/i In(n). ■ The average cost is In(n).c
Analysis continued ◼ What is 𝐄 𝑋𝑖 ? ◼ Recall 𝑋𝑖 = ቊ 1 if candidate 𝑖 has been hired 0 otherwise . ◼ Thus 𝐄 𝑋𝑖 = 𝐏𝐫 𝑋𝑖 = 1 = 1/𝑖. ❑ Candidate 𝑖 was hired iff she is the best among the first 𝑖 candidates. ◼ So 𝐄 𝑋 = σ𝑖=1 𝑛 𝐄 𝑋𝑖 = σ𝑖=1 𝑛 1/𝑖 ≈ ln 𝑛 . ◼ The average cost is ln 𝑛 ⋅ 𝑐. 7

Another strategy A more natural scenario is that we only hire once. And of course,we hope to hire the best one. But the candidates on the market also get other offers.So we need to issue offer fast. Interview one candidate each day,and decide acceptance/rejection immediately. The candidates come in a random order. 8
Another strategy ◼ A more natural scenario is that we only hire once. ◼ And of course, we hope to hire the best one. ◼ But the candidates on the market also get other offers. So we need to issue offer fast. ◼ Interview one candidate each day, and decide acceptance/rejection immediately. ◼ The candidates come in a random order. 8

Strategy Reject the first k candidates no matter how good they are. Because there may be better ones later. After this,hire the first one who is better than all the first k candidates. If all the rest n-k are worse than the best one among the first k,then hire the last one
Strategy ◼ Reject the first 𝑘 candidates no matter how good they are. ❑ Because there may be better ones later. ◼ After this, hire the first one who is better than all the first 𝑘 candidates. ◼ If all the rest 𝑛 − 𝑘 are worse than the best one among the first 𝑘, then hire the last one. 9

Pseudo-code best score =0 ■fori=1tok if score(i)>best_score best_scorescore(i) for i=k+1 to n if score(i)best_score return(i) return n 10
Pseudo-code ◼ 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡_𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 = 0 ◼ for 𝑖 = 1 to 𝑘 if 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒(𝑖) > 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡_𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡_𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 = 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒(𝑖) for 𝑖 = 𝑘 + 1 to 𝑛 if 𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒(𝑖) > 𝑏𝑒𝑠𝑡_𝑠𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑒 return(𝑖) return 𝑛 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 8 Mechanism design.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 6 Algorithms for resource allocation.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 5 NP-Complete problems.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 4 Approximation algorithms.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 3 Algorithms for data streams.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 2 Linear program. Examples, Simplex algorithms, primal-dual, strong duality(and a physical interpretation), application to games.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 1 Review of basic concepts of algorithms and complexity, probability and tail bounds.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 8:Further Topics on Random Variables 1.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 9:Further Topics on Random Variables 2.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 11:Limit Theorems.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 9:Further Topics on Random Variables 2.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 11:Limit Theorems.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 8:Further Topics on Random Variables 1.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 10:Limit Theorems.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 10:Limit Theorems.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 7:General Random Variables 3.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 7:General Random Variables 3.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 6:General Random Variables 2.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 6:General Random Variables 2.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Probability and Statistics for Engineers》课程教学资源(辅导材料)Tutorial 5:General Random Variables 1.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Online learning. Expert problem.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 11 Influence maximization on social network.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Topics in Theoretical Computer Science》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Lecture 12 Quantum computing. Quantum algorithms, BQP, quantum non-locality, quantum games.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 1 Basics.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 2 Shor's algorithm.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 3 Hidden Subgroup Problems 1.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 4 Hidden Subgroup Problems 2.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 5 Searching algorithm and quantum adversary method.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 6 Quantum query complexity.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 7 Quantum communication complexity 1.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 8 Quantum communication complexity 2.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 9 Quantum information theory 1.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 10 Quantum information theory 2.docx
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 11 Quantum information theory 3.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Quantum Computing》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 12 Quantum information theory 4.pdf
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 1 Introduction to the course.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 2 Single Source Shortest Paths.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 3 Greedy Algorithms.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 4 Randomized Algorithms.pptx
- 香港中文大学:《Design and Analysis of Algorithms》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Week 5 Dynamic Programming.pptx
