西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)06 移动互联网IPv6

移动互联网-PV6 苏锐丹
移动互联网-IPv6 苏锐丹

一些形式的地址 2001:0db8:1234:5678:9abc:def0:1234:5678 2001:0db8:0000:130F:0000:0000:087C:140B 2001:0db8:0:130F:87C:140B 2001:db8:12:/64
一些形式的地址

IPv6地址 ■Network ID ▣64位,全球地址管理IANA ■Host ID configured manually or auto-configured Figure 2-1 IPv6 Unicast Network and Host ID Format Network ID Host ID XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:YYYY:YYYY:YYYY:YYYY 64 Bits 64 Bits
IPv6地址 ◼ Network ID 64位,全球地址管理IANA ◼ Host ID configured manually or auto-configured

■地址自动配置 Using a randomly generated number ▣Using DHCPV6 Using the Extended Unique ldentifier (EUl-64) format 009027 17 FC OF 00 90 27 OF FF FE
◼ 地址自动配置 Using a randomly generated number Using DHCPv6 Using the Extended Unique Identifier (EUI-64) format

·Unicast address Identifies a single node or interface.Traffic destined for a unicast address is forwarded to a single interface. ·Multicast address Identifies a group of nodes or interfaces.Traffic destined for a multicast address is forwarded to all the nodes in the group. ·Anycast address Identifies a group of nodes or interfaces.Traffic destined to an anycast address is forwarded to the nearest node in the group.An anycast address is essentially a unicast address assigned to multiple devices with a host ID =0000:0000:0000:0000.(Anycast addresses are not widely used today.) With IPv6,broadcast addresses are no longer used
◼ With IPv6, broadcast addresses are no longer used
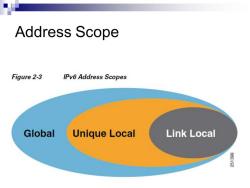
Address Scope Figure 2-3 IPv6 Address Scopes Global Unique Local Link Local
Address Scope
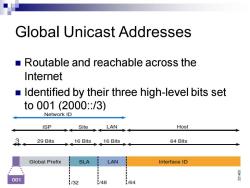
Global Unicast Addresses Routable and reachable across the Internet Identified by their three high-level bits set to001(2000:/3) Network ID ISP Site LAN Host 3 29 Bits 16Bits、16Bits 64 Bits Global Prefix SLA LAN Interface ID 001 1/32 /48 /64
Global Unicast Addresses ◼ Routable and reachable across the Internet ◼ Identified by their three high-level bits set to 001 (2000::/3)

Global routing prefix ▣service provider ■ Site level aggregator Customer of service provider ■LAN ID Individual networks in customer site
◼ Global routing prefix service provider ◼ Site level aggregator Customer of service provider ◼ LAN ID Individual networks in customer site

Unique Local Unicast Addresses Analogous to private IPv4 addresses Used for local communications,inter-site VPNs,and so forth Not routable on the Internet(routing would require IPv6 NAT) Figure 2-5 Unique Local Unicast Address Format -128 Bits- 1 Global ID 40 Bits Interface ID 1111110 Subnet ID ED00:/7 16 Bits 7 Bits 1 Bit:L=1 Locally assigned;L=0 Future Use
Unique Local Unicast Addresses ◼ Analogous to private IPv4 addresses ◼ Used for local communications, inter-site VPNs, and so forth ◼ Not routable on the Internet (routing would require IPv6 NAT)

Subnet IDs using a hierarchical addressing plan to allow for route summarization
◼ Subnet IDs using a hierarchical addressing plan to allow for route summarization
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)05 网络层Mobility.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)04 数据链路层移动性技术.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 相关支撑技术.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 应用层移动性.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 传输层移动性.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 Android应用安全 Android application security.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 移动互联网技术(Android安全).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)02 移动互联网概述.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)01 课程介绍(主讲:苏锐丹).ppt
- 《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(培训教材)Cisco Press - Building the Mobile Internet(Mark Grayson, Kevin Shatzkamer, Klaas Wierenga).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Processes.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Operating-System Structure.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Introduction(主讲:苏锐丹).pptx
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)ASCII 码——常用ASCII码.pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)ASCII码(256完整版)The ASCII Character Set.pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)C++ RC by Mississippi State U.(2009).pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)C++ Reference Card(C++ RC by Greg Book,2002).pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十六讲 标准模板库(Standard Template Library,STL).pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十五讲 文件流与输出输入重载.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十四讲 多态.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验教学大纲.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)理论教学大纲.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第1章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第2章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第3章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第4章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第5章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第8章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第10章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第1章(答案).doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第2章(答案).doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第6章 定时器、计数器(作业).doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第7章 串行口(作业).doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第3章(答案).doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第5章(答案).doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第4章(答案).doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第8章(答案).doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第9章 键盘、显示器.doc
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程授课教案(打印版)第一章 概述(负责人:伍忠东).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程授课教案(打印版)第二章 单片机硬件结构(1/2).pdf
