上海交通大学:《计算物理 Computational Physics》课程教学资源(英文)讲义课件_An Introduction

Computational Physics An Introduction Weihua Gu Department of Physics Shanghai Jiao Tong University 14/09/2015 1口“4元,4元↑重QC Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20151120
Computational Physics An Introduction Weihua Gu Department of Physics Shanghai Jiao Tong University 14/09/2015 Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 1 / 20

Info Instructor: Weihua Gu E-mail: whgu@sjtu.edu.cn QQ: 27241705730 Office: Room 1106,Physics Department Building Course Webite: http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/Comp Ftp site: ftp://whgu:cp2011@public.sjtu.edu.c (updated regularly. ¥口“1元4元↑至QC Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/0920152120
Info Instructor: Weihua Gu E-mail: whgu@sjtu.edu.cn QQ: 2724 1705 73O Office: Room 1106, Physics Department Building Course Webite: http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/ComputationalPhysic.html Ftp site: ftp://whgu:cp2011@public.sjtu.edu.cn (updated regularly.) Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 2 / 20

What is CP? What Is CP? o A interdisciplinary subject of natural science overlapping physics,applied mathematics,and computer science; a fast developing field; o focus on solving physical problems; o a powerful tool to explore new fields. Physics application C cs Math hard/software techniques 1口“4元,4元↑重QC Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/0920153120
What is CP? What Is CP? A interdisciplinary subject of natural science overlapping physics, applied mathematics, and computer science; a fast developing field; focus on solving physical problems; a powerful tool to explore new fields. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 3 / 20

What is CP? What Is CP? o A interdisciplinary subject of natural science overlapping physics,applied mathematics,and computer science; a fast developing field; o focus on solving physical problems; o a powerful tool to explore new fields. Physics application P cs Math uoneinw!S Truth hard/software techniques Fxneriment Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/0920153120
What is CP? What Is CP? A interdisciplinary subject of natural science overlapping physics, applied mathematics, and computer science; a fast developing field; focus on solving physical problems; a powerful tool to explore new fields. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 3 / 20

Objectives of CP Course Objectives of CP Course After you learn the course,you should be able to o understand basic numerical techniques,apply them to solve physical problems and explore new interesting topics, enhance programming skill, enhance problem-solving skill. enhance English skill. o enhance team-working skill. 1口回1元4元1至0QC Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20154120
Objectives of CP Course Objectives of CP Course After you learn the course, you should be able to understand basic numerical techniques, apply them to solve physical problems and explore new interesting topics, enhance programming skill, enhance problem-solving skill. enhance English skill. enhance team-working skill. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 4 / 20

Objectives of CP Course Focus on Physics-The Problem-Solving Paradigm A practical problem Laws of physics Model Numerical methods Nonlinear->linear Continuous->discrete Multidimensional->1D Simplified Model Variable coe.->constant coe. Results Programming,visualization Convergence,stability, Evaluation error analysis,time consuming 重00C Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 5120
Objectives of CP Course Focus on Physics-The Problem-Solving Paradigm Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 5 / 20

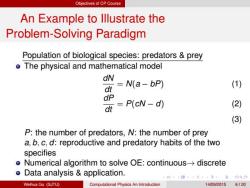
Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN dt N(a-bP) (1) dP dt =P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuousdiscrete Data analysis application. ¥口,4元4元卡重)90 Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20

Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN N(a-bP) (1) dt dP dt P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuous->discrete o Data analysis application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/092015 6120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20
Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN N(a-bP) (1) dt dP dt =P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies o Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuous->discrete o Data analysis application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20156120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20
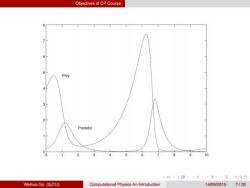
Objectives of CP Course Pre倒 3 2 Predator 0 10 4口404元,4无:至分Q0 Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20157120
Objectives of CP Course Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 7 / 20
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《计算物理 Computational Physics》课程教学资源(英文)讲义课件_Chapter 1 Errors & Uncertainties in Computations.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)沒有翅膀的飛翔——未來的真空磁懸浮列車.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(讲义)从历史看物理学的萌芽.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(讲义)part.0.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)中國飛天夢“翅膀”的成長——火箭技術的發展.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)人類的飛行夢想——從鳥到飛機的實現.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)飛向太空.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)CPA 技術——飛秒鐳射新時代.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)夢之翼.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)物理异想课程论文.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)單車上的飛翔.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)海中之鳥——飛魚的奧秘.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)讓質子飛.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)不可能完成的任務.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)飛的力量.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)飛的力量.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)飞翔的奥秘.docx
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)鳥的飛翔之謎.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)人類飛行夢想.doc
- 上海交通大学:《物理异想》课程教学资源(论文资料)淺談中國航空史.doc
- 上海交通大学:《量子力学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Chap 16 Sound and hearing.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《量子力学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Periodic potential & Harmonic oscillator.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电动力学》课程PPT教学课件_Introduction to Electrodynamics.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《电动力学》课程PPT教学课件_静电学 Electrostatics.pptx
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源(经典阅读)STEPHEN HAWKING AND LEONARD MLODINOW《The Grand Design》.pdf
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源:冶金工业出版社《电子衍射物理教程》PDF电子书.pdf
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源:材料科学丛书《透射电子显微学》PDF电子书.pdf
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源(电子书)STEPHEN HAWKING and LEONARD MLODINOW《大设计 The Grand Design》.pdf
- 《探索物质微观世界》课程教学资源(电子书)广义进化研究丛书《微漪之塘——宇宙进化的新图景》〔美〕欧文·拉兹洛.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)从经典物理到量子力学.doc
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_关于量子力学的有关观点_人脑中的量子力学.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_1、电子的镍单晶衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_2、电子金属箔衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_C70分子干涉仪.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_中子的氧化镁晶格衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_原子波相位移动.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_电子双缝干涉(德文).pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_电子双缝干涉(英文).pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_电子的光柱波衍射.pdf
- 《量子力学》课程教学资源(文献资料)波粒二象性_实物粒子波粒二象性的实验证实_评原子波相位移动.pdf
