同济大学:《工程材料》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Phase diagrams

190 悠 、O入VIW1VE农、 Chapter 5.Phase diagrams ”大餐横城工置部 w SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Chapter 5. Phase diagrams

190> Exercises 1.Define (a)phase in a material and (b)a phase diagram. 2.Write the equation for Gibbs phase rule and define each of the terms 3.What are the four Hume-rothery rules for the solid solubility of one element in another 4.Cite three variables that determine the microstructure of an alloy 5.What thermodynamic condition must be met for a state of equilibrium to exit 6.What is the difference between the states of phase equilibrium and metastability SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Exercises 1. Define (a) phase in a material and (b) a phase diagram. 2. Write the equation for Gibbs phase rule and define each of the terms 3. What are the four Hume-rothery rules for the solid solubility of one element in another 4. Cite three variables that determine the microstructure of an alloy 5. What thermodynamic condition must be met for a state of equilibrium to exit 6. What is the difference between the states of phase equilibrium and metastability

190习 TONGJI UNIVER、 Component structure property forming processing performance SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Component & structure forming & processing performance property

190> OUTLINE 1.Definition and basic concepts 2.The interpretation of diagram 3.The study of a development phase diagram 4.Study of a binary alloy phase diagram SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS OUTLINE 1. Definition and basic concepts 2. The interpretation of diagram 3. The study of a development phase diagram 4. Study of a binary alloy phase diagram

190> 5.1 Definitions Components:pure metals and/or compounds of which an alloy is composed. "system":a specific body of material under consideration.Or it may relate to the series of possible alloys consisting of the same compounds,but without regard to alloy composition. "Solvent"represents the element or compound that in the greatest amount(host atoms,host material). "Solute"is used to denote an element or compound present in a minor concentration. Solid solution SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS 5.1 Definitions Components: pure metals and/or compounds of which an alloy is composed. “system” : a specific body of material under consideration. Or it may relate to the series of possible alloys consisting of the same compounds, but without regard to alloy composition. “Solvent” represents the element or compound that in the greatest amount( host atoms, host material). ”Solute” is used to denote an element or compound present in a minor concentration. Solid solution
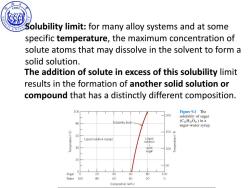
190> olubility limit:for many alloy systems and at some specific temperature,the maximum concentration of solute atoms that may dissolve in the solvent to form a solid solution. The addition of solute in excess of this solubility limit results in the formation of another solid solution or compound that has a distinctly different composition. 100 Figure 9.1 The 200 solubility of sugar Solubility limit (CnH22On)in a 80 sugar-water syrup. 60 560 Liquid solution (syrup) Liquld solution + 40 solid 100 sugar 20 50 Sugar 0 20 40 60 80 100 Water 100 80 60 40 20 0 Composition (wt%)
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Solubility limit: for many alloy systems and at some specific temperature, the maximum concentration of solute atoms that may dissolve in the solvent to form a solid solution. The addition of solute in excess of this solubility limit results in the formation of another solid solution or compound that has a distinctly different composition

190 A phase may be defined as a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristics. A phase can consider to be a pure material,but a pure material may contain two or phases. Monophase system “homogeneous'” Multiphase system "heterogeneous"or "mixture" SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS A phase may be defined as a homogeneous portion of a system that has uniform physical and chemical characteristics. Monophase system “homogeneous” Multiphase system “heterogeneous” or “mixture” A phase can consider to be a pure material, but a pure material may contain two or phases
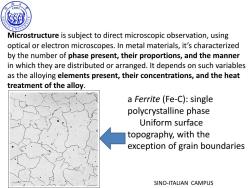
190> G Microstructure is subject to direct microscopic observation,using optical or electron microscopes.In metal materials,it's characterized by the number of phase present,their proportions,and the manner in which they are distributed or arranged.It depends on such variables as the alloying elements present,their concentrations,and the heat treatment of the alloy. a Ferrite (Fe-C):single polycrystalline phase Uniform surface topography,with the exception of grain boundaries SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Microstructure is subject to direct microscopic observation, using optical or electron microscopes. In metal materials, it’s characterized by the number of phase present, their proportions, and the manner in which they are distributed or arranged. It depends on such variables as the alloying elements present, their concentrations, and the heat treatment of the alloy. a Ferrite (Fe-C): single polycrystalline phase Uniform surface topography, with the exception of grain boundaries

190> Equilibrium is another essential concept and connected with the free energy(or entropy). free energy:function of the internal energy of a system,and also the randomness or disorder of the atoms or molecules.A system is at equilibrium if its free energy is at minimum under some specified combination of temperature,pressure,and composition. The term phase equilibrium refers to equilibrium as it applies to systems in which more than one phase may exist. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Equilibrium is another essential concept and connected with the free energy(or entropy). free energy: function of the internal energy of a system, and also the randomness or disorder of the atoms or molecules. A system is at equilibrium if its free energy is at minimum under some specified combination of temperature, pressure, and composition. The term phase equilibrium refers to equilibrium as it applies to systems in which more than one phase may exist

190> Nonequilibrium or metastable state:a state of equilibrium is never completely achieved because the rate of approach to equilibrium is extremely slow; A metastable state or microstructure may persist indefinitely experiencing only extremely slight and almost imperceptible changes as time progresses.Often,metastable structures are of more practical significance than equilibrium ones. For example,some steel and aluminum alloys rely for their strength on the development of metastable microstructures during carefully designed heat treatments SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Nonequilibrium or metastable state: a state of equilibrium is never completely achieved because the rate of approach to equilibrium is extremely slow; A metastable state or microstructure may persist indefinitely, experiencing only extremely slight and almost imperceptible changes as time progresses. Often, metastable structures are of more practical significance than equilibrium ones. For example, some steel and aluminum alloys rely for their strength on the development of metastable microstructures during carefully designed heat treatments
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 同济大学:《工程材料》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 5 Material Physical Properties.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程材料》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 4 材料特性 Material properties.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程材料》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Defect in Crystals.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程材料》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Material and Structure.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程材料》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Introduction to Engineering Material(负责人:杨玉娟).pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 12 Ideal Gas Mixture and Psychrometric Applications.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 10 Refrigeration and Heat Pump Systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 9 Gas Power Systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 8 Vapor Power Systems.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 6 Using Entropy.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 5 The Second Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 4 Control Volume Analysis.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 3 Evaluating Properties.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 2 Energy First Law of Thermodynamics.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程热力学》课程电子教案(讲稿)Chapter 1 Getting Started - Introductory Concepts and Definitions(负责人:高乃平).pdf
- 北京化工大学:《材料导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Module9 Professional Paper Writing in English.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《材料导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Module8 Presentation Skill.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《材料导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Module7 Composites.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《材料导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Module6 Ceramic Materials.pdf
- 北京化工大学:《材料导论》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Module5 Polymeric Materials.pdf
- 同济大学:《工程材料》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)Chapter 7 Fe-C Alloy.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)00 Introduction(Why are 3-D textile technologies applied to composite materials?).pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)01 3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)02 3-D textile reinforced composites for the transportation industry.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)03 Mechanical modelling of solid woven fabric composites.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)04 Macromechanical analysis of 3-D textile reinforced composites.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)05 Manufacture and design of composite grids.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)06 Knitted fabric composites.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)07 Braided structures.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)08 3-D forming of continuous fibre reinforcements for composites.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)09 Resin impregnation and prediction of fabric properties.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)Index.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials)3-D textile reinforcements in composite materials.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程教学资源(书籍文献)Microstructural Design of Fiber Composites.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(Composite materials design and applications)01 COMPOSITE MATERIALS, INTEREST, AND PROPERTIES.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(Composite materials design and applications)02 FABRICATION PROCESSES.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(Composite materials design and applications)03 PLY PROPERTIES.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(Composite materials design and applications)04 SANDWICH STRUCTURES.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(Composite materials design and applications)05 CONCEPTION AND DESIGN.pdf
- 《纺织复合材料》课程参考文献(Composite materials design and applications)06 JOINING AND ASSEMBLY.pdf
