上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 2 Energy and Energy Transfer

Lecture 2 Energy and Energy Transfer
Energy and Energy Transfer Lecture 2

Focal point of interest Temperature the measurement of heat and cold:the molecular activity Unit:oC,K,F 0°C=273.15K, T(K)=t(°C)+273.15 0C=32FT(月=32+1.8t(°C)
Focal point of interest Temperature the measurement of heat and cold : the molecular activity Unit:o C ,K, F 0 oC=273.15K, T(K)=t( oC)+273.15 0 oC=32 oF, T( o F)=32+1.8t( oC)
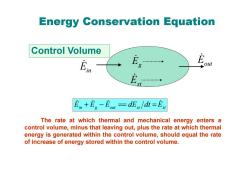
Energy Conservation Equation Control Volume 中年·”年… g out E t En+Eg-Eou =dEs /dt =Est The rate at which thermal and mechanical energy enters a control volume,minus that leaving out,plus the rate at which thermal energy is generated within the control volume,should equal the rate of increase of energy stored within the control volume
Energy Conservation Equation in g out st Est E E E dE dt + − == = The rate at which thermal and mechanical energy enters a control volume, minus that leaving out, plus the rate at which thermal energy is generated within the control volume, should equal the rate of increase of energy stored within the control volume. Control Volume Ein Eout E g Est

Energy inflow and outflow by conduction,convection,radiation Conduction across the surface: Rate equ. Ccond =-kAdI -Fourier's Law dx k--Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m-K]
Conduction across the surface: Rate equ. ——Fourier’s Law dT q A dx cond = − k k -- Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m·K] Energy inflow and outflow by conduction, convection, radiation

Conductivity for biological tissue: k,=0.419*(0.133+1.36mm)[wlmK)] m fraction of water mass in tissue k,(T)=k.x*[1+0.003(T-T】 Wdlch,1984
Conductivity for biological tissue: 0.419* (0.133 1.36 ) t w k m = + m w 0 , 0 ( ) *[1 0.003( )] t tT kT k T T =+ − fraction of water mass in tissue Wdlch, 1984 [w/(m·K)]
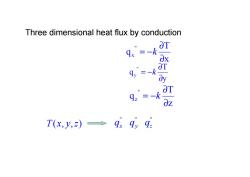
Three dimensional heat flux by conduction OT 9x =-k y =-k =-k r T(x,y,)→99,9
x T q '' x ∂ ∂ = −k y T q '' y ∂ ∂ = −k z T q '' z ∂ ∂ = −k Three dimensional heat flux by conduction T(x, y,z) '' qx '' qy '' qz
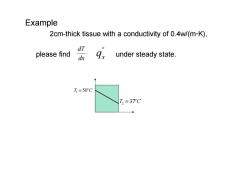
Example 2cm-thick tissue with a conductivity of 0.4w/(m-K) please find gx under steady state. T=50°C T,=37C
Example 2cm-thick tissue with a conductivity of 0.4w/(m·K), please find under steady state. T Co 1 = 50 '' qx T Co 2 = 37 dx dT
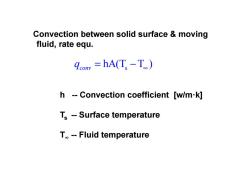
Convection between solid surface moving fluid,rate equ. com =hA(Ts -T) h --Convection coefficient [w/m-k] Ts --Surface temperature T。-Fluid temperature
Convection between solid surface & moving fluid, rate equ. s hA(T T ) conv q = − ∞ h -- Convection coefficient [w/m·k] Ts -- Surface temperature T ∞ -- Fluid temperature
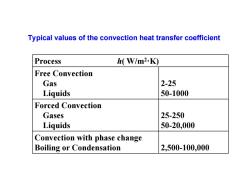
Typical values of the convection heat transfer coefficient Process h(W/m2.K) Free Convection Gas 2-25 Liquids 50-1000 Forced Convection Gases 25-250 Liquids 50-20,000 Convection with phase change Boiling or Condensation 2,500-100,000
Typical values of the convection heat transfer coefficient Process h( W/m 2·K) Free Convection Gas Liquids 2-25 50-1000 Forced Convection Gases Liquids 25-250 50-20,000 Convection with phase change Boiling or Condensation 2,500-100,000

net radiation exchange from the surface to the surrounding: 9=8o(T4-T4)A
net radiation exchange from the surface to the surrounding: 4 4 s sur εσ(T T )A rad s q = −
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 27 Thermal conductivity, Blood Perfusion Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 26:Cryosurgery.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 24&25 Cryobiology、Cryopreservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 23 Dynamic Vascular Response.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 20 Introduction to FLUENT.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 1 Introduction(张爱丽).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 19&21 Modeling in thermal treatment——heating.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 17&18 Hyperthermia treatment for tumors.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 16 Temperature Measurement Jianqi Sun.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 15_lecture 15-vasculature.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 15:Anatomy and Description of Microvasculature.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 14:Two methods to solve differential equation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 12&13 Bioheat transfer Equations.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 11 Radiation Continued.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 10:Radiation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源_果蝇 Fruit Fly.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源_生物学领域经典网站.doc
- 《工业微生物》:我国生物发酵产业发展现状及发展趋势(中国生物发酵产业协会).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)工业生物技术产业发展趋势及对我国的启示.pdf
- 《生物技术通报》:基因工程制药的研究现状与发展前景(中国农村技术开发中心:汤娇雯).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 3 Apply Energy Conservation Equation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 4 Heat Conduction Equation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 5.1 Conduction equation and examples.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 5.2 Conduction equation and examples.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 6 Thermal Resistance Method.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 7 Convection.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 8 Heat Transfer to Blood Vessels.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 1 Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 10 anatomy of vasculature and dynamic blood flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 11 Measurement of Thermal Properties for biological tissue.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 12 Hyperthermia treatment for tumors.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 2 Energy and Energy Transfer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 3 Energy and Energy Conservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 4 Solve of the Conduction Eq..pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 5-6-1 convection and blood flow convection-web.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 5 Convection.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 7 Radiation Between Surfaces.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 8 bioheat transfer equation-1.pdf
- 《生物学通报》:microRNA及其与衰老进程的关系(北京大学衰老研究中心:姜彬).pdf
- 《遗传学与社会》课程教学资源:性别决定基因的研究进展(南京铁道医学院).pdf
