西安电子科技大学:《数据结构与算法分析 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)01 Lists, Stacks, and Queues

Textbook Mark Allen Weiss,Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C,China Machine Press
Textbook ◼ Mark Allen Weiss, Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C, China Machine Press

Grading Final exam:70% ■Others:30%
Grading ◼ Final exam: 70% ◼ Others: 30%

What are Data Structures and Algorithms? Data Structures are methods of organizing large amounts of data. An algorithm is a procedure that consists of finite set of instructions which,given an input from some set of possible inputs,enables us to obtain an output if such an output exists or else obtain nothing at all if there is no output for that particular input through a systematic execution of the instructions
What are Data Structures and Algorithms? ◼ Data Structures are methods of organizing large amounts of data. ◼ An algorithm is a procedure that consists of finite set of instructions which, given an input from some set of possible inputs, enables us to obtain an output if such an output exists or else obtain nothing at all if there is no output for that particular input through a systematic execution of the instructions
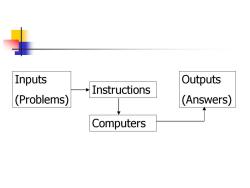
Inputs Outputs Instructions (Problems) (Answers) Computers
Instructions Inputs (Problems) Outputs (Answers) Computers
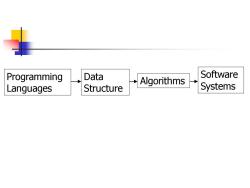
Programming Data Software Algorithms Languages Structure Systems
Programming Languages Data Structure Algorithms Software Systems

Contents Chapter 3 Lists,Stacks,and Queues Chapter 4 Trees Chapter 5 Hashing Chapter 6 Priority Queues(Heaps) Chapter 7 Sorting Chapter 8 The Disjoint Set ADT Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms Chapter 10 Algorithm Design Techniques
Contents Chapter 3 Lists, Stacks, and Queues Chapter 4 Trees Chapter 5 Hashing Chapter 6 Priority Queues (Heaps) Chapter 7 Sorting Chapter 8 The Disjoint Set ADT Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms Chapter 10 Algorithm Design Techniques

Abstract Data Types (ADTs) One of the basic rules concerning programming is to break the program down into modules. Each module is a logical unit and does a specific job. Its size is kept small by calling other modules. Modularity has several advantages.(1)It is much easier to debug small routines than large routines;(2) It is easier for several people to work on a modular program simultaneously;(3)A well-written modular program places certain dependencies in only one routing,making changes easier
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) ◼ One of the basic rules concerning programming is to break the program down into modules. ◼ Each module is a logical unit and does a specific job. Its size is kept small by calling other modules. ◼ Modularity has several advantages. (1) It is much easier to debug small routines than large routines; (2) It is easier for several people to work on a modular program simultaneously; (3) A well-written modular program places certain dependencies in only one routing, making changes easier

Abstract Data Types (ADTs) An abstract data type (ADT)is a set of operations. Abstract data types are mathematical abstractions; nowhere in an ADT's definition is there any mention of how the set of operations is implemented. Objects such as lists,sets,and graphs,along with their operations,can be viewed as abstract data types,just as integers,reals,and booleans are data types.Integers,reals,and booleans have operations associated with them,and so do ADTs
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) ◼ An abstract data type (ADT) is a set of operations. ◼ Abstract data types are mathematical abstractions; nowhere in an ADT’s definition is there any mention of how the set of operations is implemented. ◼ Objects such as lists, sets, and graphs, along with their operations, can be viewed as abstract data types, just as integers, reals, and booleans are data types. Integers, reals, and booleans have operations associated with them, and so do ADTs

Abstract Data Types (ADTs) The basic idea is that the implementation of the operations related to ADTs is written once in the program,and any other part of the program that needs to perform an operation on the ADT can do so by calling the appropriate function. If for some reason implementation details need to be changed,it should be easy to do so by merely changing the routings that perform the ADT operations. There is no rule telling us which operations must be supported for each ADT;this is a design decision
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) ◼ The basic idea is that the implementation of the operations related to ADTs is written once in the program, and any other part of the program that needs to perform an operation on the ADT can do so by calling the appropriate function. ◼ If for some reason implementation details need to be changed, it should be easy to do so by merely changing the routings that perform the ADT operations. ◼ There is no rule telling us which operations must be supported for each ADT; this is a design decision

The List ADT The form of a general list:A,A,A3,...,Ai The size of this list is M An empty list is a special list of size 0; ■ For any list except the empty list,we say that A1 follows (or succeeds)A,(/1): The first element of the list is A1,and the last element is A.We will not define the predecessor of A or the successor of Awv. The position of element A,in a list is /
The List ADT ◼ The form of a general list: A1 , A2 , A3 , …, AN; ◼ The size of this list is N; ◼ An empty list is a special list of size 0; ◼ For any list except the empty list, we say that Ai+1 follows (or succeeds) Ai (i1); ◼ The first element of the list is A1 , and the last element is AN . We will not define the predecessor of A1 or the successor of AN. ◼ The position of element Ai in a list is i
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西安电子科技大学:《数据结构与算法分析 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)02 Trees(主讲:刘静).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《数据结构与算法分析 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)05 Disjoint Set ADT.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《数据结构与算法分析 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)04 Priority Queues(Heaps).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《数据结构与算法分析 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)03 Hashing.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《数据结构与算法分析 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)08 Algorithm Design Techniques.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《数据结构与算法分析 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)07 Graph Algorithms.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《数据结构与算法分析 Data Structure and Algorithm Analysis》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)06 Algorithm Analysis and Sorting.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《算法设计技术 Algorithms Design Techniques》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Iterative Improvement for Domain-Specific Problems(Chapter 16 Network Flow Chapter 17 Matching).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《算法设计技术 Algorithms Design Techniques》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Coping with Hardness(Chapter 13 Backtracking Chapter 14 Randomized Algorithms Chapter 15 Approximation Algorithms).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《算法设计技术 Algorithms Design Techniques》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)First-Cut Techniques(Chapter 8 The Greedy Approach Chapter 9 Graph Traversal).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《算法设计技术 Algorithms Design Techniques》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Techniques Based on Recursion(Chapter 5 Induction Chapter 6 Divide and Conquer Chapter 7 Dynamic Programming).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《算法设计技术 Algorithms Design Techniques》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Chapter 01 Basic Concepts in Algorithmic Analysis(主讲:刘静).ppt
- 《计算机基础》课程教学资源(参考论文)Motif Difficulty(MD):A Predictive Measure of Problem Difficulty for Evolutionary Algorithms using Network Motifs.pdf
- 《计算机基础》课程教学资源(参考论文)An Organizational Evolutionary Algorithm for Numerical Optimization.pdf
- 《计算机基础》课程教学资源(参考论文)A Multiagent Evolutionary Algorithm for Constraint Satisfaction Problems.pdf
- 《计算机基础》课程教学资源(参考论文)Comments on “the 1993 DIMACS Graph Coloring Challenge” and “Energy Function-Based Approaches to Graph Coloring”.pdf
- 《计算机基础》课程教学资源(参考论文)Moving Block Sequence and Organizational Evolutionary Algorithm for General Floorplanning with Arbitrarily Shaped Rectilinear Blocks.pdf
- 《计算机基础》课程教学资源(参考论文)A Multi-Agent Genetic Algorithm for Global Numerical Optimization.pdf
- 《计算机基础》课程教学资源(参考论文)An Organizational Coevolutionary Algorithm for Classification.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《大学计算机基础 Fundamentals of Computers》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)Chapter 12,14,15 Lecture_Computer Software(2/2).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:Robust Speech Recognition with Speech Enhanced Deep Neural Networks.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)第九章 机器无关的优化.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)第八章 代码生成.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)第七章 运行时刻环境.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)第六章 中间代码生成.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)第五章 语法制导的翻译.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)第四章 语法分析.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)第三章 词法分析.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)第一章 引论(许畅).pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)编译课程复习(许畅).pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(实验讲义)实验一 词法分析与语法分析.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(实验讲义)实验二 语义分析.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(实验讲义)实验三 中间代码生成.pdf
- 南京大学:《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学电子教案(实验讲义)实验四 目标代码生成.pdf
- 《编译原理 Principles and Techniques of Compilers》课程教学资源(学习资料)Assemblers,Linkers,and the SPIM Simulator(MIPS32 and SPIM).pdf
- 南京大学:《软件工程导论 Introduction to Software Engineering Research》课程教学电子教案(课件讲义)04 Conduct Rigorous and Scientific Research(Experiment Design in Software Engineering Research).pdf
- 华中科技大学:《面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)课程简介(李瑞轩).pdf
- 华中科技大学:《面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 引论(李瑞轩).pdf
- 华中科技大学:《面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 C++的变量、类型及函数.pdf
- 华中科技大学:《面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 C++的类.pdf
