上海交通大学:《电动力学》课程PPT教学课件_静电学 Electrostatics

Lecture:Introduction to Electrodynamics 1.1 Electrostatics Min Chen minchen (@situ.edu.cn Laboratory for Laser Plasma Physics (LLP) Department of Physics Shanghai Jiao Tong University 13-02-25 Only discuss static electric fields.No time evolution of the source charges! 1 Calculate field from existed charge distribution. Learn fundamental knowledge of a vector field
Min Chen minchen@sjtu.edu.cn Laboratory for Laser Plasma Physics (LLP) Department of Physics Shanghai JiaoTong University 13-02-25 1.1 Electrostatics Lecture: Introduction to Electrodynamics Only discuss static electric fields. No time evolution of the source charges! Calculate field from existed charge distribution. Learn fundamental knowledge of a vector field. 1
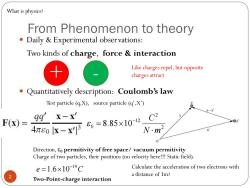
What is physics? From Phenomenon to theory Daily Experimental observations: Two kinds of charge,force interaction Like charges repel,but opposite charges attract Quantitatively description:Coulomb's law Test particle(q,X),source particle (q',X') 99'x-x' C2 F(x)= 4π0k-x3 80=8.85×1012 N.m2 Direction,Eo permitivity of free space/vacuum permitivity Charge of two particles,their positions(no velocity here!!!Static field). e=1.6×10-19C Calculate the acceleration of two electrons with 2 a distance of 1m? Two-Point-charge interaction
From Phenomenon to theory Daily & Experimental observations: Two kinds of charge, force & interaction Quantitatively description: Coulomb’s law + - Like charges repel, but opposite charges attract Direction, e0 permitivity of free space/ vacuum permitivity Charge of two particles, their positions (no velocity here!!! Static field). Two-Point-charge interaction 2 What is physics? Test particle (q,X), source particle (q’,X’) 2 2 12 0 8.85 10 N m C e e C 19 1.6 10 Calculate the acceleration of two electrons with a distance of 1m?
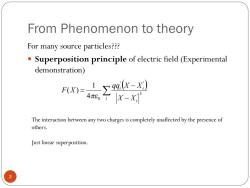
From Phenomenon to theory For many source particles??? Superposition principle of electric field (Experimental demonstration) The interaction between any two charges is completely unaffected by the presence of others. Just linear superposition. 3
From Phenomenon to theory For many source particles??? Superposition principle of electric field (Experimental demonstration) 3 i i i i X X qq X X F X 3 ' ' ' 4 0 1 ( ) e The interaction between any two charges is completely unaffected by the presence of others. Just linear superposition
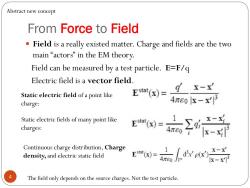
Abstract new concept From Force to Field .Field is a really existed matter.Charge and fields are the two main“actors'”in the EM theory. Field can be measured by a test particle.E=F/q Electric field is a vector field. Estaf(x)= g x-x' Static electric field of a point like charge: 4πe0k-x3 Static electric fields of many point like charges: 四高又子 Continuous charge distribution,Charge density,and electric static field E=人w千 4 The field only depends on the source charges.Not the test particle
From Force to Field Field is a really existed matter. Charge and fields are the two main “ actors ” in the EM theory. Field can be measured by a test particle. E=F/q Electric field is a vector field. Continuous charge distribution, Charge density,and electric static field Static electric field of a point like charge: Static electric fields of many point like charges: 4 Abstract new concept The field only depends on the source charges. Not the test particle
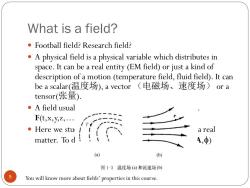
What is a field? Football field?Research field? A physical field is a physical variable which distributes in space.It can be a real entity (EM field)or just a kind of description of a motion(temperature field,fluid field).It can be a scalar(温度场),a vector(电磁场、速度场)( or a tensor(张量). .A field usual F(t,x,y,Z,… 1T4 Here we stu a real matter.Td!!t 4,φ) (a) (b) 图1-3温度场(a)和流速场(b) 5 You will know more about fields'properties in this course
What is a field? 5 Football field? Research field? A physical field is a physical variable which distributes in space. It can be a real entity (EM field) or just a kind of description of a motion (temperature field, fluid field). It can be a scalar(温度场), a vector (电磁场、速度场) or a tensor(张量). A field usually is a function of both space and time. F(t,x,y,z,……) Here we study the electromagnetic field, which is a real matter. To describe it we need vectors. (E,B) / (A,f) You will know more about fields’ properties in this course
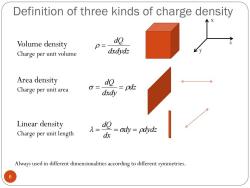
Definition of three kinds of charge density Volume density do p= Charge per unit volume dxdydz Area density Charge per unit area d№=pd dxdy Linear density 1= Charge per unit length de =ody=pdyd dx Always used in different dimensionalities according to different symmetries. 6
Volume density Charge per unit volume Area density Charge per unit area Linear density Charge per unit length dxdydz dQ dz dxdy dQ dy dydz dx dQ x y z Always used in different dimensionalities according to different symmetries. Definition of three kinds of charge density 6
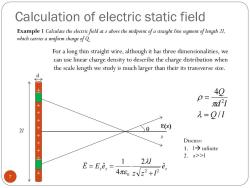
Calculation of electric static field Example 1 Calculate the electricfield at above the midpoint ofa straight line segment of length 21. which carries a uniform charge ofQ For a long thin straight wire,although it has three dimensionalities,we can use linear charge density to describe the charge distribution when the scale length we study is much larger than their its transverse size. 40 p= + πd21 九= Q/1 十 E(z) 21 0 Z ++ Discuss: l.l→infinite 2.z>>1 E=E.e.= 1 21 4πE0z√z2+12
For a long thin straight wire, although it has three dimensionalities, we can use linear charge density to describe the charge distribution when the scale length we study is much larger than their its transverse size. d Q l d l Q / 4 2 7 Calculation of electric static field + + + + + + + + + + + + E(z) 2l z q Example 1 Calculate the electric field at z above the midpoint of a straight line segment of length 2l, which carries a uniform charge of Q. z z z e z z l l E E e ˆ 2 4 1 ˆ 2 2 0 e Discuss: 1. l infinite 2. z>>l
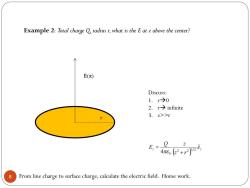
Example 2:Total charge Q radius r,what is the E atz above the center? 个 E(z) Discuss: 1.r→0 2.r→infinite 3.z>>r Q 8 From line charge to surface charge,calculate the electric field.Home work
8 Example 2: Total charge Q,radius r,what is the E at z above the center? r E(z) Discuss: 1. r0 2. r infinite 3. z>>r From line charge to surface charge,calculate the electric field. Home work. z z e z r Q z E ˆ 4 3/ 2 2 2 0 e
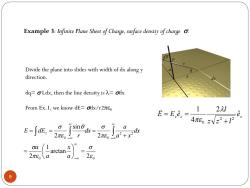
Example 3:Infinite Plane Sheet of Charge,surface density of charge. d Divide the plane into slides with width of dx along y direction. dq=oLdx,then the line density is=odx From Ex.1,we know dE=odx/r2To 12l 它=Ee,=460N2+ e. a -c0 o 2 arctan- 三 a 9
9 Example 3: Infinite Plane Sheet of Charge,surface density of charge . Divide the plane into slides with width of dx along y direction. dq= Ldx, then the line density is = dx From Ex.1, we know dE= dx/r2e0 z z z e z z l l E E e ˆ 2 4 1 ˆ 2 2 0 e 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 arctan 1 2 2 sin 2 e e e q e a x a a dx a x a dx r E dEz

Fundamental mathematical description of a classical field 1.Gradient of a scalar field P+do o⑨+eyy o=ex Ox 09+ez02 00 1 V0二 dn Along the direction of phai increase 2.Divergence of a vector field The flux of a vector field A go through an area dS w-Jas 10
Fundamental mathematical description of a classical field 10 1. Gradient of a scalar field Along the direction of phai increase 2. Divergence of a vector field The flux of a vector fieldA go through an area dS
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《电动力学》课程PPT教学课件_Introduction to Electrodynamics.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《量子力学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Periodic potential & Harmonic oscillator.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《量子力学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Chap 16 Sound and hearing.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《计算物理 Computational Physics》课程教学资源(英文)讲义课件_An Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《计算物理 Computational Physics》课程教学资源(英文)讲义课件_Chapter 1 Errors & Uncertainties in Computations.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)沒有翅膀的飛翔——未來的真空磁懸浮列車.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(讲义)从历史看物理学的萌芽.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(讲义)part.0.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)中國飛天夢“翅膀”的成長——火箭技術的發展.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)人類的飛行夢想——從鳥到飛機的實現.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)飛向太空.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)CPA 技術——飛秒鐳射新時代.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)夢之翼.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)物理异想课程论文.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)單車上的飛翔.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)海中之鳥——飛魚的奧秘.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)讓質子飛.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)不可能完成的任務.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)飛的力量.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)飛的力量.doc
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源(经典阅读)STEPHEN HAWKING AND LEONARD MLODINOW《The Grand Design》.pdf
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源:冶金工业出版社《电子衍射物理教程》PDF电子书.pdf
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源:材料科学丛书《透射电子显微学》PDF电子书.pdf
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源(电子书)STEPHEN HAWKING and LEONARD MLODINOW《大设计 The Grand Design》.pdf
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源(电子书)广义进化研究丛书《微漪之塘——宇宙进化的新图景》〔美〕欧文·拉兹洛.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)从经典物理到量子力学.doc
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_关于量子力学的有关观点_人脑中的量子力学.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_1、电子的镍单晶衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_2、电子金属箔衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_C70分子干涉仪.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_中子的氧化镁晶格衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_原子波相位移动.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_电子双缝干涉(德文).pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_电子双缝干涉(英文).pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_电子的光柱波衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_评原子波相位移动.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_评电子的光柱波衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_超流氦3的双缝干涉.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_过氟烷基化合物纳米球的干涉.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_波粒二象性的揭示轨迹_双缝实验简史.doc
