《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Multiple hypothesis testing

ONTNU Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges Ingelin Steinsland ingelins@math.ntnu.no Norwegian University of Science and Technology Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.1/28
NTNUMultiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges Ingelin Steinsland ingelins@math.ntnu.no Norwegian University of Science and Technology Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.1/28

ONTNU Outline Single hypothesis testing Multiple hypothesis testing Quantities and issues 0 False discovery rates ● Future challenges .Within false discovery rates. Multiple hypothesis tests,the right tool? Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.2/28
NTNU Outline Single hypothesis testing Multiple hypothesis testing Quantities and issues False discovery rates Future challenges Within false discovery rates. Multiple hypothesis tests, the right tool? Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.2/28

ONTNU Single hypothesis testing,example Typical question:Does treatment A give the wished effect? Hypothesis: H=0:Non or negative effect. H=1:Positive effect Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.3/28
NTNU Single hypothesis testing, example Typical question: Does treatment A give the wished effect? Hypothesis: H = 0: Non or negative effect. H = 1: Positive effect Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.3/28

ONTNU Single hypothesis testing,example Typical question:Does treatment A give the wished effect? Hypothesis: I=0:Non or negative effect. H-1:Positive effect Collect data. IF the collected data is very unlikely given H=0; H=0 rejected and H=1 accepted. Treatment A has positive effect. ELSE H=0 accepted. ● Treatment A does not have significant positive effect. Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.3/28
NTNU Single hypothesis testing, example Typical question: Does treatment A give the wished effect? Hypothesis: H = 0: Non or negative effect. H = 1: Positive effect Collect data. IF the collected data is very unlikely given H = 0; H = 0 rejected and H = 1 accepted. Treatment A has positive effect. ELSE H = 0 accepted. Treatment A does not have significant positive effect. Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.3/28

ONTNU Single hypothesis testing ●Hypothesis test: pH=0:0∈曰o versus 。H=1:0∈Θ1(Θ0∩Θ1=0) Test statistics:T(X),observed t. Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.4/28
NTNU Single hypothesis testing Hypothesis test: H = 0 : θ ∈ Θ0 versus H = 1 : θ ∈ Θ1 (Θ0 ∩ Θ1 = ∅). Test statistics: T(X), observed t. Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.4/28

ONTNU Single hypothesis testing ●Hypothesis test: pH=0:0∈曰o versus 。H=1:0∈Θ1(Θ0∩Θ1=0) Test statistics:T(X),observed t. ●Rejection region:T oIft∈T reject H=O. .IftT accept H=0. Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.4/28
NTNU Single hypothesis testing Hypothesis test: H = 0 : θ ∈ Θ0 versus H = 1 : θ ∈ Θ1 (Θ0 ∩ Θ1 = ∅). Test statistics: T(X), observed t. Rejection region: Γ If t ∈ Γ reject H = 0. If t ∈/ Γ accept H = 0. Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.4/28
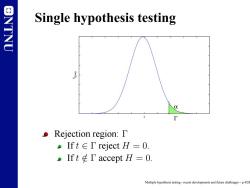
ONTNU Single hypothesis testing 0 Rejection region:D pIft∈T reject H=O. .Ift T accept H=0. Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.4/28
NTNU Single hypothesis testing Γ α f T|H=0 t Rejection region: Γ If t ∈ Γ reject H = 0. If t ∈/ Γ accept H = 0. Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.4/28
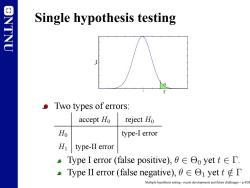
ONTNU Single hypothesis testing Two types of errors: accept Ho reject Ho Ho type-I error Hu type-II error .Type I error(false positive),θ∈yet t∈T. TypeⅡerror(false negative),O∈Θ1 yett Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.4/28
NTNU Single hypothesis testing Γ α f T|H=0 t Two types of errors: accept H0 reject H0 H0 type-I error H1 type-II error Type I error (false positive), θ ∈ Θ0 yet t ∈ Γ. Type II error (false negative), θ ∈ Θ1 yet t ∈/ Γ Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.4/28

ONTNU Single hypothesis testing Want to control type I error rate; Pr(t∈TH=0), and minimise type II error rate; Pr(tH=1). ·Power=1-Pr(tTH=1) Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.4/28
NTNU Single hypothesis testing Γ α f T|H=0 t Want to control type I error rate; Pr(t ∈ Γ|H = 0), and minimise type II error rate; Pr(t ∈/ Γ|H = 1). Power = 1 − Pr(t ∈/ Γ|H = 1). Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.4/28
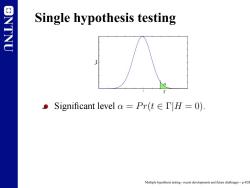
ONTNU Single hypothesis testing 。Significant level a=Pr(t∈TlH=O) Multiple hypothesis testing-recent developments and future challenges-p.4/28
NTNU Single hypothesis testing Γ α f T|H=0 t Significant level α = Pr(t ∈ Γ|H = 0). Multiple hypothesis testing - recent developments and future challenges – p.4/28
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第四讲 多元正态(II).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第三讲 多元正态(I).pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Lattice and Other Graphics in R.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)A visual tour of interactive graphics with R.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)A Survey on Multivariate Data Visualization.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)30 Years of Multidimensional Multivariate Visulization.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第二讲 多元数据的可视化技术.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第一讲 简介及描述性统计(主讲:张伟平).pdf
- 《实用统计软件》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Dan Bruns, Chattanooga, TN, An Introduction to the Simplicity and Power of SAS/Graph.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第十四讲 SAS介绍.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第十三讲 MatLab介绍(二).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第十二讲 MatLab介绍(一).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第十一讲 R中的数值优化方法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第十讲 Expectation-Maximization(EM算法)方法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第九讲 Markov Chain Monte Carlo(二)马尔科夫蒙特卡罗方法.pdf
- 《实用统计软件》课程教学资源(阅读材料)A History of Markov Chain Monte Carlo——Subjective Recollections from Incomplete Data.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第八讲 Markov Chain Monte Carlo(一)马尔科夫蒙特卡罗方法.pdf
- 《实用统计软件》课程教学资源(阅读材料)T. DiCiccio and B.Efron(1996), Bootstrap Confidence Intervals, Statistical Science, 3,189-228.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第七讲 Boostrap方法和Jackknife方法(自助和刀切).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《实用统计软件》课程课件讲义(统计计算与软件)第六讲 Monte Carlo方法在统计推断中的应用.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Outlier detection.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)R package - mvoutlier论文.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第五讲 多元正态均值向量的推断.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)EM algorithm.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第六讲 两均值向量的比较.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第七讲 主成分分析.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Overview - Principal component analysis.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Face Recognition using PCA.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第八讲 因子分析.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第九讲 判别与分类.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Least Squares Linear Discriminant Analysis.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Statistical Classification.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)SVM in R.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十讲 聚类分析.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Cluster Validation.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)Spectral cluster.pdf
- 《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(阅读材料)A tutorial on Spectral clustering.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十一讲 典型相关分析和多维标度法.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十二讲 多元多重线性回归——估计.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《多元统计分析》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第十三讲 多元多重线性回归——检验.pdf
