Mobility Weakens the Distinction between Multicast and Unicast

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Mobility Weakens the Distinction between Multicast and Unicast xinbing I Wang Dept.of Electronic Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Shanghai,China
Mobility Weakens the Distinction between Multicast and Unicast Xinbing Wang Dept. of Electronic Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Shanghai, China

Outline 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ▣Introduction >Previous works Motivation System model and main idea The impact of mobility on capacity for restricted mobility model The impact of mobility on delay for restricted mobility model ▣Discussion Conclusion and future direction 2
2 Outline ❑ Introduction ➢ Previous works & Motivation ❑ System model and main idea ❑ The impact of mobility on capacity for restricted mobility model ❑ The impact of mobility on delay for restricted mobility model ❑ Discussion ❑ Conclusion and future direction

Previous Works Motivation 上浒充通大¥ What is multicast? SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY One source to m destinations oo Data copy is necessary One copy may be sent to multiple destinations The number of flows is reduced comparing with unicast 0 0o0 O a Xiangyang Li [1] [1]X.Li,"Multicast Capacity of Large Scale Wireless Ad Hoc Networks",IEEE/ACM Trans.Networking,Vol.17,No.3,pp. 950-961,Jan.2008.(citation:234) 3
Previous Works & Motivation What is multicast? ➢ One source to m destinations 3 ✓ Data copy is necessary ✓ One copy may be sent to multiple destinations ✓ The number of flows is reduced comparing with unicast Xiangyang Li [1] [1] X. Li, “Multicast Capacity of Large Scale Wireless Ad Hoc Networks”, IEEE/ACM Trans. Networking, Vol.17, No. 3, pp. 950-961, Jan. 2008.(citation:234)
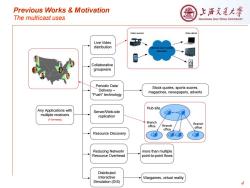
Previous Works Motivation 上浒充通大¥ The multicast uses SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Video sources Video clients Live Video distribution ntemet and mobile networks Collaborative groupware Periodic Data Delivery- Stock quotes,sports scores, "Push"technology magazines,newspapers,adverts Hub site Any Applications with Server/Web-site multiple receivers replication (1-to-many) Branch Branch office Branch office office Resource Discovery Reducing Network/ more than multiple Resource Overhead point-to-point flows Distributed Interactive Wargames,virtual reality Simulation (DIS) 4
Previous Works & Motivation The multicast uses 4 Any Applications with multiple receivers (1-to-many) Collaborative groupware Reducing Network/ Resource Overhead Live Video distribution Server/Web-site replication Resource Discovery Periodic Data Delivery – "Push" technology Stock quotes, sports scores, magazines, newspapers, adverts more than multiple point-to-point flows Distributed Interactive Simulation (DIS) Wargames, virtual reality Video sources Internet and mobile networks Video clients Hub site Branch office Branch office Branch office
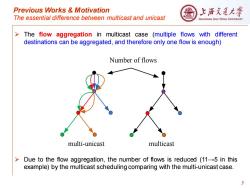
Previous Works Motivation 上游充通大 The essential difference between multicast and unicast SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY The flow aggregation in multicast case (multiple flows with different destinations can be aggregated,and therefore only one flow is enough) Number of flows multi-unicast multicast > Due to the flow aggregation,the number of flows is reduced (11-5 in this example)by the multicast scheduling comparing with the multi-unicast case. 5
Previous Works & Motivation The essential difference between multicast and unicast ➢ The flow aggregation in multicast case (multiple flows with different destinations can be aggregated, and therefore only one flow is enough) ➢ Due to the flow aggregation, the number of flows is reduced (11→5 in this example) by the multicast scheduling comparing with the multi-unicast case. 5 multi-unicast multicast Number of flows
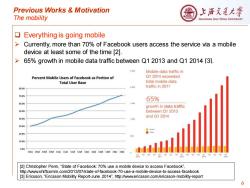
Previous Works Motivation 上浒充通大¥ The mobility SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Everything is going mobile > Currently,more than 70%of Facebook users access the service via a mobile device at least some of the time [2]. > 65%growth in mobile data traffic between Q1 2013 and Q1 2014 I31. 2500 Mobile data traffic in Percent Mobile Users of Facebook as Portion of Q1 2014 exceeded Total User Base total mobile data 2000 traffic in 2011 80,0% 70.0% 65% 60,0% 1500 growth in data traffic 50,0% between Q1 2013 and Q1 2014 40.0% 1.D00 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% 10q110q210g310g411g1110211q311c412q112q212q312q413q113q2 02000401 2004 [2]Christopher Penn,"State of Facebook:70%use a mobile device to access Facebook", http://www.shiftcomm.com/2013/07/state-of-facebook-70-use-a-mobile-device-to-access-facebook [3]Ericsson,"Ericsson Mobility Report-June 2014",http://w.ericsson.com/ericsson-mobility-report 6
Previous Works & Motivation The mobility ❑ Everything is going mobile ➢ Currently, more than 70% of Facebook users access the service via a mobile device at least some of the time [2]. ➢ 65% growth in mobile data traffic between Q1 2013 and Q1 2014 [3]. 6 [2] Christopher Penn, “State of Facebook: 70% use a mobile device to access Facebook”, http://www.shiftcomm.com/2013/07/state-of-facebook-70-use-a-mobile-device-to-access-facebook [3] Ericsson, “Ericsson Mobility Report-June 2014”, http://www.ericsson.com/ericsson-mobility-report
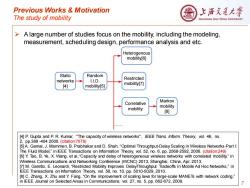
Previous Works Motivation 上浒充通大粤 The study of mobility SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY > A large number of studies focus on the mobility,including the modeling, measurement,scheduling design,performance analysis and etc. Heterogenous mobility[6] Static Random networks 1.D. Restricted [4] mobility[5] mobility[7] Markov Correlative mobility mobility [8] [4]P.Gupta and P.R.Kumar,"The capacity of wireless networks",IEEE Trans.Inform.Theory,vol.46,no. 2,pp.388-4042000.(citation:7678) [5]A.Gamal,J.Mammen,B.Prabhakar and D.Shah,"Optimal Throughput-Delay Scaling in Wireless Networks-Part I: The Fluid Model,"in IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,vol.52,no.6,pp.2568-2592,2006.(citation:249) [6]Y.Tao,B.Ye,X.Wang,et al.,"Capacity and delay of heterogeneous wireless networks with correlated mobility,"in Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC)2013,Shanghai,China,Apr.2013. [7]M.Garetto,E.Leonardi,"Restricted Mobility Improves DelayThroughput Tradeoffs in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks,"in IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,vol.56,no.10,pp.5010-5029,2010. [8]C.Zhang,X.Zhu and Y.Fang,"On the improvement of scaling laws for large-scale MANETs with network coding," in IEEE Joumal on Selected Areas in Communications,vol.27,no.5,pp.662-672,2009
Previous Works & Motivation The study of mobility 7 Static networks [4] Random I.I.D. mobility[5] Restricted mobility[7] Correlative mobility Markov mobility [8] Heterogenous mobility[6] …… ➢ A large number of studies focus on the mobility, including the modeling, measurement, scheduling design, performance analysis and etc. [4] P. Gupta and P. R. Kumar, "The capacity of wireless networks", IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, vol. 46, no. 2, pp.388 -404 2000. (citation:7678) [5] A. Gamal, J. Mammen, B. Prabhakar and D. Shah, “Optimal Throughput-Delay Scaling in Wireless Networks-Part I: The Fluid Model,” in IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 2568-2592, 2006. (citation:249) [6] Y. Tao, B. Ye, X. Wang, et al.,“Capacity and delay of heterogeneous wireless networks with correlated mobility,” in Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC) 2013, Shanghai, China, Apr. 2013. [7] M. Garetto, E. Leonardi, “Restricted Mobility Improves DelayThroughput Tradeoffs in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks,” in IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, vol. 56, no. 10, pp. 5010-5029, 2010. [8] C. Zhang, X. Zhu and Y. Fang, “On the improvement of scaling laws for large-scale MANETs with network coding,” in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 662-672, 2009
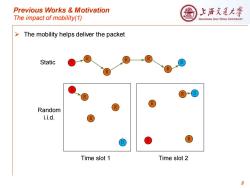
Previous Works Motivation 上浒充通大¥ The impact of mobility(1) SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY >The mobility helps deliver the packet Static R R R R Random R i.i.d. R ® Time slot 1 Time slot 2 8
Previous Works & Motivation The impact of mobility(1) ➢ The mobility helps deliver the packet 8 S D S Static Random i.i.d. R R R R R R D S R D Time slot 1 Time slot 2 R R R R
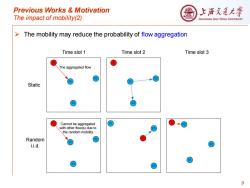
Previous Works Motivation 上游充通大警 The impact of mobility(2) SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY > The mobility may reduce the probability of flow aggregation Time slot 1 Time slot 2 Time slot 3 The aggregated flow 02 D2 DI Static D3 D3 Cannot be aggregated 2 with other flow(s)due to (D3 the random mobility Random DI i.i.d. 9
Previous Works & Motivation The impact of mobility(2) ➢ The mobility may reduce the probability of flow aggregation 9 S D1 D2 D3 The aggregated flow S D1 D2 D3 Time slot 1 Time slot 2 Static Random i.i.d. S D1 D2 D3 S D1 D2 D3 S D1 D2 D3 Time slot 3 Cannot be aggregated with other flow(s) due to the random mobility

Previous Works Motivation 上浒充通大¥ Our view on the impact of mobility SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY >According to the mentioned impacts above,we can conclude that: The mobility helps deliver the packet-The mobility improves the capacity. The mobility may reduce the probability of flow aggregation-The mobility weakens the distinction between multicast and unicast. 10
Previous Works & Motivation Our view on the impact of mobility ➢ According to the mentioned impacts above, we can conclude that: ✓ The mobility helps deliver the packet → The mobility improves the capacity. ✓ The mobility may reduce the probability of flow aggregation → The mobility weakens the distinction between multicast and unicast. 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- Mobility Weakens the Distinction between Multicast and Unicast.pdf
- Impact of Social Relation and Group Size in Multicast Ad Hoc Networks.pptx
- Impact of Social Relation and Group Size in Multicast Ad Hoc Networks.pdf
- Optimal Secrecy Capacity-Delay Tradeoff in Large-Scale Mobile Ad Hoc Networks.pdf
- Two-Dimensional Route Switching in Cognitive Radio Networks:A Game-Theoretical Framework.ppt
- Two-Dimensional Route Switching in Cognitive Radio Networks:A Game-Theoretical Framework.pdf
- Node Density and Delay in Large-Scale Wireless Networks with Unreliable Links.pdf
- Multicast Capacity with Max-Min Fairness for Heterogeneous Networks.pdf
- Asymptotic Analysis on Secrecy Capacity in Large-Scale Wireless Networks.ppt
- Asymptotic Analysis on Secrecy Capacity in Large-Scale Wireless Networks.pdf
- Mobility Increases the Connectivity of Wireless Networks.pdf
- Capacity Scaling of General Cognitive Networks.pdf
- Multicast Performance With Hierarchical Cooperation.pdf
- Delay and Capacity Tradeoff Analysis for MotionCast.pdf
- Achieving 100% Throughput in TCP/AQM Under Aggressive Packet Marking With Small Buffer.pdf
- DRIMUX:Dynamic Rumor Influence Minimization with User Experience in Social Networks.pdf
- Coverage and Energy Consumption Control in Mobile Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor Networks.pdf
- Optimal Determination of Source-destination Connectivity in Random Graphs.ppt
- MotionCast:On the Capacity and Delay Tradeoffs.ppt
- Fundamental Relationship between Node Density and Delay in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks with Unreliable Links.ppt
- Are we connected? Optimal Determination of Source-destination Connectivity in Random Networks.pdf
- Asymptotic Analysis on Content Placement and Retrieval in MANETs.pdf
- Connectivity Analysis in Wireless Networks with Correlated Mobility and Cluster Scalability.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《VB程序设计基础》课程教学资源(教学大纲)Programming of Visual Basic.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《VB程序设计基础》课程教学资源(授课教案)第一章 VB概述.doc
- 甘肃农业大学:《VB程序设计基础》课程教学资源(作业习题)VB习题1.pdf
- 甘肃农业大学:《VB程序设计基础》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)C语言概述.ppt
- 同济大学:《Visual Basic程序设计简明教程》配套PPT课件讲稿(第三版)第1章 Visual Basic程序设计概述、第2章 VB可视化编程基础、第3章 VB语言基础.ppt
- 同济大学:《Visual Basic程序设计简明教程》配套PPT课件讲稿(第三版)第4章 VB控制结构、第5章 数组和自定义类型、第6章 过程.ppt
- 同济大学:《Visual Basic程序设计简明教程》配套PPT课件讲稿(第三版)第7章 用户界面设计、第8章 数据文件、第9章 图形操作.ppt
- 同济大学:《Visual Basic程序设计简明教程》配套PPT课件讲稿(第三版)第10章 数据库应用基础.ppt
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 C++的初步知识(主讲:祝元仲)C++ Programming.pdf
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 数据类型与表达式 Data Types & Expression.pdf
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 程序设计初步.pdf
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 函数与预处理.pdf
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 数组 Arrays.pdf
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 指针.pdf
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 类和对象.pdf
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 运算符重载.pdf
- 川北医学院:《C++程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第11章 继承与派生.pdf
