西安电子科技大学:《操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Operating-System Structure

Operating-System Structures
Operating-System Structures

Outline Operating System Services User Operating System Interface ·System Calls ·Types of System Calls ·System Programs Operating System Design and Implementation Operating System Structure Operating System Debugging Operating System Generation ·System Boot
Outline • Operating System Services • User Operating System Interface • System Calls • Types of System Calls • System Programs • Operating System Design and Implementation • Operating System Structure • Operating System Debugging • Operating System Generation • System Boot
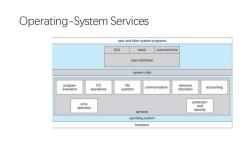
Operating-System Services user and other system programs GUI batch command line usor interfaces system calls program VO file resource communication execution operations systems allocation accounting error protection detection and secunty services operating system hardware
Operating-System Services

User Interfaces -Means by which users can issue commands to the system. a command-line interface e.g.sh,csh,ksh,tcsh,etc.) a GUl interface e.g.Windows,X-Windows,KDE,Gnome,etc. or a batch command systems.The latter are generally older systems using punch cards of job-control language,JCL,but may still be used today for specialty systems designed for a single purpose
• User Interfaces - Means by which users can issue commands to the system. • a command-line interface ( e.g. sh, csh, ksh, tcsh, etc. ), • a GUI interface ( e.g. Windows, X-Windows, KDE, Gnome, etc. ) • or a batch command systems. The latter are generally older systems using punch cards of job-control language, JCL, but may still be used today for specialty systems designed for a single purpose

Program Execution-The OS must be able to load a program into RAM,run the program,and terminate the program,either normally or abnormally.(process lifecycle) 1/O Operations -The OS is responsible for transferring data to and from 1/O devices,including keyboards,terminals,printers,and storage devices. File-System Manipulation -In addition to raw data storage,the OS is also responsible for maintaining directory and subdirectory structures,mapping file names to specific blocks of data storage, and providing tools for navigating and utilizing the file system
• Program Execution - The OS must be able to load a program into RAM, run the program, and terminate the program, either normally or abnormally.(process lifecycle) • I/O Operations - The OS is responsible for transferring data to and from I/O devices, including keyboards, terminals, printers, and storage devices. • File-System Manipulation - In addition to raw data storage, the OS is also responsible for maintaining directory and subdirectory structures, mapping file names to specific blocks of data storage, and providing tools for navigating and utilizing the file system

Communications -Inter-process communications,IPC,either between processes running on the same processor,or between processes running on separate processors or separate machines. May be implemented as either shared memory or message passing,or some systems may offer both. Error Detection -Both hardware and software errors must be detected and handled appropriately.Some systems may include complex error avoidance or recovery systems,including backups, RAID drives,and other redundant systems.Debugging and diagnostic tools aid users and administrators in tracing down the cause of problems
• Communications - Inter-process communications, IPC, either between processes running on the same processor, or between processes running on separate processors or separate machines. May be implemented as either shared memory or message passing, ( or some systems may offer both. ) • Error Detection - Both hardware and software errors must be detected and handled appropriately. Some systems may include complex error avoidance or recovery systems, including backups, RAID drives, and other redundant systems. Debugging and diagnostic tools aid users and administrators in tracing down the cause of problems

Resource Allocation -E.g.CPU cycles,main memory,storage space,and peripheral devices. Accounting -Keeping track of system activity and resource usage, either for billing purposes or for statistical record keeping that can be used to optimize future performance
• Resource Allocation - E.g. CPU cycles, main memory, storage space, and peripheral devices. • Accounting - Keeping track of system activity and resource usage, either for billing purposes or for statistical record keeping that can be used to optimize future performance

Protection and Security-Preventing harm to the system and to resources,either through wayward internal processes or malicious outsiders. Authentication,ownership,and restricted access are obvious parts of this system. Highly secure systems may log all process activity down to excruciating detail,and security regulation dictate the storage of those records on permanent non-erasable medium for extended times in secure off-site facilities
• Protection and Security - Preventing harm to the system and to resources, either through wayward internal processes or malicious outsiders. • Authentication, ownership, and restricted access are obvious parts of this system. • Highly secure systems may log all process activity down to excruciating detail, and security regulation dictate the storage of those records on permanent non-erasable medium for extended times in secure ( off-site ) facilities

User Operating-System Interface ·Command Interpreter Graphical User Interface,GUl 。Choice of interface
User Operating-System Interface • Command Interpreter • Graphical User Interface, GUI • Choice of interface

Command Interpreter Gets and processes the next user request,and launches the requested programs. In some systems the CI may be incorporated directly into the kernel. More commonly the Cl is a separate program that launches once the user logs in or otherwise accesses the system
- Command Interpreter • Gets and processes the next user request, and launches the requested programs. • In some systems the CI may be incorporated directly into the kernel. • More commonly the CI is a separate program that launches once the user logs in or otherwise accesses the system
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西安电子科技大学:《操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Introduction(主讲:苏锐丹).pptx
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)ASCII 码——常用ASCII码.pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)ASCII码(256完整版)The ASCII Character Set.pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)C++ RC by Mississippi State U.(2009).pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)C++ Reference Card(C++ RC by Greg Book,2002).pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十六讲 标准模板库(Standard Template Library,STL).pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十五讲 文件流与输出输入重载.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十四讲 多态.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十三讲 继承与派生.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十二讲 运算符重载与自动类型转换.pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)C++ vector使用方法.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十一讲 类与对象(III)面向对象提高.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第十讲 类与对象(II)面向对象进阶.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九讲 类与对象(I)面向对象基础.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第八讲 排序算法.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第七讲 输入输出与(C 语言)文件操作.pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)Pointers and Memory.pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)内存分配——栈和堆.pdf
- 《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)Fast and stable matrix multiplication.pdf
- 华东师范大学:《C++ 语言程序设计》课程教学资源(应用阅读)Gauss消去法求解线性方程组.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Processes.pptx
- 《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(培训教材)Cisco Press - Building the Mobile Internet(Mark Grayson, Kevin Shatzkamer, Klaas Wierenga).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)01 课程介绍(主讲:苏锐丹).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)02 移动互联网概述.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 移动互联网技术(Android安全).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 Android应用安全 Android application security.pptx
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 传输层移动性.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 应用层移动性.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)03 相关支撑技术.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)04 数据链路层移动性技术.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)05 网络层Mobility.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《移动互联网技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件)06 移动互联网IPv6.ppt
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)实验教学大纲.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(教案讲义,打印版)理论教学大纲.pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第1章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第2章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第3章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第4章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第5章(作业,打印版).pdf
- 兰州交通大学:《单片机原理与接口技术》课程教学资源(课后作业)第8章(作业,打印版).pdf
