西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 5 Steering system

Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering The steering system is used to control the direction of the vehicle. 1.Mode of Turning First,deflecting the wheels a relative angle to the body to achieve steering;Second,by changing the driving force on both sides of the running gears to achieve steering;Third,both changing the driving forces on both sides of the running gears and deflecting the wheels a relative angle to the body to achieve steering 械电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System The steering system is used to control the direction of the vehicle. 1. Mode of Turning First, deflecting the wheels a relative angle to the body to achieve steering; Second, by changing the driving force on both sides of the running gears to achieve steering; Third, both changing the driving forces on both sides of the running gears and deflecting the wheels a relative angle to the body to achieve steering. Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering
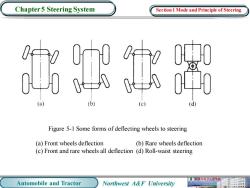
Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering 服 (d) Figure 5-1 Some forms of deflecting wheels to steering (a)Front wheels deflection (b)Rare wheels deflection (c)Front and rare wheels all deflection (d)Roll-waist steering 机械电子工程模 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System (a) Front wheels deflection (b) Rare wheels deflection (c) Front and rare wheels all deflection (d) Roll-waist steering Figure 5-1 Some forms of deflecting wheels to steering Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering

Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering 2.Analysis of Wheeled Vehicles Steering Theory 2.1 Kinematic Analysis According to the pure rolling requirements of the wheels when steering,the following three conditions should be met when steering for the 4X2 rear-wheel drive wheeled vehicles: (1)Achieving the front wheel deflection via the drivers' manipulation,and the degree of wheel deflection determines the vehicles'turning radius. (2)To achieve pure rolling of the two front wheels,it is required that the inside wheel's deflection angle a is larger than the outside wheel's deflection angle B,and the two angles should meet the following equation; M cotB-cota= L 械电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System 2. Analysis of Wheeled Vehicles Steering Theory 2.1 Kinematic Analysis According to the pure rolling requirements of the wheels when steering, the following three conditions should be met when steering for the 4×2 rear-wheel drive wheeled vehicles: (1) Achieving the front wheel deflection via the drivers’ manipulation, and the degree of wheel deflection determines the vehicles' turning radius. (2) To achieve pure rolling of the two front wheels, it is required that the inside wheel’s deflection angle α is larger than the outside wheel’s deflection angle β, and the two angles should meet the following equation; L M cot − cot= Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering

Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering If the front and rear wheels are out phase when turning,the equation is; M cotB-cota= 2L (3)The distances traveled by the two driving wheels is not equal when steering because the rotating speed of the outside wheel is faster than that of the inner wheel,namely; n2_R+0.5B ni R-0.5B 机被与电子工程学聚 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System If the front and rear wheels are out phase when turning, the equation is; L M 2 cot − cot= (3) The distances traveled by the two driving wheels is not equal when steering because the rotating speed of the outside wheel is faster than that of the inner wheel, namely; R 0.5B R 0.5B n n 1 2 − + = Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering
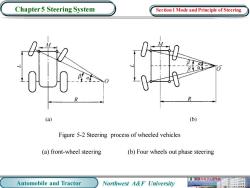
Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering (a】 (6) Figure 5-2 Steering process of wheeled vehicles (a)front-wheel steering (b)Four wheels out phase steering 业机械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System Figure 5-2 Steering process of wheeled vehicles (a) front-wheel steering (b) Four wheels out phase steering Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering

Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering 2.2 Dynamic Analysis Assumptions: (1)Four-wheel vehicles'front wheels are directly installed on the same front axle,and the middle part of the front axle is hinged to the body; (2)The speed of vehicle is low when steering,so the centrifugal inertia force can not be considered 机被与电子工程原 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System 2.2 Dynamic Analysis Assumptions: (1) Four-wheel vehicles’ front wheels are directly installed on the same front axle, and the middle part of the front axle is hinged to the body; (2) The speed of vehicle is low when steering, so the centrifugal inertia force can not be considered. Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering
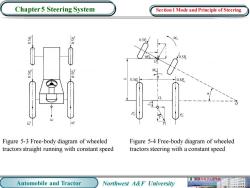
Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering Figure 5-3 Free-body diagram of wheeled Figure 5-4 Free-body diagram of wheeled tractors straight running with constant speed tractors steering with a constant speed 械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System Figure 5-3 Free-body diagram of wheeled tractors straight running with constant speed Figure 5-4 Free-body diagram of wheeled tractors steering with a constant speed Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering

Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering When vehicles moving forward,the traction balance equation is; Pa PaI P92=Pre Prg+Pr When steering,the traction balance equation is; PP+Prcosa+Pasina+P'cosy When steering,the total steering resisting moment acted by the ground relative to Q2 point is the sum of all the resisting moment; M M-e+Mo+PiLrsiny+LPresin a When steering,the steering moment on the wheels acted by ground is; MB =0.5B(P2 -P)+LPBcosa Assuming P2=P the above equation can be written as; MB LPRcosa According to the conditions of stable steering,the steering moment should equal to the steering resisting moment,namely; 机被与电子工程学根 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System Pq = Pq1 + Pq2 = Pf c + Pf q + PT When vehicles moving forward, the traction balance equation is; When steering, the traction balance equation is; P P P cosα P sinα P cosγ q f q f c B T = + + + When steering, the total steering resisting moment acted by the ground relative to Q2 point is the sum of all the resisting moment; M M = M z c + M z q + PT LT sinγ + LPf csin When steering, the steering moment on the wheels acted by ground is; MB = 0.5B(Pq 2 − Pq 1 ) + LPB cos Assuming Pq2 = Pq1 , the above equation can be written as; MB = LPB cos According to the conditions of stable steering, the steering moment should equal to the steering resisting moment, namely; Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering

Chapter 5 Steering System Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering MB=MZ LPecosa=M-e+M-+P;Lrsiny+LPresina The steering force Pe can be obtained from the above equation: Pn-Msc+Man+PiLrsiny+LPnsina Lcosa The engine load will increases when vehicles is steering. Assuming that the traction force is B=Prcosy when vehicles are straight running,it can be concluded that the thrust of the inside driving wheel need to increase P,when steering by comparison the balance equations of steering and straight running,namely AP=P-P=Pesina-(1-cosa)Pre 城电子工程学酸 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System The steering force PB can be obtained from the above equation: Lcosα M M P L sinγ LP sinα P z c z q T T f c B + + + = The engine load will increases when vehicles is steering. Assuming that the traction force is when vehicles are straight running, it can be concluded that the thrust of the inside driving wheel need to increase when steering by comparison the balance equations of steering and straight running, namely P P cosγ T T = q q q B cosα Pf c ΔP = P − P = P sinα −(1− ) ΔPq MB = M LPB cosα = Mz c + Mz q + PT LT sinγ + LPf csinα Section 1 Mode and Principle of Steering

Chapter 5 Steering System Section 2 Wheeled Vehicle's Steering System 1.The Basic Components of Deflecting Wheels Steering System Deflecting wheels steering system consists of control mechanism, steering gear,steering linkage,differential,etc..Its purpose is to change the people's manipulate into the appropriate steering wheel deflection and to ensure that the internal and external steering wheels'deflection angles a,B satisfy the Ackerman formula. Steering linkages usually have two forms:Steering Trapezium type and two-tension bar type. 机械电子工程学擦 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 5 Steering System 1. The Basic Components of Deflecting Wheels Steering System Deflecting wheels steering system consists of control mechanism, steering gear, steering linkage, differential, etc.. Its purpose is to change the people’s manipulate into the appropriate steering wheel deflection and to ensure that the internal and external steering wheels’ deflection angles α, β satisfy the Ackerman formula. Steering linkages usually have two forms: Steering Trapezium type and two-tension bar type. Section 2 Wheeled Vehicle’s Steering System
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 4 Running system.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 3 Coupling and Drive Axle.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 2 Transmission.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 1 Clutch.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Introduction.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 10 Engine working conditions and features.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 8 & 9 Starting system & Gasoline ignition system.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 7 Engine cooling system.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 6 Lubricating system.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 5 Gasoline fuel supply system.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 4 Diesel fuel supply system.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 3 Ventilation system.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 2 Crank-connecting rod mechanism and parts.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,上册)Introduction and course overview.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版,下册)第四章 柴油机燃油供给系统.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版,下册)第六章 制动系统.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版,下册)第八章 拖拉机汽车动力学.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版,下册)第五章 转向系统.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(中文版,下册)第九章 车辆的使用性能.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 6 Brake system.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 7 Power takeoff systems of tractors.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 8 Dynamics of vehicles.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《汽车拖拉机学》课程PPT教学课件(英文版,下册)Chapter 9 Operational performance of vehicles.ppt
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学大纲 Engineering Drawing(负责人:林大匀).pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)前言(编写:刘晶).pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)目录.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)第一章 点线面.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)第三章 组合体.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)第二章 立体.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)第七章 零件图.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)第五章 机件表达方法.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)第六章 标准件与常用件.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)第四章 轴测投影图.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)参考文献.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(学习指导书)第八章 装配图.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《工程制图》课程教学大纲 Engineering Drawing(主讲教师:冯开平).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(讲义)工程制图学习指南.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(教学设计)第二章 正投影法基础.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《工程制图》课程教学资源(教学设计)第三章 组合体.pdf
