上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05. Analysis

上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 5.Analysis 强 SHANG 1日日G ERSITY
5. Analysis

上游充通大¥ Outline SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Analysis:Bridging What to How 国 Models for Analysis Activities during object modeling Object Identifications Identify Associations ·Identify Aggregates ·Identify Attributes Reviewing the Analysis Model Managing Analysis Case Study Software Engineering
Software Engineering Outline Analysis: Bridging What to How Models for Analysis Activities during object modeling • Object Identifications • Identify Associations • Identify Aggregates • Identify Attributes • Reviewing the Analysis Model Managing Analysis Case Study
上降充通大学 1.Analysis:Bridging What to How SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Do the right things Do the things right Analysis What How Software Engineering
Software Engineering 1. Analysis: Bridging What to How Do the right things Do the things right What How Analysis

上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 2.Models for Analysis Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2. Models for Analysis

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 2.1 Reality and Model Reality R: Real Things,People,Processes happening during some time,Relationship between things Model M:Abstractions from (really existing or only thought of things,people processes and relationships between these abstractions. Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.1 Reality and Model Reality R: Real Things, People, Processes happening during some time, Relationship between things Model M: Abstractions from (really existing or only thought of ) things, people , processes and relationships between these abstractions

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 2.2 Why models? ④Ve use models To abstract away from details in the reality,so we can draw complicated conclusions in the reality with simple steps in the model To get insights into the past or presence To make predictions about the future Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.2 Why models? We use models • To abstract away from details in the reality, so we can draw complicated conclusions in the reality with simple steps in the model • To get insights into the past or presence • To make predictions about the future

上大学2.3 What is a“good'model? SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Relationships,which are valid in reality R,are also valid in model M. I:Mapping of real things in reality R to abstractions in the model M abbildet (Interpretation) f:relationship between abstractions in M f:relationship between real things in R In a good model the following diagram is commutative: [lt preserves relationships among the objects it represents.] fu M M I R R fR Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.3 What is a “good” model? Relationships, which are valid in reality R, are also valid in model M. • I : Mapping of real things in reality R to abstractions in the model M abbildet (Interpretation) • fM: relationship between abstractions in M • fR: relationship between real things in R In a good model the following diagram is commutative: [It preserves relationships among the objects it represents.] fM fR M M R R I I
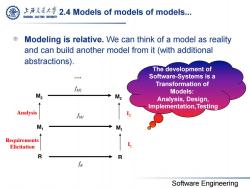
上充大¥2.4 Models of models of models. SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Modeling is relative.We can think of a model as reality and can build another model from it(with additional abstractions). The development of Software-Systems is a Transformation of fv2 Models: M2 M2 Analysis,Design, Implementation,Testing Analysis fv M M, Requirements Elicitation R R Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.4 Models of models of models... Modeling is relative. We can think of a model as reality and can build another model from it (with additional abstractions). fM1 fR M1 M1 R R Requirements Elicitation I1 M2 M2 Analysis I2 fM2 …. The development of Software-Systems is a Transformation of Models: Analysis, Design, Implementation,Testing
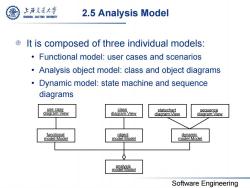
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 2.5 Analysis Model It is composed of three individual models: Functional model:user cases and scenarios Analysis object model:class and object diagrams Dynamic model:state machine and sequence diagrams use case class statechart sequence diagram:View diagram:View diagram:View diagram:View functional object dynamic model:Model model:Model model:Model analysis model:Model Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.5 Analysis Model It is composed of three individual models: • Functional model: user cases and scenarios • Analysis object model: class and object diagrams • Dynamic model: state machine and sequence diagrams analysis model:Model dynamic model:Model object model:Model functional model:Model use case diagram:View class diagram:View statechart diagram:View sequence diagram:View

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Products of requirements elicitation and analysis. Requirements elicitation Requirements Specification nonfunctional requirements functional model Analysis Analysis Model dynamic model analysis object model System design Object design Software Engineering
Software Engineering Products of requirements elicitation and analysis. Analysis functional model nonfunctional requirements analysis object model Requirements elicitation dynamic model Requirements Analysis Model Specification System design Object design
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04. Requirements Elicitation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03. Project Organization and Management.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02. Modeling with UML.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)11.Testing.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)10.Mapping Models to Code.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)01. Introduction to Software Engineering.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)00. Course Introduction.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)chapter03 数值计算.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)chapter02 程序基本构件.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)chapter01 课程简介、计算机与程序.ppt
- 《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(课程参考书PDF电子版)How to Think Like a Computer Scientist Learning with Python.pdf
- 《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(课程参考书PDF电子版)Python Programming:An Introduction to Computer Science(2002版).pdf
- 《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(课程参考书PDF电子版)PYTHON programming:AN INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE(JOHN ZELLE).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(上机课)第二次上机_第二次上机题目_11.1.doc
- 《Embedded System LAB》教学资源:KEIL Tools by ARM Getting Startedu Creating Applications withμVision®(uv4).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)chapter9 模拟与设计.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)chapter11 数据集合体.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Chapter10 类的定义.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)chapter08 控制结构(循环语句).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《程序设计思想与方法》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)chapter07 控制结构(条件语句).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06. System Design-Decomposing the System.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07.System Design-Addressing Design Goals.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08. Object Design-Reusing Pattern Solutions.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)09. Object Design-Specifying Interfaces.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源_About Practical Course.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源_Review Guideline SOFTWARE ENGINEERING.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)0.Plan_4. 计划阶段指南.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)0.Plan_可行性研究报告.doc
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)0.Plan_项目开发计划.doc
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)1.Define_小组作业2.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)1.Define_词汇表.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)1.Define_软件需求规约.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)1.Define_需求定义阶段指南.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)2.Analysis_分析阶段指南.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)2.Analysis_软件需求规约.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)3.Design_设计阶段指南.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)3.Design_软件架构文档.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)3.Design_软件设计模型.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)4. Build_构造阶段指南.docx
- 上海交通大学:《面向对象软件工程 Software Engineering》课程教学资源(作业)4. Build_模块开发卷宗.docx
