北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-6

Part A.Answer all eight questions(5 marks each). 1.Why is Ka2Pb(ag)(1 M)+2 e.The reduction is Pb()(2 M)+2 e Pb(s).The overall reaction is therefore Pb(2 M)Pb(1 M).For this reaction,Q==0.5.According to the Nernst cquation,EER().Since Q1 In(Q)and so E>E,But since 0 nF 7.Melting ice is an endothermic process.Why is it spontaneous? Because the process has a positive entropy change. 8.For the reaction H2O=HO initially at equilibrium,which direction will the equilibrium shift (left or right)if the pressure is increased? 1
Part A. Answer all eight questions (5 marks each). 1. Why is Ka2 Eo , But since Eo = 0, E > 0 7. Melting ice is an endothermic process. Why is it spontaneous? Because the process has a positive entropy change. 8. For the reaction H2O(l) = H2O(g) initially at equilibrium, which direction will the equilibrium shift (left or right) if the pressure is increased? 1

Left(so as to decrease the pressure as per le Chatelier's principle). Part B.Answer any five of the eight questions(CI-C8).If you answer more than five,the best five will be used to calculate your mark (20 marks each). B1.(a)Aluminum metal is produced by the reduction of aluminum ions in a molten solution according to Al+3eAl What mass of aluminum metal can be produced using a current of 100,000 A over a period of8 hours? t105C1s(8hx3600sh-=29,849mole n-F 96487C(mol e-)-1 but each mole of Al requires 3 moles of the electrons to be reduced to the metal.Thus,the number of moles of Al produced in this time is 29.849/3=9950 moles Als Mass Al(s)27.0 g mol"x 9950 mol 2.69 x 105g=269 kg B1.(b)For the galvanic reaction+CZnCa 50C.calculate the cell potential (in Volts)if [Cd"]=0.068 M and [Zn]=1.00 M. E°=-0.40V+0.76V=+0.36V Q=IZn"1.00M ICd10.069M=14.7 T=50℃+273=323K E=Er-Rno=038v.8aaenCg23 2(96487Cmo') =0.32V 2
Left (so as to decrease the pressure as per le Chatelier’s principle). Part B. Answer any five of the eight questions (C1 – C8). If you answer more than five, the best five will be used to calculate your mark (20 marks each). B1. (a) Aluminum metal is produced by the reduction of aluminum ions in a molten solution according to Al+3 (l) + 3 e⎯ → Al(l). What mass of aluminum metal can be produced using a current of 100,000 A over a period of 8 hours? 5 1 1 it 10 C/ s(8h 3600sh ) n 2 F 96487C(mol e ) − 9,849 mol e− − − × = = = but each mole of Al+3 requires 3 moles of the electrons to be reduced to the metal. Thus, the number of moles of Al(s) produced in this time is 29,849 / 3 = 9950 moles Al(s). Mass Al(s) = 27.0 g mol-1 x 9950 mol = 2.69 x 105 g = 269 kg B1. (b) For the galvanic reaction Zn(s) + Cd+2 (aq) → Zn+2 (aq) + Cd(s) at 50o C, calculate the cell potential (in Volts) if [Cd+2 (aq)] = 0.068 M and [Zn+2 (aq)] = 1.00 M. Eo = -0.40 V + 0.76 V = +0.36 V 2 (aq) 2 (aq) [Zn ] 1.00M Q 1 [Cd ] 0.068M + + = == 4.7 T = 50o C + 273 = 323 K 1 1 o 1 RT 8.314JK mol (323K) E E ln(Q) 0.36V nF 2(96487C mol ) 0.32 V − − − =− = − = 2
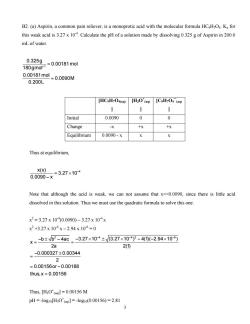
B2.(a)Aspirin,a common pain reliever,is a monoprotic acid with the molecular formula HCHO.K for this weak acid is 3.27x 104 Calculate the pH of a solution made by dissolving 0.325 g of Aspirin in 200.0 mL of water. 0.325g =0.00181mol 180gmol-1 0.00181mol =0.0090M 0.200L Initial 0.0090 0 0 Change +X Equilibrium 0.0090.X Thus at equilibrium, x(x) =3.27×10 0.0090-× Note that although the acid is weak.we can not assume that x<<00090.since there is little acid dissolved in this solution.Thus we must use the quadratic formula to solve this one x2=3.27x10(0.0090)-3.27x104x x2+3.27x104x-2.94x106=0 ×=-b±B2-490-3.27x10-±327×10y-40-2.94×10可 2a 2(① -0.000327±0.00344 =0.001560r-0.00188 thus,×=0.00156 Thus,[H3O'(]=0.00156 M pH=-log1o[H30a=-log10(0.00156)=2.81
B2. (a) Aspirin, a common pain reliever, is a monoprotic acid with the molecular formula HC9H7O4. Ka for this weak acid is 3.27 x 10-4. Calculate the pH of a solution made by dissolving 0.325 g of Aspirin in 200.0 mL of water. 1 0.325g 0.00181mol 180gmol 0.00181mol 0.0090M 0.200L − = = [HC9H7O4(aq) ] [H3O+ (aq) ] [C9H7O4¯(aq) ] Initial 0.0090 0 0 Change -x +x +x Equilibrium 0.0090 - x x x Thus at equilibrium, x(x) 4 3.27 10 0.0090 x − = × − Note that although the acid is weak, we can not assume that x<<0.0090, since there is little acid dissolved in this solution. Thus we must use the quadratic formula to solve this one. x 2 = 3.27 x 10-4(0.0090) – 3.27 x 10-4 x x 2 +3.27 x 10-4 x – 2.94 x 10-6 = 0 2 4 4 2 b b 4ac 3.27 10 (3.27 10 ) 4(1)( 2.94 10 ) x 2a 2(1) 0.000327 0.00344 2 0.00156or 0.00188 thus,x 0.00156 − − −± − −×± × −−× = = − ± = = − = −6 Thus, [H3O+ (aq)] = 0.00156 M pH = -log10[H3O+ (aq)] = -log10(0.00156) = 2.81 3

B2.(b)Calculate the pH of a basic buffer made by dissolving 0.125 moles of NHCls and 0.25 moles of NH)in 500 mL of water.Ko for NH)is 1.8 x 10 pK=14-pKb=14-(log1o(K)=14-(log101.8x10=9.25 [acid][NH"(ag)]=0.125 mol /0.5 L=0.25 M [base]=[NH3()=0.25 mol /0.5 L=0.50 M pH=k-loans明-925-log.25-955 B3.Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of strontium carbonate,SrCOs given the following data: Srg+%02e→Sr0g △H°=-592 kJ mol SrC03s→SrOs+C02gl △H°=+234 kJmol C(onpe)+02g→C0e AH=-394 kJ mol The reaction whose enthalpy we want is S+C+1.This reaction is obtained by adding the above reactions as follows: Srs+hO2g→SrOs △H°=-592 kJ mol" C(gaphite))+O2g)→CO2g △H°=-394 kJmol SrOs+CO2g→SrCO3s △H°=-(+234kmo) Srg+C(graphite)+1.502g→SrC03g△H°=(←592-394-234)=-1220 kJmol
B2. (b) Calculate the pH of a basic buffer made by dissolving 0.125 moles of NH4Cl(s) and 0.25 moles of NH3(aq) in 500 mL of water. Kb for NH3(aq) is 1.8 x 10-5. pKa = 14 – pKb = 14 – (-log10(Ka) = 14 – (-log10(1.8 x 10-5) = 9.25 [acid] = [NH4 + (aq)] = 0.125 mol / 0.5 L = 0.25 M [base] = [NH3(aq)] = 0.25 mol / 0.5 L = 0.50 M a 10 10 [acid] .25 pH pK log 9.25 log 9.55 [base] .5 =− = − = B3. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of strontium carbonate, SrCO3(s) given the following data: Sr(s) + ½ O2(g) → SrO(s) ΔHo = −592 kJ mol-1 SrCO3(s) → SrO(s) + CO2(g) ΔHo = +234 kJ mol-1 C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔHo = −394 kJ mol-1 The reaction whose enthalpy we want is Sr(s) + C(graphite) + 1.5 O2(g) → SrCO3(s). This reaction is obtained by adding the above reactions as follows: Sr(s) + ½ O2(g) → SrO(s) ΔHo = −592 kJ mol-1 C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔHo = −394 kJ mol-1 SrO(s) + CO2(g) → SrCO3(s) ΔHo = − (+234 kJ mol-1) ________________________________________________ Sr(s) + C(graphite) + 1.5 O2(g) → SrCO3(s) ΔHo = (– 592 – 394 – 234) = – 1220 kJ mol-1 4

B4.Use the data below to calculate the equilibrium constant at 1000 K for the reaction 2Hlg)→H2e+l2e △H°kJmo) S(J mol) 26.5 206.6 H2xg) 0.0 130.6 12g0 62.4 260.7 △H°=△H'Hg)+△HI2g)-2△H'(Hg) =0+62.4-2(26.5)=9.4 kJ mol △S°=△Sr'Hg)+△SrL2g)-2△Sr'Hlg) =130.6+260.7-2(206.6)=-21.9JKmo △G°=△H°.TAS9 =9400-1000(-21.9=+31,300Jmor K-d0.em0023 (b)If p=0.002 atm at equilibrium,calculate Pe and pr2. PnP=0.023 P p,P,=0.023p=0.023(0.002atm)2=9.27×10-8atm Thus,p4,=P2=(9.27×108atm2)v2=3.04×10atm B5.(a)What hybridization is each of the four indicated atoms using in the molecule of Aspirin shown below? 5
B4. Use the data below to calculate the equilibrium constant at 1000 K for the reaction 2 HI(g) → H2(g) + I2(g) ΔHf o (kJ mol-1) So (J mol-1) HI(g) 26.5 206.6 H2(g) 0.0 130.6 I2(g) 62.4 260.7 ΔHo = ΔHf 0 (H2(g)) + ΔHf 0 (I2(g)) – 2 ΔHf 0 (HI(g)) = 0 + 62.4 – 2(26.5) = 9.4 kJ mol-1 ΔSo = ΔSf 0 (H2(g)) + ΔSf 0 (I2(g)) – 2 ΔSf 0 (HI(g)) = 130.6 + 260.7 – 2(206.6) = –21.9 J K-1 mol-1 ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo = 9400 – 1000(-21.9) = +31,300 J mol-1 0 1 1 1 G 31300 Jmol RT 8.314 JK mol (1000K) Ke e 0.023 − − − ⎡⎤ ⎡ −Δ − ⎤ ⎢⎥ ⎢ ⎥ ⎢⎥ ⎢ ⎣⎦ ⎣ ⎥⎦ == = (b) If pHI = 0.002 atm at equilibrium, calculate pH2 and pI2. 2 2 2 2 H I 2 HI 2 2 H I HI p p 0.023 p p p 0.023p 0.023(0.002atm) 9.27 10 atm − = = = =× 8 2 Thus, 2 2 8 2 1/ 2 4 p p (9.27 10 atm ) 3.04 10 atm H I − − == × = × B5. (a) What hybridization is each of the four indicated atoms using in the molecule of Aspirin shown below? 5
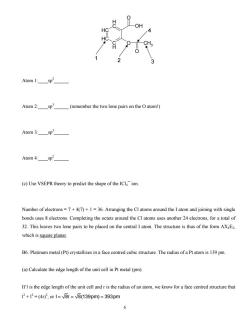
Atom 1:sp2 Atom 2:sp3(remember the two lone pairs on the O atom!) Atom 3:sp Atom 4:sp2 (c)Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the IClion. Number of electrons=7+4(7)+1=36.Arranging the Cl atoms around the I atom and joining with single bonds uses8 electrons.Completing the octets around the Cl atoms uses another 24 electrons,for a total of 32.This leaves two lone pairs to be placed on the central I atom.The structure is thus of the form AXE which is square planar B6.Platinum metal (Pt)crystallizes in a face centred cubic structure.The radius of a Pt atom is 139 pm. (a)Calculate the edge length of the unit cell in Pt metal (pm). If I is the edge length of the unit cell and r is the radius of an atom.we know for a face centred structure tha 12+2=(42,or1=V8r=V8(139pm)=393pm 6
O 6 Atom 1:____sp2 ______ Atom 2:____sp3 ______ (remember the two lone pairs on the O atom!) Atom 3:____sp3 ______ Atom 4:____sp2 ______ (c) Use VSEPR theory to predict the shape of the ICl4¯ ion. Number of electrons = 7 + 4(7) + 1 = 36. Arranging the Cl atoms around the I atom and joining with single bonds uses 8 electrons. Completing the octets around the Cl atoms uses another 24 electrons, for a total of 32. This leaves two lone pairs to be placed on the central I atom. The structure is thus of the form AX4E2, which is square planar. B6. Platinum metal (Pt) crystallizes in a face centred cubic structure. The radius of a Pt atom is 139 pm. (a) Calculate the edge length of the unit cell in Pt metal (pm). If l is the edge length of the unit cell and r is the radius of an atom, we know for a face centred structure that l 2 + l2 = (4r)2 , or l 8r 8(139pm) 393pm == = CH CH C H C H OH O CH3 O 1 2 3 4

(b)Calculate the density of Pt metal(g cm). 195.1gmor1 p= mass 4602x180moF volume (393×10-10cm) =21.4gcm3 7
(b) Calculate the density of Pt metal (g cm-3). 1 23 1 3 10 3 195.1gmol 4 mass 6.02 10 mol 21.4gcm volume (393 10 cm) − − − − ⎛ ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠ × ρ= = = × 7
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-5.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-4.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-3.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-2.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-1.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学(双语)期末考试模拟试卷-B-试题.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学(双语)期末考试模拟试卷-B-答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学(双语)期末考试模拟试卷-A-答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学(双语)期中考试模拟试卷-B-试题.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学(双语)期中考试模拟试卷-B-答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学(双语)期末考试模拟试卷-A-试题.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学(双语)期中考试试卷-A-试题.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学(双语)期中考试试卷-A-答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)期末模拟题(含答案).doc
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)无机化学考试卷模拟和部分答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)期末模拟题——2015-2016学年第二学期课程考试试卷答案(C卷).doc
- 《无机化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)09 物质的颜色与结构的关系.pdf
- 《无机化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)08 五种常见装饰植物对甲醛的吸收能力比较研究.pdf
- 《无机化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)07 室内空气污染的危害及其防治措施研究.pdf
- 《无机化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)06 人工消雨方法.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-7.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-10.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-8.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)自测题及答案-9.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)作业习题(中英文)安排及部分答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第三章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第二章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第五章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第六章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第四章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第七章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第九章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第八章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十一章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十三章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十二章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十四章自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十三-十四章综合自我练习题及答案.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《无机化学》课程电子教案(试卷习题)第十五章自我练习题及答案.pdf
