上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_Chapter 3 Bubble or droplet translation

Bubble or droplet translation
Bubble or droplet translation
Introduction Forces on particle can radically modified them,and in turn to change the interaction between particles and continuous phase. This chapter consider the translation of disperse phase consists of deformable particles
Introduction • Forces on particle can radically modified them, and in turn to change the interaction between particles and continuous phase. • This chapter consider the translation of disperse phase consists of deformable particles

Dimensional analysis Translation stress may deform particles ●Need to consider -Deformation parameters Impacts on translation velocity and shape Surface tension will be force restrain the deformation ·Assumptions: Steady translation Driven by gravity
Dimensional analysis • Translation stress may deform particles • Need to consider – Deformation parameters – Impacts on translation velocity and shape • Surface tension will be force restrain the deformation • Assumptions: – Steady translation – Driven by gravity

Dimensional analysis Surface tension force,SR When magnitude of deform force approaches SR, deformation happens. For Re>1,the deform force PLW2R2 So define We =2pLW2R/S For Re>1,deformation happens when We ~1 Therefore woo need to be defined,so F(Re,We,Fr)=0 To define a new parameter We3 Hm Fr2Re4 mp PLu PL S3
Dimensional analysis • Surface tension force, SR • When magnitude of deform force approaches SR, deformation happens. – For Re>1, the deform force • So define – For Re>1, deformation happens when We ~1 • Therefore need to be defined, so To define a new parameter
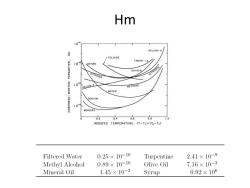
Hm 108 HELIUM-4 -TOLUENE FREON-12 OXYGEN OXYGEN NITROGEN NITROGEN 10 HELIUM-4 METHANE WATER SODIUM MERCURY 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 REDUCED TEMPERATURE. (T-T,)/(Te-T) Filtered Water 0.25×10-10 Turpentine 2.41×10-9 Methyl Alcohol 0.89×10-10 Olive Oil 7.16×10-3 Mineral Oil 1.45×10-2 Syrup 0.92×106
Hm

Bubble shapes and terminal velocities When the departure from sphericity happens ·Re1 in some irregular case,therefore deformation happens ·Re>>1 Fr≈O(1) We>1→Re>Hm If Hm1,deform happens since Re<<1
Bubble shapes and terminal velocities • When the departure from sphericity happens • Re1 in some irregular case, therefore deformation happens • Re>>1 – If Hm1, deform happens since Re<<1

Bubble shapes and terminal velocities Experimentally,deformation causes ellipsoidal bubbles oscillation both in shape and trajectories. When bubble size increases further reaching We=20, it acquires a new shape,spherical-cap bubble w=子gRc)=(gR)话 Where for a spherical gas bubble with same volume Woo =(8gRB/3Cp)=2.3(gRB) -BUBBLE VOLUME
Bubble shapes and terminal velocities • Experimentally, deformation causes ellipsoidal bubbles oscillation both in shape and trajectories. • When bubble size increases further reaching We=20, it acquires a new shape, spherical-cap bubble – Where for a spherical gas bubble with same volume

Bubble shapes and terminal velocities Spherical-cap bubble -Woo/(gRB)constant Re>200 90 80 60 50 0 60 ★。 12 2.0 10 24 0.8 0.5 10 102 103 10 105 REYNOLDS NUMBER,Re=2 WooRa/v
Bubble shapes and terminal velocities • Spherical-cap bubble – constant Re>200
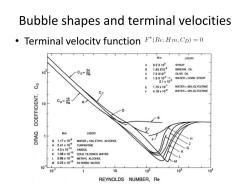
Bubble shapes and terminal velocities Terminal velocity function F(Re,Hm,CD)=0 Hm LIQUID A 9.2X105 SYRUP 24 0 1.45X102 MINERAL OL 0 7.2X103 OLIVE OIL 0 1.5X10→ WATER+CORN SYRUP 2.1x103 E 1.75x102 WATER+56%GLYCERINE 4.18×109 WATER+42%GLYCERINE LN3IO30 10 Co-36 Hm LIQUID G1.17x109 WATER+13%ETHYL ALCOHOL H 2.41x109 TURPENTINE 4.3x1010 VARSOL K 1.08x1010 COLD FILTERED WATER 0.89x1010 METHYL ALCOHOL M0.25x1010 FILTERED WATER 10L 101 1 10 102 103 10 REYNOLDS NUMBER,Re
Bubble shapes and terminal velocities • Terminal velocity function

Marangoni effects Marangoni effects,force due to the surface tension e gradient affects the translation velocity. The gradient can be caused by temperature gradient, electric potential. The thermocapillary effects For most liquid,surface tension decreases linearly with temperature -ds/dT,for pure liquid/vapor interfaces (in kg/s2 K). Water 2.02×10-4 Methane 1.84×10-4 Hydrogen 1.59×10-4 Butane 1.06×10-4 Helium-4 1.02×10-4 Carbon Dioxide 1.84×10-4 Nitrogen 1.92×10-4 Ammonia 1.85×10-4 Oxygen 1.92×10-4 Toluene 0.93×10-4 Sodium 0.90×10-4 Freon-12 1.18×10-4 Mercury 3.85×10-4 Uranium Dioxide 1.11×10-4
Marangoni effects • Marangoni effects, force due to the surface tension gradient affects the translation velocity. • The gradient can be caused by temperature gradient, electric potential. • The thermocapillary effects – For most liquid, surface tension decreases linearly with temperature
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_Chapter 2 Single particle motion.pdf
- 《可再生能源》教学资源(阅读资料)04-Tony-Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading.pdf
- 《可再生能源》教学资源(阅读资料)03-RSER2503.pdf
- 《可再生能源》教学资源(阅读资料)02-Impacts of main factors on bioethanol fermentation.pdf
- 《可再生能源》教学资源(阅读资料)01-A review of methane production.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第14讲 低温测试技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第13讲 真空技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12讲 低温绝热技术及低温贮运设计.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12讲 低温绝热技术及低温贮运设计.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10讲 脉管制冷机及热声低温制冷机.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第09讲 低温制冷机.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第08讲 空气分离系统.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07讲 精馏塔的理论计算、变压吸附及膜分离.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第06讲 气体分离基础.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第05讲 气体液化(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第04讲 气体液化(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第03讲 低温的获得方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第02讲 低温材料与流体物性.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第01讲 课程介绍及低温工程导论(黄永华、王如竹).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《工程热力学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第7章 气体和蒸汽的流动 Gas and Steam Flow.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_Chapter 4 Bubble growth and collapse.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_Chapter 1 Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_多相流与传热教学大纲(中英文).doc
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Introduksjon HPPS-Summer.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Kap-3-one stage.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)NTNU - EPT - introduction.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Presentation NTNU DD program.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Refrigerants.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Refrigerants.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Refrigeration I.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)RnLib software_NKF-2014-03-13-RnLib-Eikevik.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)中文版NKF-2014-03-13-RnLib-Eikevik.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汽液两相流动与传热 Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flow Boiling Heat Transfer》研究生课程PPT教学课件_第一章 两相流概述.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《制冷原理与设备》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)制冷的作用、制冷发展史、突破性的进展和挑战、制冷方式、制冷的基本热力学原理.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物质能源转化与利用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第3讲 生物质构建与组成.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物质能源转化与利用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第4讲 生物质燃料特性.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物质能源转化与利用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第2讲 生物质能概述.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物质能源转化与利用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第1讲 能源概述(罗永浩).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《电机学 Electric Machinery》课程教学资源(GE讲义)交流电机共性问题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电机学 Electric Machinery》课程教学资源(GE讲义)直流电机.pdf
