上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture8-Information-Bullwhip

JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY 96 Supply Chain Management Lecture 8 Value of Information Instructor(s) Prof.Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering SEIEE AU406
Supply Chain Management Instructor(s) SEIEE AU406 + - Value of Information Prof. Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering Lecture 8

Introduction Value of using any type of information technology Potential availability of more and more information throughout the supply chain Implications this availability on effective design and management of the integrated supply chain SEIEE AU406
+ - SEIEE AU406 Introduction Value of using any type of information technology Potential availability of more and more information throughout the supply chain Implications this availability on effective design and management of the integrated supply chain

Information Types Inventory levels Orders Production ■Delivery status SEIEE AU406
+ - SEIEE AU406 Information Types Inventory levels Orders Production Delivery status

More Information Helps reduce variability in the supply chain. a Helps suppliers make better forecasts, accounting for promotions and market changes. Enables the coordination of manufacturing and distribution systems and strategies. Enables retailers to better serve their customers by offering tools for locating desired items. Enables retailers to react and adapt to supply problems more rapidly. Enables lead time reductions. SEIEE AU406
+ - SEIEE AU406 More Information Helps reduce variability in the supply chain. Helps suppliers make better forecasts, accounting for promotions and market changes. Enables the coordination of manufacturing and distribution systems and strategies. Enables retailers to better serve their customers by offering tools for locating desired items. Enables retailers to react and adapt to supply problems more rapidly. Enables lead time reductions

Bullwhip Effect While customer demand for specific products does not vary much Inventory and back-order levels fluctuate considerably across their supply chain P&G's disposable diapers case Sales quite flat Distributor orders fluctuate more than retail sales Supplier orders fluctuate even more SEIEE AU406
+ - SEIEE AU406 Bullwhip Effect While customer demand for specific products does not vary much Inventory and back-order levels fluctuate considerably across their supply chain P&G’s disposable diapers case Sales quite flat Distributor orders fluctuate more than retail sales Supplier orders fluctuate even more
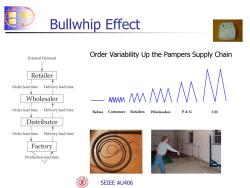
Bullwhip Effect External Demand Order Variability Up the Pampers Supply Chain Retailer Order lead time Delivery lead time Wholesaler 一讯 Order lead time Delivery lead time Babies Customers Retailers Wholesalers P&G 3M Distributor Order lead time Delivery lead time Factory Production lead time SEIEE AU406
SEIEE AU406 + - Bullwhip Effect Order Variability Up the Pampers Supply Chain
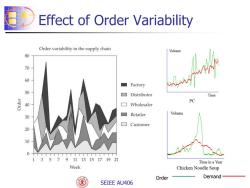
Effect of Order Variability Order variability in the supply chain Volume 80 70 60 Factory 50 □ Distributor Time PC 40 口 Wholesaler Retailer Volume 30 Customer 20 10 13579111315171921 Time in a Year Week Chicken Noodle Soup Order Demand SEIEE AU406
SEIEE AU406 + - Effect of Order Variability Order Demand
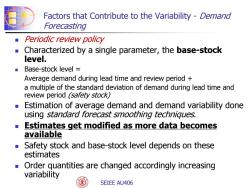
Factors that Contribute to the variability-Demano Forecasting Periodic review policy Characterized by a single parameter,the base-stock level. Base-stock level Average demand during lead time and review period a multiple of the standard deviation of demand during lead time and review period (safety stock) Estimation of average demand and demand variability done using standard forecast smoothing techniques. Estimates get modified as more data becomes available Safety stock and base-stock level depends on these estimates Order quantities are changed accordingly increasing variability SEIEE AU406
+ - SEIEE AU406 Factors that Contribute to the Variability - Demand Forecasting Periodic review policy Characterized by a single parameter, the base-stock level. Base-stock level = Average demand during lead time and review period + a multiple of the standard deviation of demand during lead time and review period (safety stock) Estimation of average demand and demand variability done using standard forecast smoothing techniques. Estimates get modified as more data becomes available Safety stock and base-stock level depends on these estimates Order quantities are changed accordingly increasing variability

Factors that Contribute to the variability- Lead Time Increase in variability magnified with increasing lead time. Safety stock and base-stock levels have a lead time component in their estimations. With longer lead times: a small change in the estimate of demand variability implies a significant change in safety stock and base-stock level,which implies significant changes in order quantities leads to an increase in variability SEIEE AU406
+ - SEIEE AU406 Increase in variability magnified with increasing lead time. Safety stock and base-stock levels have a lead time component in their estimations. With longer lead times: a small change in the estimate of demand variability implies a significant change in safety stock and base-stock level, which implies significant changes in order quantities leads to an increase in variability Factors that Contribute to the Variability – Lead Time

Factors that Contribute to the variability- Batch Ordering Retailer uses batch ordering,as with a(Q,R) or a min-max policy Wholesaler observes a large order,followed by several periods of no orders,followed by another large order,and so on. ■ Wholesaler sees a distorted and highly variable pattern of orders. Such pattern is also a result of: Transportation discounts with large orders Periodic sales quotas/incentives SEIEE AU406
+ - SEIEE AU406 Factors that Contribute to the Variability – Batch Ordering Retailer uses batch ordering, as with a (Q,R) or a min-max policy Wholesaler observes a large order, followed by several periods of no orders, followed by another large order, and so on. Wholesaler sees a distorted and highly variable pattern of orders. Such pattern is also a result of: Transportation discounts with large orders Periodic sales quotas/incentives
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture7-2-Aggregated-Planning.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture7-1-Forecasting.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture6-Global_SCM.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture5-2networkdesign.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture5-1distribution.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture4-metric.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture3-Strategic_fit.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture2-Demand forecasting.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture11-Optimal-Product-Availability.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture11-examples-Product.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture10-Safe-Inventory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture10-examples-safty-inventory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture1-Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Beer_Game_instruction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_amazon financial statement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_homework_sol2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_homework_sol1.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_homework_hw2_scm2014.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_homework_hw1_scm2014.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《职业生涯发展与规划》课程教学资源(学习文件)大学生职业生涯规划书(二).docx
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_Lecture9-Cycle-Inventory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_lecture9-examples-cycle-inventory.pdf
- 上海交通大学:SCM供应链管理 Supply Chain Managment》课程教学资料_lecture notes_LP and Excel solver.pdf
- 公共行政与公共管理经典译丛:[美]乔治·弗雷德里克森《公共行政的精神 The Spirit of Public Administration》.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)对政治与行政二分原则的审查(中国人民大学:张康之).pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读书籍)[美]戴维·奥斯本、特德·盖布勒《改革政府:企业家精神如何改革着公共部门》.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)政治与行政两分法——思想渊源及其评价.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)政治与行政二分法批判的批判.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)政治与行政二分理论研究综述.pdf
- 政府治理与改革系列:(美)珍妮特·V·登哈特、罗伯特·B·登哈特《新公共服务:服务,而不是掌舵》THE NEW PUBLIC SERVICE SERVING, NOT STEERING.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)西方政治与行政关系的历史演变及趋势.pdf
- 《中国行政管理》:“协同政府”——新公共管理改革的新阶段.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)从新公共管理到整体性治理.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)从竞争治理迈向整体治理.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)全观型治理——理论与制度化策略.pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读书籍)[美]彼得·圣吉《第五项修炼——学习型组织的艺术与实务》PDF电子书(The Fifth Discipline).pdf
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(参考资料)上海市城市管理行政执法条例.docx
- 《公共行政概论》课程教学资源(阅读书籍)【英】罗素《权力论》中文版.pdf
- 现代西方思想文库:【美】戴维·伊斯顿《政治生活的系统分析》A SYSTEM ANALYSIS OF POLITICAL LIEE.pdf
- 公共行政与公共管理经典译丛(经典教材系列)托马斯·R·戴伊《理解公共政策》(第十二版).pdf
