《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)33 出血热病毒

第三篇医学相关病毒第34章出血热病毒Haemorrhagic Fever virus石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
第三 篇 医 学 相关 病 毒 第第3434章章 出 血热 病 毒 出 血热 病 毒 Haemorrhagic Haemorrhagic Fever virus Fever virus 石石河 子 大 学 病 原 生 物 学 与 免 疫 学 教 研室 河 子 大 学 病 原 生 物 学 与 免 疫 学 教 研室

教学大纲■掌握内容汉坦病毒主要生物学性状,包括形态结构培养特性、抗原分型及抵抗力;流行环节及致病性:微生物学检查法。亲新疆出血热病毒致病性及传播媒介■了解内容肾综合征出血热病毒及新疆出血热病毒防治原则:非洲出血热病毒(埃博拉病毒和马堡热病毒)的传播方式及引起疾病石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
教 学 大 纲 掌 握 内 容 掌 握 内 容 汉汉 坦坦 病病 毒毒 主主 要要生 生 物 物 学 学 性 性 状 状 , 包包 括括 形形 态态 结结构构 、 培 养 特 性 、抗 原 分 型 及 抵 抗 力 ; 流 行环 节及 培 养 特 性 、抗 原 分 型 及 抵 抗 力 ; 流 行环 节及 致致病 性 病 性 ;;微微 生生 物物 学学 检 检 查查 法 法 。 新新 疆疆 出出 血血热热 病病 毒毒 致致 病 性 及 传 播 媒 介 病 性 及 传 播 媒 介 了 解内 容 了 解内 容 肾肾综综合 征 出 血热 病 毒 及 新 疆 出 血热 病 毒 防 治 合 征 出 血热 病 毒 及 新 疆 出 血热 病 毒 防 治 原 则 ; 非洲 出 血热 病 毒 ( 埃 博 拉 病 毒 和 马 堡 原 则 ; 非洲 出 血热 病 毒 ( 埃 博 拉 病 毒 和 马 堡 热 病 毒 ) 的 传 播 方 式 及 引 起疾 病 热 病 毒 ) 的 传 播 方 式 及 引 起疾 病 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室

HistoryHaemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS: later renamedhantavirus disease.HVD)first recognized in Heilongjiang,Chinain the 1930s.and came to the attention of the West during theKoreanwarwhenover3000UNtroopswereafflictedIt transpired that thediseasewasnot new andhad beendescribed by the Chinese 1000 years earlierIn1974,thecausative was isolatedfrom theKoreanStrippedfieldmiceandwas called Hantaan virusIn1995,a new disease entity called hantavirus pulmonarysyndromewasdescribedin the“four corners"regionoftheU.S石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
History Haemorrhagic Haemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS: later renamed (HFRS: later renamed hantavirus disease, HVD) first ) first recognized in Heilongjiang, China recognized in Heilongjiang, China in the 1930s, and in the 1930s, and came to the attention of the West during the came to the attention of the West during the Korean war Korean war when over 3000 UN troops were afflicted when over 3000 UN troops were afflicted It transpired that the disease was not new and had been It transpired that the disease was not new and had been described by the described by the Chinese 1000 years earlier Chinese 1000 years earlier In 1974, the causative was isolated from the Korean In 1974, the causative was isolated from the Korean Stripped field Stripped field mice mice and was called and was called Hantaan Hantaan virus virus In 1995, a new disease entity called hantavirus pulmonary In 1995, a new disease entity called hantavirus pulmonary syndrome was described in the syndrome was described in the “four corners four corners”region of the U.S. region of the U.S. 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
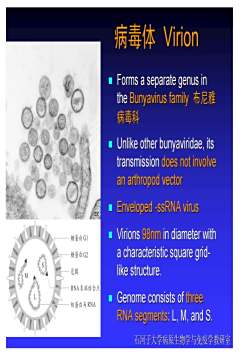
病毒体 Virion Forms a separate genus inthe Bunyavirus family 布尼雅病毒科 Unlike other bunyaviridae, itstransmissiondoes not involvean arthropod vectorEnveloped-ssRNA virusVirions 98nm in diameter with糖蛋白 G1a characteristic square grid糖蛋白G2like structure包膜RNA末端结合点Genome consists of three核蛋白与RNARNA segments: L, M, and S石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
病 毒 体 病 毒 体 Virion Virion Forms a separate genus in Forms a separate genus in the the Bunyavirus Bunyavirus family family 布布 尼尼 雅 病病 毒毒 科 Unlike Unlike othe other r bunyaviridae bunyaviridae, its , its transmission transmission does not does not involve involve anan arthropod vector arthropod vector Enveloped Enveloped -ssRNA ssRNA virus virus Virions Virions 98nm in diameter with in diameter with a characteristic square grid a characteristic square grid- like structure. like structure. Genome consists of Genome consists of three three RNA segments RNA segments: L, M, and S. : L, M, and S. 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室

基于中和试验的血清型Based NTSubtypes of Hantaviruses黑线姬黑线姬鼠型新动汇褐家鼠型■欧洲棕背鼠型小家鼠■草原田鼠型■巴尔干姬鼠型■小家鼠型石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
基 于 中 和 试验的 血清 型 基 于 中 和 试验的 血清 型 Subtypes of Hantaviruses Based NT Subtypes of Hantaviruses Based NT 黑黑线线姬 鼠型 姬 鼠型 褐褐家 鼠型 家 鼠型 欧 洲 棕 背鼠型 欧 洲 棕 背鼠型 草草原 田 鼠型 原 田 鼠型 巴 尔 干 姬 鼠型 巴 尔 干 姬 鼠型 小 家 鼠型 小 家 鼠型 黑线姬 姬 田田 鼠 小小 家家 鼠 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室

根据抗原和基因结构分型(10型(汉滩型)Hantaane(汉城型 Seoul type Puumala type■Sin Nombre(辛诺柏型)石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
根根 据 据 抗 抗 原 原 和 和 基 基 因因 结结构 构 分 分 型 型 (( 1010型 型 )) Hantaan Hantaan(( 汉汉 滩滩 型型 )) Seoul type Seoul type(( 汉汉 城城 型型 )) Puumala Puumala type type Sin Sin Nombre Nombre(( 辛辛诺诺柏柏 型型 )) 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室

流行病毒学Epidemiology Natural host: Rodent Apodemus agrarius(Stripped feld mice,黑线姬鼠)■传染源:黑线姬鼠、褐家鼠、大林姬鼠 Viral contamination comes from rodent urinestool, salivary secretion Seasonal and regional distribution (autumn andwinter, OCct.-Jan.) The infection route is still uncertain. Thepossible entries are respiratory tract, mouthand direct contact石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
流 行病 毒 学 流 行病 毒 学 Epidemiology Epidemiology Natural host: Natural host: Rodent Rodent Apodemus Apodemus agrarius agrarius ((Stripped field mice, Stripped field mice, 黑线姬姬 鼠)) 传传 染染 源源 :: 黑黑线线姬姬 鼠鼠、褐、褐家 家 鼠鼠、大 、大 林林 姬姬 鼠鼠 Viral contamination comes from rodent urine, Viral contamination comes from rodent urine, stool, salivary secretion stool, salivary secretion Seasonal and regional distribution Seasonal and regional distribution (autumn and (autumn and winter, Oct. winter, Oct.-Jan.) Jan.) The infection route The infection route is still uncertain. The is still uncertain. The possible entries are possible entries are respiratory tract, mouth, respiratory tract, mouth, and direct contact and direct contact 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室

Rodent Carriers of HantavirusesStrippedfield mouse(Apodemus agrariusBank vole(Clethrionomys glareolus)Rat(Rattus)Deer Mouse(Peromyscus maniculatus)石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
Rodent Carriers of Hantaviruses Rodent Carriers of Hantaviruses Stripped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius) Bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus) Deer Mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) Rat (Rattus) 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室

临床特点Clinical Features Incubation: 2 weeks, HFRS Pathogenesis mechanism is unknownImmunological reaction may play role极低的隐性感染率Very low subclinicalinfection rate (1-4%)病后稳定的免疫力,一般不再发病 Stablehumoral immunity.no repeat infection石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
临 床 特 点 临 床 特 点 Clinical Features Clinical Features Incubation: 2 weeks, HFRS Incubation: 2 weeks, HFRS Pathogenesis Pathogenesis mechanism is unknown mechanism is unknown. . Immunological reaction may play role Immunological reaction may play role 极 低 的 隐 性 感 染 率 极 低 的 隐 性 感 染 率 Very low Very low subclinical subclinical infection rate (1 infection rate (1-4%) 4%) 病 后 稳定 的 免 疫 力 , 一 般不 再 发 病 病 后 稳定 的 免 疫 力 , 一 般不 再 发 病 Stable Stable humoral immunity. no repeat infection humoral immunity. no repeat infection 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室

致病性 Pathogenesis The mulisystem pathology of HVD ischaracterized by damage to capllaries andsmall vessel walls,resulting in vasodilation andcongestion with hemorrhagesClassically,hantavirus disease consists ofdistinct phases. These phases may be blurredin moderate or mild cases石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
致致病 性 病 性 Pathogenesis Pathogenesis The The multisystem multisystem pathology pathology of HVD is of HVD is characterized by damage to characterized by damage to capillaries and capillaries and small vessel walls small vessel walls, resulting in , resulting in vasodilation vasodilation and and congestion with congestion with hemorrhages hemorrhages Classically, hantavirus disease consists of 5 Classically, hantavirus disease consists of 5 distinct phases. These phases may be blurred distinct phases. These phases may be blurred in moderate or mild cases in moderate or mild cases 石河子大学病原生物学与免疫学教研室
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)寄生虫总论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)原虫概述-阿米巴.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)机会性致病原虫(上).pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)疟原虫-2/2.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)疟原虫-1/2.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)鞭毛虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)机会性致病原虫(下).pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)线虫概论、蛔虫、鞭虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)蛲虫、钩虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)细粒、多房棘球、微小膜壳绦虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)绦虫概论、猪、牛带绦虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)吸虫概论、肝、肠吸虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)丝虫、旋毛虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)医学节肢动物——昆虫纲(上).pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)肺、血吸虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)医学节肢动物——昆虫纲(下).pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2013)医学节肢动物——蜱螨.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2012)原虫概论及阿米巴原虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2012)人体寄生虫学总论.pdf
- 《病原生物学(人体寄生虫学)》课程教学课件(2012)原虫——鞭毛虫.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)35 逆转录病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)38 病原性真菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)32 肝炎病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)28 衣原体.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)29 螺旋体.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)31 肠道病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)30 呼吸道病毒.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)27 支原体.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)26 立克次体.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)23 布鲁菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)21 结核分枝杆菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)20 棒状杆菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)17 弧菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)15 志贺菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)18 梭菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)16 沙门菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)14 埃希菌属菌.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)11 葡萄球菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)12 链球菌属.pdf
- 《病原生物学(医学微生物学)》课程教学课件(讲稿)13 奈瑟菌属.pdf
