《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Fundamentals of Wireless Communication Chapter8 MIMO II:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures

ECS Vireless oundations 8.MIMO II:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 1
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 1 8. MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures

8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures EECS Wireless oundations Outline Transceiver architectures for fast fading (V-BLAST family) Transceiver architecture for slow fading (D-BLAST) Multiple antennas in networks:SDMA Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 2
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 2 Outline • Transceiver architectures for fast fading (V-BLAST family) • Transceiver architecture for slow fading (D-BLAST) • Multiple antennas in networks: SDMA

8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures ECS Nireless oundations Transmitter and Receiver CSI Can decompose the MIMO channel into a bunch of orthogonal sub-channels. Can allocate power and rate to each sub-channel according to waterfilling [n]) AWGN decode coder k information {wn》 streams 交nl AWGN U* In)) decoder coder (o) (o) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 3
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 3 Transmitter and Receiver CSI • Can decompose the MIMO channel into a bunch of orthogonal sub-channels. • Can allocate power and rate to each sub-channel according to waterfilling

8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures ECS Wireless oundations Analogy with OFDM x[1]=d[N-L+1] 山 xL-1]=dW-1 yL-1] d0] Cyelic x[L]=d[o] ☑ Remove yILl Channel 0 prefix prefix IDFT DFT dy-1 dN-1] x[N+L-1]=d[N-1] y[N+L-1] [N+L-1 Major difference: In MIMO,the U and V matrices depend on the channel H. In OFDM,the IDFT and DFT matrices do not. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 4 Analogy with OFDM Major difference: In MIMO, the U and V matrices depend on the channel H. In OFDM, the IDFT and DFT matrices do not

8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures vireless oundations Receiver CSI Only The channel matrix H and its singular values 2's are random and unknown to the transmitter. P AWGN coder w[m] rate R x[m] 文y[m] .... H(m] Joint decoder AWGN coder rate Rm Has to fix a Q and a power allocation independent of H. Q=I and uniform power allocation is optimal in many cases. It is not trivial to come up with capacity-achieving architectures. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 5
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 5 Receiver CSI Only The channel matrix H and its singular values i 2 's are random and unknown to the transmitter. Has to fix a Q and a power allocation independent of H. Q=I and uniform power allocation is optimal in many cases. It is not trivial to come up with capacity-achieving architectures
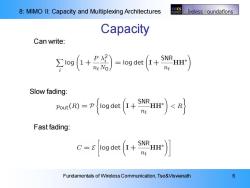
8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures EECS Wireless oundations Capacity Can write: o)-lo det) Slow fading: 0=+ur)s Fast fading: c=8+5r】 Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 6
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 6 Capacity Can write: Slow fading: Fast fading:

8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures EECS Vireless oundations Fast Fading Capacity for I.I.D.Rayleigh Fading C[bits/s/Hz]35 30 nt=nr =1 nt=1 nr=4 25 nt=nr=4 20 15 10 5 -10 10 20 30 SNR[dB] Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 7
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 7 Fast Fading Capacity for I.I.D. Rayleigh Fading

8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures CS ireless F oundations d.o.f.min(nt,nr)determines the high SNR slope. C[bits/s/Hz]35 C[bits/s/Hz】70 30 nt=nr=1 60 nt=1 nr=4 nt=nr=1 25 nt=nr=4 nt=1nr=8 nt=nr=8 20 40 15 30 10 20 5 10 -10 10 30 -10 10 20 30 SNR[dB] SNRIdB] Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 8
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 8 d.o.f. determines the high SNR slope

8:MIMO Il:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures ireless oundations Fast Fading Capacity:Low SNR n,-fold power gain at low SNR [bits/s/Hz] 4 3.5 nt=1n,=4 nt=n=4 .5 -30 -20 -10 、10 SNR[dB] Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 9
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 9 Fast Fading Capacity: Low SNR nr – fold power gain at low SNR

8:MIMO II:Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures ECS ireless oundations Nature of Performance Gain At high SNR (d.o.f.limited):min(nt,n,)-fold d.o.f.gain MIMO is crucial. At low SNR(power limited):n,-fold power gain.Only need multiple receive antennas. At all SNR,min(nt,n,)-fold gain due to a combination of both effects. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 10
8: MIMO II: Capacity and Multiplexing Architectures Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 10 Nature of Performance Gain • At high SNR (d.o.f. limited): min(nt ,nr )-fold d.o.f. gain. MIMO is crucial. • At low SNR (power limited): nr -fold power gain. Only need multiple receive antennas. • At all SNR, min(nt ,nr )-fold gain due to a combination of both effects
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Fundamentals of Wireless Communication Chapter6 Opportunistic Communication and Multiuser Diversity.ppt
- 《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Fundamentals of Wireless Communication Chapter5 Capacity of Wireless Channels.ppt
- 《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Fundamentals of Wireless Communication Chapter4 Cellular Systems:Multiple Access and Interference Management.ppt
- 《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Fundamentals of Wireless Communication Chapter3 Diversity.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 9 多用户MIMO.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 8 多天线分集复用折中.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 7 MIMO容量与多天线复用技术.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 6 MIMO信道模型.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 5 多用户容量和机会通信.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 4 衰落信道容量.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 3 蜂窝系统与干扰分集.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 2-3 频率分集技术.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 2-2 空间分集技术.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 2-1 时间分集技术.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(教案讲义)Lecture 1 信道模型(主讲:郑贱平).pdf
- 《无线通信理论》课程教学资源(参考教材)Fundamentals of Wireless Communication(英文版,共八部分).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《信号检测与估值》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,2019)第四章 波形信号检测.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《信号检测与估值》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,2019)第三章 统计信号估计(主讲:郑贱平).pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《信号检测与估值》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,2019)第二章 衰落信道上的信号检测.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《信号检测与估值》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,2019)第一章 高斯信道上的信号检测.pdf
- 安徽医科大学:《单片机原理与应用》课程教学大纲(生物医学工程专业)Application and principle of single chip microcomputer.pdf
- 西门子PLC培训教程(课件讲稿,共六章).pdf
- 电子电路分析制作与调试(PPT课件讲稿)直流可调稳压电源制作与调试.pdf
- 信阳师范大学(信阳师范学院):电子信息工程专业培养方案(2019版).pdf
- 信阳师范大学(信阳师范学院):电子科学与技术专业培养方案(2019版).pdf
- 信阳师范大学(信阳师范学院):电子信息工程专业课程教学大纲汇编(2015版).doc
- 信阳师范大学(信阳师范学院):电子科学与技术专业课程教学大纲汇编(2015版).doc
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)《模拟电子线路》实验讲义(共十一个实验).pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)数字钟电路图.pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)多功能数字钟电路设计《数字电子技术》课程设计指导.pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)《电子技术基础实验》设计性实验报告范例.pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)《数字信号处理》实验指导书.pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)《PLC原理与应用》实验课程讲义(PLC实验指导讲义S7-200,共十一个实验).pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)三人表决电路.pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)《数字电子技术基础实验》讲义——集成单稳态触发的基本应用.pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)TFG1900A系列函数/任意波形发生器使用指南.pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)数字存储示波器GDS-1000A-U示波器使用手册.pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)《自动控制理论》实验指导书(共十一个实验).pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)《微型计算机原理及应用》实验讲义(共六个实验).pdf
- 信阳师范大学:《电工电子》课程教学资源(实验讲义,打印版)《模拟电子线路》实验讲义(共十一个实验).pdf
