上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 19&21 Modeling in thermal treatment——heating

Modeling in thermal treatment ------heating
Modeling in thermal treatment ‐‐‐‐‐‐heating

Predicting temp.distribution during hyperthermia 。Importance: -control of heating to provide sufficient thermal dose to tumor tissue but spare the surrounding healthy tissue (temp.elevation duration) -Technical difficulties of monitoring tissue temperature o Modeling: ot pc- =V.k,VT+(pc)p Wi (Ta-T)+gmb+gh t
Predicting temp. distribution during hyperthermia • Importance: – control of heating to provide sufficient thermal dose to tumor tissue but spare the surrounding healthy tissue (temp. elevation & duration) – Technical difficulties of monitoring tissue temperature • Modeling: ( ) ( ) t b b a mb h T c k T c wT T q q t
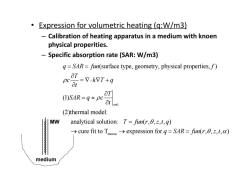
● Expression for volumetric heating(q:W/m3) - Calibration of heating apparatus in a medium with knoen physical properities. -Specific absorption rate (SAR:W/m3) g=SAR=fin(surface type,geometry,physical properties,f) =V.kWT+q pc 8t aT (SAR=g≈pcat (2)thermal model: MW analytical solution:T=fun(r,0,z,t,q) >cure fit to Tmeeusexpression for q=SAR=fin(r,,t,) medium
• Expression for volumetric heating (q:W/m3) – Calibration of heating apparatus in a medium with knoen physical properities. – Specific absorption rate (SAR: W/m3) t=0 mecus (surface type, geometry, physical properties, ) (1) (2)thermal model: analytical solution: ( , , , , ) cure fit to T expression for q SAR fun f T c kT q t T SAR q c t T fun r z t q q S AR fun r z t ( , , , , ) medium MW
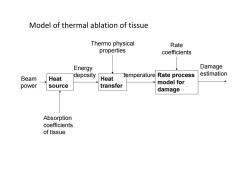
Model of thermal ablation of tissue Thermo physical Rate properties coefficients Energy Damage estimation Beam Heat deposity Heat temperature Rate process model for power source transfer damage Absorption coefficients of tissue
Model of thermal ablation of tissue Damage Rate process estimation model for q rzt n (, ,) damage Heat source Heat transfer Beam power Absorption coefficients of tissue Energy deposity Thermo physical properties temperature Rate coefficients T rzt (, ,) (, ) r z
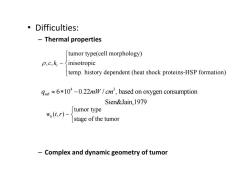
。Difficulties: Thermal properties tumor type(cell morphology) P,c,k,~inisotropic temp.history dependent (heat shock proteins-HSP formation) 6*10*-0.22mW/cm',based on oxygen consumption Sien&Jain,1979 w(t.r)-s tumor type stage of the tumor Complex and dynamic geometry of tumor
• Difficulties: – Thermal properties – Complex and dynamic geometry of tumor b tumor type (, ) stage of the tumor w tr tumor type(cell morphology) , , inisotropic temp. history dependent (heat shock proteins-HSP formation) t c k 4 3 6 10 0.22 / , based on oxygen consumption Sien&Jain,1979 mb q mW cm

Mechanisms of heat induced damage Cytoplasmic and nuclear protein denaturation DNA and RNA changes and cellular membrane function change Tissue necrosis,coagulation and vaporization of tissue Damage degree function of tissue temperature and treatment time
Mechanisms of heat induced damage • Cytoplasmic and nuclear protein denaturation • DNA and RNA changes and cellular membrane function change • Tissue necrosis, coagulation and vaporization of tissue Damage degree : function of tissue temperature and treatment time

The thermodynamics of heat inactivation Life of a cell sustained by various metabolic activities rough ribosome endoplasmic mitochondrion reticulum plasma -o membrane cytoplasm microtubules (part of cytoskeleton) 9 lysosome nucleus smooth nucleolus endoplasmic chromatin reticulum nuclear pore nuclear envelope free ribosome Golgi complex centriole
The thermodynamics of heat inactivation Life of a cell sustained by various metabolic activities

Death caused by accumulation of inactivation of n different reactions and inactivation of chromosomal proteins the damage of each reaction or protein inactivation follows Arrhenius function =k, YT-AGIRT e dt h
Death caused by accumulation of inactivation of n different reactions and inactivation of chromosomal proteins the damage of each reaction or protein inactivation follows Arrhenius function G RT / s d T k e dt h

o--the total damage k.the rate of damage y--the Boltzmann's constant,1.38X 10-23 J/K h--the Planck's constant,6.63x10-34 J-s △G-the Gibbs free energy of inactivation △G=△H-T△S 4s--the entropy of inactivation (cal/K/mole) 4H--the enthalpy of the inactivation An approximate expression for k k,=2.05×(10)l0×T×e4s2×eaH/27
ω --the total damage ks – the rate of damage γ-- the Boltzmann’s constant, 1.38× 10−23 J/K h -- the Planck’s constant, 6.6310‐34 J‐s ΔG --the of inactivation Δs -- the entropy of inactivation (cal/K/mole) ΔH-- the enthalpy of the inactivation ΔG =ΔH‐TΔs Gibbs free energy 10 /2 /2 2.05 (10) s HT s k Te e An approximate expression for ks

Gibbs free energy a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful"or process-initiating work obtainable from an isothermal,isobaric thermodynamic system. the chemical potential that is minimized when a system reaches equilibrium at constant pressure and temperature A convenient criterion of spontaneity for processes with constant pressure and temperature
the chemical potential that is minimized when a system reaches equilibrium at constant pressure and temperature A convenient criterion of spontaneity for processes with constant pressure and temperature a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process‐initiating work obtainable from an isothermal, isobaric thermodynamic system. Gibbs free energy
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 17&18 Hyperthermia treatment for tumors.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 16 Temperature Measurement Jianqi Sun.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 15_lecture 15-vasculature.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 15:Anatomy and Description of Microvasculature.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 14:Two methods to solve differential equation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 12&13 Bioheat transfer Equations.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 11 Radiation Continued.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 10:Radiation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源_果蝇 Fruit Fly.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源_生物学领域经典网站.doc
- 《工业微生物》:我国生物发酵产业发展现状及发展趋势(中国生物发酵产业协会).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)工业生物技术产业发展趋势及对我国的启示.pdf
- 《生物技术通报》:基因工程制药的研究现状与发展前景(中国农村技术开发中心:汤娇雯).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)医药生物工程导论——人口与健康.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)中国五大生物产业的国际竞争力.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物工程导论》课程教学资源(阅读资料)Public biotech 2009—the numbers.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《细胞工程》精品课程教学资源(学习文献)第7讲 文献-immobilization.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《细胞工程》精品课程教学资源(学习文献)第7讲 文献-hairy root culture2.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《细胞工程》精品课程教学资源(学习文献)第7讲 文献-hairy root culture.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《细胞工程》精品课程教学资源(学习文献)第7讲 文献-fed-batch culture.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 1 Introduction(张爱丽).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 20 Introduction to FLUENT.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 23 Dynamic Vascular Response.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 24&25 Cryobiology、Cryopreservation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 26:Cryosurgery.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)Lecture 27 Thermal conductivity, Blood Perfusion Measurement.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 2 Energy and Energy Transfer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 3 Apply Energy Conservation Equation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 4 Heat Conduction Equation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 5.1 Conduction equation and examples.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 5.2 Conduction equation and examples.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 6 Thermal Resistance Method.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 7 Convection.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 8 Heat Transfer to Blood Vessels.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 1 Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 10 anatomy of vasculature and dynamic blood flow.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 11 Measurement of Thermal Properties for biological tissue.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 12 Hyperthermia treatment for tumors.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 2 Energy and Energy Transfer.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物传热学教与学 Bioheat Transfer》课程教学资源(电子讲义)lecture 3 Energy and Energy Conservation.pdf
