《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Spectral cluster

Clustering Lecture 6:Spectral Methods Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1
Clustering Lecture 6: Spectral Methods Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1

Outline ·Basics Motivation,definition,evaluation ·Methods -Partitional Hierarchical Density-based -Mixture model -Spectral methods Advanced topics Clustering ensemble Clustering in MapReduce -Semi-supervised clustering,subspace clustering,co-clustering, etc
Outline • Basics – Motivation, definition, evaluation • Methods – Partitional – Hierarchical – Density-based – Mixture model – Spectral methods • Advanced topics – Clustering ensemble – Clustering in MapReduce – Semi-supervised clustering, subspace clustering, co-clustering, etc. 2

Motivation Complex cluster shapes - K-means performs poorly because it can only find spherical clusters Density-based approaches are sensitive to parameters 。Spectral approach Use similarity graphs to encode local neighborhood information Data points are vertices of the graph Connect points which are "close" 1.5 15 3
Motivation • Complex cluster shapes – K-means performs poorly because it can only find spherical clusters – Density-based approaches are sensitive to parameters • Spectral approach – Use similarity graphs to encode local neighborhood information – Data points are vertices of the graph – Connect points which are “close” 3 -2 -1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 -2 -1.5 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2
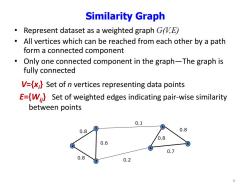
Similarity Graph Represent dataset as a weighted graph G,E) All vertices which can be reached from each other by a path form a connected component Only one connected component in the graph-The graph is fully connected V=x;}Set of n vertices representing data points E={W}Set of weighted edges indicating pair-wise similarity between points 0.1 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.6 6 0.7 0.8 3 0.2 4
0.1 0.2 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.8 E={Wij} Set of weighted edges indicating pair-wise similarity between points Similarity Graph • Represent dataset as a weighted graph G(V,E) • All vertices which can be reached from each other by a path form a connected component • Only one connected component in the graph—The graph is fully connected 1 2 6 { , ,..., } v v v 1 2 3 4 5 6 V={xi } Set of n vertices representing data points 4
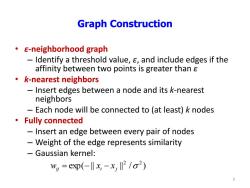
Graph Construction E-neighborhood graph Identify a threshold value,s,and include edges if the affinity between two points is greater than k-nearest neighbors Insert edges between a node and its k-nearest neighbors Each node will be connected to (at least)k nodes ·Fully connected Insert an edge between every pair of nodes Weight of the edge represents similarity -Gaussian kernel: w,=eXp(-‖x,-x,2/o2) 5
Graph Construction • ε-neighborhood graph – Identify a threshold value, ε, and include edges if the affinity between two points is greater than ε • k-nearest neighbors – Insert edges between a node and its k-nearest neighbors – Each node will be connected to (at least) k nodes • Fully connected – Insert an edge between every pair of nodes – Weight of the edge represents similarity – Gaussian kernel: exp( || || / ) 2 2 wij xi xj 5

sneighborhood Graph 。e-neighborhood Compute pairwise distance between any two objects Connect each point to all other points which have distance smaller than a threshold s Weighted or unweighted Unweighted-There is an edge if one point belongs to the &-neighborhood of another point Weighted-Transform distance to similarity and use similarity as edge weights 6
ε-neighborhood Graph • ε-neighborhood – Compute pairwise distance between any two objects – Connect each point to all other points which have distance smaller than a threshold ε • Weighted or unweighted – Unweighted—There is an edge if one point belongs to the ε–neighborhood of another point – Weighted—Transform distance to similarity and use similarity as edge weights 6

KNN Graph ·Directed graph Connect each point to its k nearest neighbors ·kNN graph Undirected graph An edge between x;and x;:There's an edge from x;to X;OR from x;to x;in the directed graph 。Mutual kNN graph Undirected graph Edge set is a subset of that in the kNN graph An edge between x;and x;:There's an edge from x;to X;AND from x;to x;in the directed graph 7
kNN Graph • Directed graph – Connect each point to its k nearest neighbors • kNN graph – Undirected graph – An edge between xi and xj : There’s an edge from xi to xj OR from xj to xi in the directed graph • Mutual kNN graph – Undirected graph – Edge set is a subset of that in the kNN graph – An edge between xi and xj : There’s an edge from xi to xj AND from xj to xi in the directed graph 7
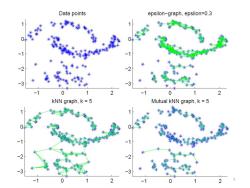
Data points epsilon-graph,epsilon=0.3 -1 -1 米 米 米 米 米 -2 -2 米 米 -3 米 米 米 -3 0 1 2 0 1 2 kNN graph,k =5 Mutual kNN graph,k =5 米 2 -3 -3 2 1 2 3
8
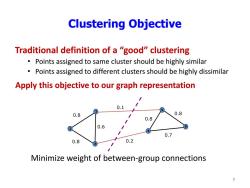
Clustering Objective Traditional definition of a "good"clustering Points assigned to same cluster should be highly similar Points assigned to different clusters should be highly dissimilar Apply this objective to our graph representation 0.1 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.6 6 0.7 0.8 0.2 Minimize weight of between-group connections 9
Clustering Objective Traditional definition of a “good” clustering • Points assigned to same cluster should be highly similar • Points assigned to different clusters should be highly dissimilar Minimize weight of between-group connections 0.1 0.2 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.8 1 2 3 4 5 6 Apply this objective to our graph representation 9

Graph Cuts Express clustering objective as a function of the edge cut of the partition Cut:Sum of weights of edges with only one vertex in each group We wants to find the minimal cut between groups C2 cut(C1,C2)=∑w C ieCl,jEC2 0.1 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.6 6 cut(C1,C2)=0.3 2 0.7 0.8 0.2 10
Graph Cuts • Express clustering objective as a function of the edge cut of the partition • Cut: Sum of weights of edges with only one vertex in each group • We wants to find the minimal cut between groups 1 2 , 1 2 ( , ) i C j C C C wij cut 0.1 0.2 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.8 0.8 1 2 3 4 5 6 0.8 cut(C1 , C2 ) = 0.3 10 C1 C2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Cluster Validation.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十讲 聚类分析.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)SVM in R.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Statistical Classification.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Least Squares Linear Discriminant Analysis.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第九讲 判别与分类.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第八讲 因子分析.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Face Recognition using PCA.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Overview - Principal component analysis.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第七讲 主成分分析.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第六讲 两均值向量的比较.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)EM algorithm.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第五讲 多元正态均值向量的推断.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)R package - mvoutlier论文.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Outlier detection.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Multiple hypothesis testing.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第四讲 多元正态(II).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第三讲 多元正态(I).pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Lattice and Other Graphics in R.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)A visual tour of interactive graphics with R.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)A tutorial on Spectral clustering.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十一讲 典型相关分析和多维标度法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十二讲 多元多重线性回归——估计.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十三讲 多元多重线性回归——检验.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Visual Hypothesis Tests in Multivariate Linear Models - Heplot.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Model selection in linear regression.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Multivariate Linear Models in R.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十四讲 多元方差分析.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Types of Sums of Squares.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)附录——矩阵代数(主讲:张伟平).pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)北师大矩阵代数讲稿.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Matrix Cook Book.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一讲 参数统计与非参数统计——回顾与简介.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Introduction Review of R.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Binomial Distribution - Hypothesis Testing, Confidence Intervals(CI), and Reliability.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)with Implementation in S-PLUS.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Association Between Variables.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Fisher's Exact Test , When to use Fisher's exact test.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Conditonal versus unconditional exact tests for comparing two binomials.pdf
- 《实用非参数统计》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Chi square test with both margins fixed.pdf
