佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第2章 血液 BLOOD

Chapter3 BLOOD 1.Components and properties of blood 2.Plasma 3.Physiology of blood cells 4.Hemostasis and Blood coagulation 5.Blood Group
Chapter3 BLOOD 1.Components and properties of blood 3. Physiology of blood cells 4.Hemostasis and Blood coagulation 2.Plasma 5. Blood Group
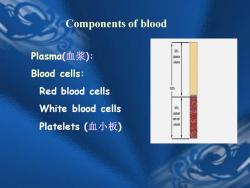
Components of blood Plasma(血浆) e Blood cells: Red blood cells 100% White blood cells 4 Platelets(血小板) voimne
Components of blood Plasma(血浆): Blood cells: Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets (血小板)
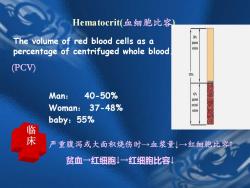
Hematocrit(血细胞比容) The volume of red blood cells as a 然 阳 percentage of centrifuged whole blood volume (PCV) 103 Man: 40-50% Woman: 37-48% baby:55% 案 严重腹泻或大面积烧伤时→血浆量↓→红细胞比容 贫血→红细胞↓→红细胞比容
(PCV) Man: 40-50% Woman: 37-48% baby:55% 临 床 严重腹泻或大面积烧伤时→血浆量↓→红细胞比容↑ 贫血→红细胞↓→红细胞比容↓ The volume of red blood cells as a percentage of centrifuged whole blood. Hematocrit(血细胞比容)

Serum After the clot forms,it retracts, extruding fluid Serum The difference between plasma and serum: Clot retracts absence of fibrinogen and clotting from sides factors in serum
The difference between plasma and serum: absence of fibrinogen and clotting factors in serum Serum After the clot forms, it retracts, extruding fluid

Physical &Chemical properties of blood (1)Specific gravity(比重): depending on hematocrit and protein composition. Vhole:1.05~1.06 plasma:1.025~1.035 red blood cells:1.090 (②)Viscosity(血液的粘滞性) 液体流动时,由于液体分子间相互碰撞磨擦而产 生阻力,以致流动缓慢并表现粘着的特性
(2) Viscosity(血液的粘滞性) 液体流动时,由于液体分子间相互碰撞磨擦而产 生阻力,以致流动缓慢并表现粘着的特性。 Physical &Chemical properties of blood (1)Specific gravity(比重): depending on hematocrit and protein composition. Whole: 1.05~1.06 plasma: 1.025~1.035 red blood cells: 1.090

(3)Osmotic Pressure(渗透压): 溶质具有吸引水分子透过半透膜的力量 The osmotic pressure of a solution depends on the number of solute particles in the solution,not on there chemical composition and size. classification Crystalloid osmotic pressure(晶体渗透压):pressure generated by all crystal substances,particularly electrolytes.770KPa Colloid osmotic pressure(胶体渗透压):pressure generated by plasma proteins,particularly albumin
溶质具有吸引水分子透过半透膜的力量 The osmotic pressure of a solution depends on the number of solute particles in the solution, not on there chemical composition and size. classification: Crystalloid osmotic pressure(晶体渗透压): pressure generated by all crystal substances, particularly electrolytes. 770KPa (3)Osmotic Pressure(渗透压): Colloid osmotic pressure(胶体渗透压): pressure generated by plasma proteins, particularly albumin
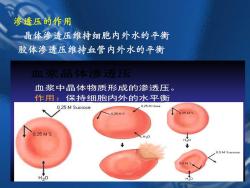
渗透压的作用 晶体渗透压维持细胞内外水的平衡 胶体渗透压维持血管内外水的平衡 血浆晶体渗透压 血浆中晶体物质形成的参透压。 作用:保持细胞内外的水平衡衡 0.25 M Sucrose 0.25 M Urea .0.25MS 0.25MS 0.25Ms H20 0.5 M Sucrose 0.5MS H20 H20
渗透压的作用 晶体渗透压维持细胞内外水的平衡 胶体渗透压维持血管内外水的平衡 血浆晶体渗透压 血浆中晶体物质形成的渗透压。 作用:保持细胞内外的水平衡

(4)pH Normal range:pH7.35~7.45 pH7.45=碱中毒; pH7.8,危及生命。 Buffer system: 红细胞缓冲对:KHb/HHb,KHbO2/HHbO2 血浆缓冲对:NaHC03/H2CO3,Na2 HPO NaH2PO4, 蛋白质钠盐/蛋白质
(4)pH Normal range:pH为7.35~7.45• pH7.45=碱中毒; pH7.8,危及生命。 Buffer system: 红细胞缓冲对:KHb/HHb, KHbO2 /HHbO2 血浆缓冲对:NaHC03/H2CO3 , Na2HPO4NaH2PO4, 蛋白质钠盐/蛋白质

Function of blood (1)Transportation 02 and CO2 Nutrients(glucose,amino acid,lipids ,etc) Waste products Hormones (2)Nutrient (3)Regulation Ph;temperature (4)Protection Blood coagulation;immunity
Function of blood (1)Transportation O2 and CO2 Nutrients(glucose,amino acid,lipids ,etc) Waste products Hormones (2) Nutrient (3)Regulation Ph;temperature (4)Protection Blood coagulation; immunity

Plasm(血浆) Composition: Water:90~92%, Proteins:6~8% Inorganic constituents(无机盐):1% Nutrients:glucose amino acid lipids ,vit Waste products: Dissolved gas:02 &CO2 Hormones
Composition: Water: 90~92%, Proteins:6~8% Inorganic constituents(无机盐):1% Nutrients:glucose amino acid lipids ,vit Waste products: Dissolved gas:O2 &CO2 Hormones Plasm(血浆)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第1章 细胞生理 Cellular physiology.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第9章 神经系统.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第8章 肌肉.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第7章 泌尿.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第6章 能量代谢与体温(体温及其调节).ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第5章 消化与吸收 Digestion and Absorption.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第4章 呼吸 Respiration.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第3章 循环生理(血液循环 Blood circulation).ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第12章 泌乳.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第11章 繁殖.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第10章 内分泌.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第2章 血液.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)第1章 细胞生理 Cellular physiology.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,中文版)绪论 Animal physiology(主讲:王丙云).ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(授课教案,英文版)第12章 泌乳.doc
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(授课教案,英文版)第11章 繁殖.doc
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(授课教案,英文版)第9章 神经系统.doc
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(授课教案,英文版)第10章 内分泌.doc
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(授课教案,英文版)第8章 肌肉.doc
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(授课教案,英文版)第7章 泌尿.doc
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第3章 循环生理(血液循环 Blood Circulation).ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第4章 呼吸 Respiration.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第5章 消化与吸收 Digestion and Absorption.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第6章 能量代谢与体温 Energy Metabolism and Body Temperature.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)绪论 Animal physiology.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第10章 内分泌 Endocrine.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第11章 繁殖 Reproduction.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第12章 泌乳 Lactation.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第7章 泌尿 Urine.ppt
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):《动物生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件,英文版)第8章 肌肉 Muscle Contraction.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)绪论.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第一章 生物的进化.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第二章 家畜的生长发育.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第七章 选配体系(关于选配).ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第三章 家畜的外形体质与生产力.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第九章 繁育体系.ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第五章 选择基础理论(关于数量遗传学).ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第五章 选择基础理论(质量性状选择方法).ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第五章 选择基础理论(关于选择).ppt
- 甘肃农业大学:《动物育种学》课程PPT教学课件(家畜育种学)第八章 品种、品种资源保存及引种.ppt
