同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)07 Timber Connections
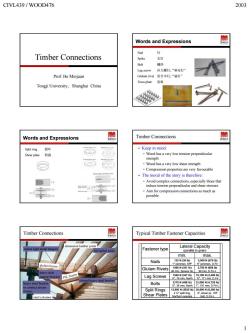
CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Words and Expressions Nail 钉 Timber Connections Spike 长钉 Bolt 棋栓 Lag screw拉力蝶钉,“麻花钉 Prof.He Minjuan Glulam rivet胶合木钉,“扇钉” Truss plate齿板 Tongji University,Shanghai China Words and Expressions 园 Timber Connections Split ring裂环 .Keep in mind Shear plate约盘 Wood has a very low sheat streneth Compression properties are very favourable The moral of the story is therefore: Avoid complex com Timber Connections Typical Timber Fastener Capacities Fastener type Lateral Capacity Nails Glulam rivets Lag Screws Bolts Split Rings 1
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 1 Timber Connections Prof. He Minjuan Tongji University, Shanghai China Words and Expressions Nail 钉 Spike 长钉 Bolt 螺栓 Lag screw 拉力螺钉,“麻花钉” Glulam rivet 胶合木钉,“扁钉” Truss plate 齿板 Words and Expressions Split ring 裂环 Shear plate 剪盘 Timber Connections Keep in mind: • Wood has a very low tension perpendicular strength • Wood has a very low shear strength • Compression properties are very favourable The moral of the story is therefore: • Avoid complex connections, especially those that induce tension perpendicular and shear stresses • Aim for compression connections as much as possible Timber Connections steel columns dimension lumber joists heavy steel bracket to connect atrium trusses riveted heavy steel bracket toe nailed joists nailed light metal hangers heavy steel support bracket Typical Timber Fastener Capacities Fastener type Lateral Capacity (parallel to grain) min. max. Nails 132 N (30 lb) 1” common, SPF 3,000 N (675 lb) 6” common, D-Fir Glulam Rivets 1560 N (351 lb) 40 mm, Spruce GL 2,700 N (608 lb) 90 mm, D.Fir-L Lag Screws 1540 N (347 lb) ¼”, 70 mm, North 15,100 N (3,400 lb) ¾”, 171 mm, D.Fir Bolts 2170 N (488 lb) ½”, 38 mm, North 21,000 N (4,725 lb) 1”, 191 mm, D.Fir-L Split Rings Shear Plates 12,600 N (2835 lb) 2 ½” split ring, Northern species 36,800 N (8,280 lb) 4”, shear pl., 7/8” bolt, D.Fir-L

CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Traditional connections Compression structure Compression connections Compression connections Compression connections Compression connections
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 2 Traditional connections Compression structure Compression connections Compression connections Compression connections Compression connections for tension members Compression connections

CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Compression connections Beam on column support The onnector-less Beam on column support Face mounted beam hangers with timber rivets tohe Saddle beam hangers Bolted beam supports ■ 3
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 3 Compression connections The connector-less connection Beam on column support Compression perpendicular to grain stresses Assure adequate bearing area Simple beam supports Beam on column support Use a hardwood block to reduce bearing stresses Face mounted beam hangers with timber rivets notch Compression perpendicular to grain Saddle beam hangers seat saddle Bolted beam supports

CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Support connections Haunch connections Connection Design 胞 Connectors loaded at an angle to the grain Calculate connection force 90 0 fast Hankinson's Interaction Equation .fastener availability N,= PO. .ductility requirement ·Calculate capacity Psin0+O.cos20 Nail connections Nailed trusses 4
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 4 Support connections Haunch connections Connection Design Calculate connection force Choose fastener type based on • available space • fastener capacity • structural configuration • aesthetics • fastener availability • ductility requirement Calculate capacity Connectors loaded at an angle to the grain 2 2 P sin Q cos P Q N r r r r r Pr Qr Nr θ Hankinson’s Interaction Equation θ = 90o θ = 0o Nail connections Nailed trusses
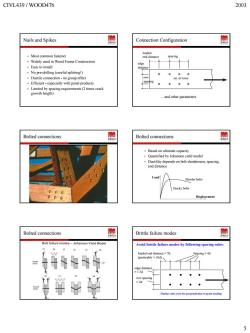
CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Nails and Spikes Connection Configuration Most common fastener Widely used in Wood Frame Construction .Easy to install No pre-drilling (careful splitting!) Ductile connection-no group effect Efficientespecially with panel products Bolted connections Bolted connections 园 ield model Du 0c Displacement Bolted connections 园 Brittle failure modes Bolt failure modes-Johansen Yield Model Avoid britte failure modes by following spacing rue 库华好5 >7 帝华平
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 5 Nails and Spikes Most common fastener Widely used in Wood Frame Construction Easy to install No pre-drilling (careful splitting!) Ductile connection - no group effect Efficient - especially with panel products Limited by spacing requirements (2 times crack growth length) Connection Configuration loaded end distance spacing edge distance row spacing no. of rows …and other parameters Bolted connections Bolted connections Based on ultimate capacity Quantified by Johansen yield model Ductility depends on bolt slenderness, spacing, end distance Load Displacement Slender bolts Stocky bolts Bolted connections Brittle failure modes Avoid brittle failure modes by following spacing rules: loaded end distance > 7d (preferably > 10d) Spacing > 4d edge distance > 1.5d row spacing > 2d Similar rules exist for perpendicular to grain loading
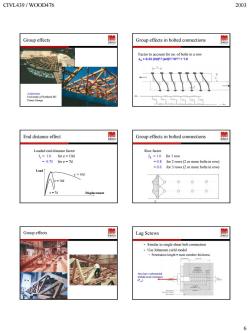
CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Group effects Group effects in bolted connections 55℃ End distance effect Group effects in bolted connections Loaded end distance factor Row factor J=1.0 for e=10d Jg=1.0 for I row =0.75 for e=7d =0.8 for 2 rows(2or more bolts in row) Load -0.6 for 3 rows (2 or more bolts in row) 000 Displacement 000 Group effects Lag Screws Similar to single shear bolt connection Use Johansen yield model Penetration length main member thickness 6
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 6 Group effects Auditorium University of Northern BC Prince George Group effects in bolted connections Factor to account for no. of bolts in a row JG = 0.33 (l/d)0.5 (s/d)0.2 N-0.3 10d e = 10d e = 7d Group effects in bolted connections Row factor JR = 1.0 for 1 row = 0.8 for 2 rows (2 or more bolts in row) = 0.6 for 3 rows (2 or more bolts in row) Group effects Lag Screws Similar to single shear bolt connection Use Johansen yield model • Penetration length = main member thickness Also have substantial withdrawal resistance (Prw)

CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Split Rings and Shear Plates 脚 Split Rings and Shear Plates High strength fasteners splat ring Installation of Split Rings and Shear Plates Shear plate installation Installation special tool Load Splt Rings and Shear Plates Large split ring connections ◆Stress conditions ◆Failure mod 7
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 7 Split Rings and Shear Plates High strength fasteners • Provide larger grip surface on wood Wood failure modes typical shear plates split ring Split Rings and Shear Plates Installation of Split Rings and Shear Plates Installation: • special tools • tight fit • ideal for pre-fabrication Shear plate installation Load transfer with Split Rings and Shear Plates Large split ring connections
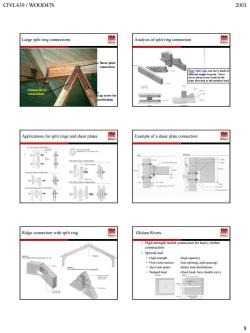
CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Large split ring connections Analysis of split ring connection ote:Split rings can carry loa Applications for split rings and shear plates Example of a shear plate connection 骨 Ridge connection with split ring Glulam Rivets Special nail High strength Wedged head (fixed head,force double cuv) 0 8
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 8 Large split ring connections Shear plate connection Glulam Rivet connections Lag screw for positioning Analysis of split ring connection Note: Split rings can carry loads at different angles to grain. Shear plates always carry loads in the same direction as the member load Applications for split rings and shear plates Example of a shear plate connection Ridge connection with split ring Glulam Rivets High strength nailed connection for heavy timber construction Special nail • High strength (high capacity) • Oval cross-section (less splitting, tight spacing) • Steel side plates (better load distribution) • Wedged head (fixed head, force double curv)

CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Beam hanger connections with glulam rivets Glulam Rivet connection geometry 8888 8888 On-site installation of glulam rivet connection 园 Load directions d(V Failure Mode Erection of Atrium Trusses 9
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 9 Beam hanger connections with glulam rivets Glulam Rivet connection geometry LP needed for calculating capacity On-site installation of glulam rivet connection Load directions loaded perpendicular to grain (V) loaded parallel to grain (T) loaded in withdrawal (T) seat takes vertical load (V) T V Failure Mode Erection of Atrium Trusses

CIVL439/WOOD476 2003 Erection of Atrium Trusses Trusses with light metal gauge connectors with Glulam Rivet Failure modes Failure modes 2)Tensile failure of plate N.-on.(KpKsrK:)u 58 06 t factor for hee 3)Shear failure of plate 。5 86 1/41 065 Calculating tooth resistance Net areas for tooth resistance N=0.8(Test value)(A) d less 10
CIVL439 / WOOD476 2003 10 Erection of Atrium Trusses Steel plates fastened to PSL members with Glulam Rivets On-site bolted connection Trusses with light metal gauge connectors Failure modes (1) Teeth pulling out Nu = φ nu (KDKSFKT )JH φ = 0.6 JH is a moment factor for heel connections 1 Slope JH slope 1 / 4 to 1 / 3 0.8 > 1 / 3 to 1 / 2.4 0.75 > 1 / 2.4 to 1 / 2.2 0.7 > 1 / 2.2 0.65 Failure modes (2) Tensile failure of plate Tr = φ tp φ = 0.6 (3) Shear failure of plate Vr = φ vp φ = 0.6 Calculating tooth resistance Nu and Ns are based on test values (N/mm2 ) listed in CCMC reports Nu = 0.8 (Test value)(Agross) or Nu = (Test value) (Anet) Where Agross is the total area covered by the truss plate, and Anet is the total area covered less the end zones as shown in the next slide Net areas for tooth resistance end distance a = max (12mm or 0.5 tooth length) edge distance e = max (6mm or 0.25 tooth length)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)06 Design of Wood Members.pdf
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)05 Modern Timber Structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)04 Design of Timber Structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)03 Earthquake Design of Wood Structures.pdf
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)02 Strength of Wood.pdf
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)01 Introduction of this course(负责人:何敏娟).pdf
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(试卷习题)习题(解答).doc
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(试卷习题)习题(试题).doc
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷二.doc
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(试卷习题)试卷一.doc
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)术语词典.doc
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)Capacity of Oriented Strand Board Shear Walls with Overdriven Sheathing Nails.pdf
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)Bolted joints in glulam and structural timber composites.pdf
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)Analytical Model for Sheathing-to-Framing Connections in Wood Shear Walls and Diaphragms.pdf
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)An experimental and numerical study of the effect of friction in single dowel joints.pdf
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)Three-dimensional finite solid element model for Japanese post and beam connection.pdf
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)Determination of embedding strength of wood for dowel-type fasteners.pdf
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)CYCLIC PERFORMANCE OF PERFORATED WOOD SHEAR WALLS WITH OVERSIZE OSB PANELS.pdf
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)Contact-free measurements and numerical analyses of the strain distribution in the joint area of steel-to-timber dowel joints.pdf
- 《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(参考文献)COMPARISON OF STATIC AND DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF TIMBER SHEAR WALLS.pdf
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)08 Light frame wood constructions.pdf
- 同济大学:《木结构 Timber Engineering》课程教学资源(电子教案)09 Earthquake Resistance Design.pdf
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(画法几何与阴影透视)投影法与三视图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(画法几何与阴影透视)线与平面、平面与平面的相对位置.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(画法几何与阴影透视)投影变换 projection change.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(画法几何与阴影透视)立体表面的交线(截交线与相贯线的画法).ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(画法几何与阴影透视)轴测投影图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(建筑制图)组合体的投影图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(建筑制图)建筑形体的表达方法.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(建筑制图)建筑施工图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(建筑制图)透视投影 perspective projection.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第2章 点、线、面的投影 2.2 直线的投影.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第2章 点、线、面的投影 2.1 三视图与点的投影.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第7章 工程形体的表达方法.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第9章 结构施工图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第1章 制图基础.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第6章 组合体的投影图.ppt
- 安徽科技学院:《画法几何与建筑制图》课程PPT教学课件(工程制图)第8章 建筑施工图(房屋施工图).ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 3 Bond and Anchorage.ppt
- 同济大学:《高等混凝土结构理论》课程电子教案(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Bending and Compression Behavior of RC Structural Members.ppt
