《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)橡胶 Rubber(PPT讲稿)

Introduction to Polymer Science RUBBER 橡胶
RUBBER 橡胶 Introduction to Polymer Science

Part 1 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE RUBBER
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE RUBBER Part 1

PROPERTIES OF RUBBER/ELASTOMER An elastomer is a polymer with the property of elasticity.The term, which is derived from elastic polymer,is often used interchangeably with the term rubber,although the latter is preferred when referring to vulcanisates. o Elastomers are amorphous polymers existing above their glass transition temperature,so that considerable segmental motion is possible.At ambient temperatures rubbers are thus relatively soft and deformable. The elasticity is derived from the ability of the long chains to reconfigure themselves to distribute an applied stress.The covalent cross-linkages ensure that the elastomer will return to its original configuration when the stress is removed. Their primary uses are for seals,adhesives and molded flexible parts
PROPERTIES OF RUBBER/ELASTOMER An elastomer is a polymer with the property of elasticity. The term, which is derived from elastic polymer, is often used interchangeably with the term rubber, although the latter is preferred when referring to vulcanisates. Elastomers are amorphous polymers existing above their glass transition temperature, so that considerable segmental motion is possible. At ambient temperatures rubbers are thus relatively soft and deformable. The elasticity is derived from the ability of the long chains to reconfigure themselves to distribute an applied stress. The covalent cross-linkages ensure that the elastomer will return to its original configuration when the stress is removed. Their primary uses are for seals, adhesives and molded flexible parts

CHARACTERISTIC OF ELASTOMERIC PROPERTY o small elastic modulus ·Steel:20000MPa; PE:200MPa(crystallized);PS:2500MPa; 。Rubber:0.2-8MPa o large strain 。Steel:<1% ·Rubber:300~1000% o elastic modulus of the rubber increased with the temperature The motion and retractive force of the chain segments increased with the temperature,resulted in a high resistance of deformation. o The high elastic deformation of the rubber is time dependent,i.e. mechanical relaxation o The deformation process have obvious thermal effect
small elastic modulus Steel:20000MPa; PE:200MPa (crystallized); PS:2500MPa; Rubber: 0.2-8MPa large strain Steel: <1% Rubber: 300~1000% elastic modulus of the rubber increased with the temperature The motion and retractive force of the chain segments increased with the temperature, resulted in a high resistance of deformation. The high elastic deformation of the rubber is time dependent , i. e. mechanical relaxation The deformation process have obvious thermal effect. CHARACTERISTIC OF ELASTOMERIC PROPERTY
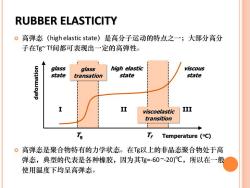
RUBBER ELASTICITY 。高弹态(high elastic state)是高分子运动的特点之一;大部分高分 子在Tg~Tf间都可表现出一定的高弹性。 glass glass high elastic viscous state transation state state II viscoelastic III transition Tg T Temperature (C) 。高弹态是聚合物特有的力学状态。在Tg以上的非晶态聚合物处于高 弹态,典型的代表是各种橡胶,因为其Tg≈-60~-20)℃,所以在一般 使用温度下均呈高弹态
RUBBER ELASTICITY 高弹态是聚合物特有的力学状态。在Tg以上的非晶态聚合物处于高 弹态,典型的代表是各种橡胶,因为其Tg≈-60 ~-20)℃,所以在一般 使用温度下均呈高弹态。 高弹态(high elastic state)是高分子运动的特点之一;大部分高分 子在Tg~ Tf间都可表现出一定的高弹性。 deformation Temperature (oC) I glass state high elastic state viscous state II III Tg Tf glass transation viscoelastic transition
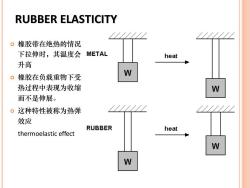
RUBBER ELASTICITY 。橡胶带在绝热的情况 下拉伸时,其温度会 METAL heat 升高 。橡胶在负载重物下受 W 热过程中表现为收缩 而不是伸展。 。这种特性被称为热弹 效应 RUBBER heat thermoelastic effect W W
RUBBER ELASTICITY 橡胶带在绝热的情况 下拉伸时,其温度会 升高 橡胶在负载重物下受 热过程中表现为收缩 而不是伸展。 这种特性被称为热弹 效应 thermoelastic effect
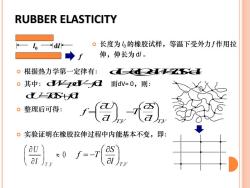
RUBBER ELASTICITY dl 。长度为的橡胶试样,等温下受外力f作用拉 伸,伸长为d。 。根据热力学第一定律有: 一又 。其中:d名乙 而dVO,则: aAa 。整理后可得: 。实验证明在橡胶拉伸过程中内能基本不变,即: al 0f=-7 al
RUBBER ELASTICITY 长度为 l0 的橡胶试样,等温下受外力f 作用拉 伸,伸长为dl 。 d d d dd UQWTSW =− = − d d d WpV fl = − l0 dl f 根据热力学第一定律有: 其中: 而dV≈ 0,则: 整理后可得: 实验证明在橡胶拉伸过程中内能基本不变,即: d d d U TS fl = + TV TV , , U S f T l l = − , 0 T V U l T V, S f T l = −

RUBBER ELASTICITY 。橡胶弹性体的聚合物分子链都是通过弱的。当拉伸时,分子链排列由于取 分子间色散力聚集在一起的,因此在外力 向作用变得规整,从而导致结 作用下分子链能快速相对滑动,产生明显 晶,进一步增加了材料的强度。 形变。 硫化反应引入了交联结构,使 Breakage 得链段一旦达到所能伸展的极 限,要继续产生形变必须使拉 伸力达到引起化学键的断裂或 结晶区破坏的程度。 Crystallization 。交联,将分子链通过化学键网 络固定,这使得橡胶能“记忆” Orientation 最初的形状,即在微观上保持 分子链的原位置。 Force applied
RUBBER ELASTICITY 当拉伸时,分子链排列由于取 向作用变得规整,从而导致结 晶,进一步增加了材料的强度。 硫化反应引入了交联结构,使 得链段一旦达到所能伸展的极 限,要继续产生形变必须使拉 伸力达到引起化学键的断裂或 结晶区破坏的程度。 交联,将分子链通过化学键网 络固定,这使得橡胶能“记忆” 最初的形状,即在微观上保持 分子链的原位置。 橡胶弹性体的聚合物分子链都是通过弱的 分子间色散力聚集在一起的,因此在外力 作用下分子链能快速相对滑动,产生明显 形变
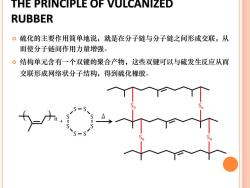
THE PRINCIPLE OF VULCANIZED RUBBER 。硫化的主要作用简单地说,就是在分子链与分子链之间形成交联,从 而使分子链间作用力量增强。 。结构单元含有一个双键的聚合产物,这些双键可以与硫发生反应从而 交联形成网络状分子结构,得到硫化橡胶
THE PRINCIPLE OF VULCANIZED RUBBER 硫化的主要作用简单地说,就是在分子链与分子链之间形成交联,从 而使分子链间作用力量增强。 结构单元含有一个双键的聚合产物,这些双键可以与硫发生反应从而 交联形成网络状分子结构,得到硫化橡胶

Part 2 ORIGIN OF THE RUBBER
ORIGIN OF THE RUBBER Part 2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)有关橡胶加工的一些问题探讨(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)高分子化学与物理——天然橡胶的改性(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)天然橡胶机械使用及维护(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)2011年天胶投资主题——供需PK政策(PPT报告).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)天然橡胶(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)全球天然橡胶产业链简析(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程授课教案(讲义,主讲:教师姓名:廖小雪、何映平).doc
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学大纲 Natural rubber processing.doc
- 海南大学:《材料力学》课程授课教案(整合版,负责人:王涛).doc
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 10 材料的变形机理和回复、再结晶与热加工.ppt
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 材料加工成形的流动现象与力学基础.ppt
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 8 材料加工成形的传热过程.ppt
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 7 固态相变.ppt
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 材料的制取 6.2 烧结.ppt
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 材料的制取 6.1 凝固与结晶.ppt
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 5 相图 5.2 二元相图 Binary phase diagrams.pdf
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 5 相图 5.1 三元相图 Ternary phase diagram.ppt
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 4 固体中原子及分子的运动(主讲:李长久).ppt
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 晶体缺陷 3 2 位错.pptx
- 海南大学:《材料科学基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 晶体缺陷 3 1 点缺陷、位错.pptx
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)橡胶加工原理和工艺(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)橡胶加工工艺(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)橡胶加工工艺绪论 Rubber Processing Technology(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)天然高分子材料——天然橡胶及其他产胶植物(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)高分子材料——橡胶(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学资源(参考资料)产胶和排胶的基础理论(PPT讲稿).ppt
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)天然橡胶加工学绪论(主讲:廖小雪).pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第一章 新鲜胶乳.pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第三章 浓缩天然胶乳的生产.pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第二章 鲜胶乳的保存.pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第四章 特种浓缩胶乳及改性胶乳.pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第五章 天然生胶加工的基本工艺.pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第七章 其它类型的天然橡胶.pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第八章 制胶废水的处理.pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第六章 标准天然橡胶的生产4比3格式.pdf
- 海南大学:《天然橡胶加工学》课程教学课件(讲稿)第九章 天然橡胶的应用性质.pdf
- 高分子纳米复合材料(课件讲稿).pdf
- 电活性高分子(课件讲稿).pdf
- 北京城市学院:《建筑工程材料》课程教学大纲(负责人:李文利).pdf
- 北京城市学院:《建筑工程材料》课程授课教案(各章讲义).pdf
