上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_Chapter 4 Bubble growth and collapse

Bubble growth and collapse
Bubble growth and collapse

Introduction Gas bubbles can grow or collapse in flow Introducing many important phenomena General assumptions in this chapter Flow far away from bubble is at rest -Spherical symmetric bubble Single bubble
Introduction • Gas bubbles can grow or collapse in flow • Introducing many important phenomena • General assumptions in this chapter – Flow far away from bubble is at rest – Spherical symmetric bubble – Single bubble

Rayleigh-Plesset equation Looking for a function for bubble radius R(t) ·Assumptions: Liquid temperature Too constant Liquid pressure Po()is a known input Liquid density pL constant Liquid viscosity constant and uniform Bubble is homogeneous,Ta(t)and pE()are uniform
Rayleigh-Plesset equation • Looking for a function for bubble radius • Assumptions: – Liquid temperature constant – Liquid pressure is a known input – Liquid density constant – Liquid viscosity constant and uniform – Bubble is homogeneous , and are uniform
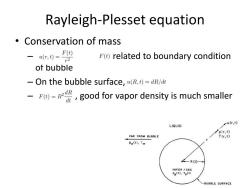
Rayleigh-Plesset equation 。Conservation of mass -4(,)=F F()related to boundary condition of bubble -On the bubble surface,u(R,t)=dR/dt -good for vapor density is much smaller u(r,t) LIQUID p(r,t) FAR FROM BUBBLE T(r,t) Poo(t],Too ∠-R(t)+ VAPOR GAS Pe(t).Te(t] -BUBBLE SURFACE
Rayleigh-Plesset equation • Conservation of mass – related to boundary condition of bubble – On the bubble surface, – , good for vapor density is much smaller

Rayleigh-Plesset equation N-S equation in r direction 1∂p0u,0u pLar=t+“ar {品 ·Introducing u=F(t)/r2 1 Op 1 dF 2F2 PL Orr2 dt r5 ·Integrate to get p-Poo 1dF 1F2 PL r dt 2r4 Net force on the surface radially outward 2S (Orr)r=R+PB-R Orr =-p+2uLou/Or. AuL dR PB -(p)r-R-R dt 2S replacing (p),=R R pB(t)-p∞() d2R 3 dR 2 AvL dR 2S PL -2 dt R dt PLR
Rayleigh-Plesset equation • N-S equation in r direction • Introducing • Integrate to get • Net force on the surface radially outward • replacing

Bubble content effect Assume bubble contains non-condensable gas Partial pressure poo at reference size and temp. pa)=ma+o(是)(货) Te need to be determined,rewrite the R-P equation: pv(T)-Poe(t)pv(TB)-pv(To) PL PL ()() d2R 3 dR AvL dR 2S =R d2+2( +R dt PLR First term is driving term Thermal term,which is considered later
Bubble content effect • Assume bubble contains non-condensable gas – Partial pressure at reference size and temp. • TB need to be determined, rewrite the R-P equation: – First term is driving term – Thermal term, which is considered later

Bubble content Taylor expansion on the first term Pv(TB)-PV(Too)=A(TB-Too) PL -A can be derived from Clausius-Clapeyron relation A=1= Pv(To)L(Too) PL dT PLToo 。Determine(Ts-To) -First step:heat diffusion equation,relates (Ta-T(ar/an +()买-是() Second step:energy balance,relates (aT/ar),-R R(t). dR kL dt PyC r-R (TB-Too) R(t)
Bubble content • Taylor expansion on the first term – A can be derived from Clausius-Clapeyron relation • Determine – First step: heat diffusion equation, relates – Second step: energy balance, relates

Bubble content However,the heat diffusion equation is hard to solve analytically Approximated solution for RT。-IB(器)),R mo-()/r盟 du -Using results from former 人) [R(x)2 dx [fR4(g)d划 It can introduce to R-P equation
Bubble content • However, the heat diffusion equation is hard to solve analytically • Approximated solution – for – Using results from former – It can introduce to R-P equation
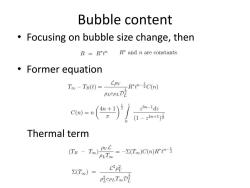
Bubble content Focusing on bubble size change,then R=Rt" R*and n are constants. 。Former equation T。-TBd=CovR--iCm) PLCPLD ca=n)产f Thermal term (Ta-T)t--(Ts )C(n) PLToo C2py ∑(T)= PiePLTooDE
Bubble content • Focusing on bubble size change, then • Former equation Thermal term
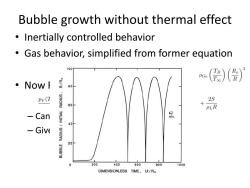
Bubble growth without thermal effect Inertially controlled behavior Gas behavior,simplified from former equation 100 ()() ·NoWf 80 Pv(1 2S 60 PLR Can etc. 40 -Give 20- 0 200 400 600 800 1000 DIMENSIONLESS TIME,U/R
Bubble growth without thermal effect • Inertially controlled behavior • Gas behavior, simplified from former equation • Now R-P equation – Can be solved numerically – Given constants and initial conditions
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_Chapter 3 Bubble or droplet translation.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_Chapter 2 Single particle motion.pdf
- 《可再生能源》教学资源(阅读资料)04-Tony-Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading.pdf
- 《可再生能源》教学资源(阅读资料)03-RSER2503.pdf
- 《可再生能源》教学资源(阅读资料)02-Impacts of main factors on bioethanol fermentation.pdf
- 《可再生能源》教学资源(阅读资料)01-A review of methane production.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第14讲 低温测试技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第13讲 真空技术.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12讲 低温绝热技术及低温贮运设计.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12讲 低温绝热技术及低温贮运设计.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10讲 脉管制冷机及热声低温制冷机.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第09讲 低温制冷机.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第08讲 空气分离系统.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第07讲 精馏塔的理论计算、变压吸附及膜分离.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第06讲 气体分离基础.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第05讲 气体液化(2/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第04讲 气体液化(1/2).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第03讲 低温的获得方法.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第02讲 低温材料与流体物性.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《低温原理及应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第01讲 课程介绍及低温工程导论(黄永华、王如竹).pdf
- 上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_Chapter 1 Introduction.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《多相流和传热 Multiphase flow and heat transfer》课程教学资源_多相流与传热教学大纲(中英文).doc
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Introduksjon HPPS-Summer.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Kap-3-one stage.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)NTNU - EPT - introduction.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Presentation NTNU DD program.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Refrigerants.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Refrigerants.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)Refrigeration I.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)RnLib software_NKF-2014-03-13-RnLib-Eikevik.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《heat pumping processes and systems》课程资源(教学资料)中文版NKF-2014-03-13-RnLib-Eikevik.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《汽液两相流动与传热 Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flow Boiling Heat Transfer》研究生课程PPT教学课件_第一章 两相流概述.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《制冷原理与设备》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)制冷的作用、制冷发展史、突破性的进展和挑战、制冷方式、制冷的基本热力学原理.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《生物质能源转化与利用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第3讲 生物质构建与组成.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物质能源转化与利用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第4讲 生物质燃料特性.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物质能源转化与利用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第2讲 生物质能概述.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《生物质能源转化与利用》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第1讲 能源概述(罗永浩).ppt
- 上海交通大学:《电机学 Electric Machinery》课程教学资源(GE讲义)交流电机共性问题.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电机学 Electric Machinery》课程教学资源(GE讲义)直流电机.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《电机学 Electric Machinery》课程教学资源(GE讲义)异步电机 Asynchronous Machine(AM).pdf
