《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 Indexing and Hashing

Chapter 12:Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B+-Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition in SQL Multiple-Key Access Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.2 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Chapter 12: Indexing and Hashing Basic Concepts Ordered Indices B+-Tree Index Files B-Tree Index Files Static Hashing Dynamic Hashing Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hashing Index Definition in SQL Multiple-Key Access

Basic Concepts Indexing mechanisms used to speed up access to desired data. E.g.,author catalog in library Search Key-attribute to set of attributes used to look up records in a file. An index file consists of records(called index entries)of the form search-key pointer Index files are typically much smaller than the original file Two basic kinds of indices: Ordered indices:search keys are stored in sorted order Hash indices:search keys are distributed uniformly across “buckets”using a“nash function". Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.3 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Basic Concepts Indexing mechanisms used to speed up access to desired data. E.g., author catalog in library Search Key - attribute to set of attributes used to look up records in a file. An index file consists of records (called index entries) of the form Index files are typically much smaller than the original file Two basic kinds of indices: Ordered indices: search keys are stored in sorted order Hash indices: search keys are distributed uniformly across “buckets” using a “hash function”. search-key pointer

Index Evaluation Metrics Access types supported efficiently.E.g., records with a specified value in the attribute or records with an attribute value falling in a specified range of values. Access time Insertion time Deletion time Space overhead Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.4 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Index Evaluation Metrics Access types supported efficiently. E.g., records with a specified value in the attribute or records with an attribute value falling in a specified range of values. Access time Insertion time Deletion time Space overhead

Ordered Indices In an ordered index,index entries are stored sorted on the search key value.E.g.,author catalog in library. Primary index:in a sequentially ordered file,the index whose search key specifies the sequential order of the file. Also called clustering index The search key of a primary index is usually but not necessarily the primary key. Secondary index:an index whose search key specifies an order different from the sequential order of the file.Also called non-clustering index. Index-sequential file:ordered sequential file with a primary index. Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Ordered Indices In an ordered index, index entries are stored sorted on the search key value. E.g., author catalog in library. Primary index: in a sequentially ordered file, the index whose search key specifies the sequential order of the file. Also called clustering index The search key of a primary index is usually but not necessarily the primary key. Secondary index: an index whose search key specifies an order different from the sequential order of the file. Also called non-clustering index. Index-sequential file: ordered sequential file with a primary index

Dense Index Files Dense index-Index record appears for every search-key value in the file. E.g.index on ID attribute of instructorrelation 10101 10101 Srinivasan Comp.Sci. 65000 12121 12121 Wu Finance 90000 15151 15151 Mozart Music 40000 22222 22222 Einstein Physics 95000 32343 32343 El Said History 60000 33456 33456 Gold Physics 87000 45565 45565 Katz Comp.Sci. 75000 58583 58583 Califieri History 62000 76543 76543 Singh Finance 80000 76766 76766 Crick Biology 72000 83821 83821 Brandt Comp.Sci. 92000 98345 98345 Kim Elec.Eng. 80000 Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Dense Index Files Dense index — Index record appears for every search-key value in the file. E.g. index on ID attribute of instructor relation
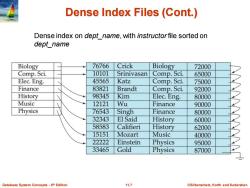
Dense Index Files(Cont.) Dense index on dept name,with instructorfile sorted on dept name Biology 76766 Crick Biology 72000 Comp.Sci. 10101 Srinivasan Comp.Sci. 65000 Elec.Eng. 45565 Katz Comp.Sci. 75000 Finance 83821 Brandt Comp.Sci. 92000 History 98345 Kim Elec.Eng. 80000 Music 12121 Wū Finance 90000 Physics 76543 Singh Finance 80000 32343 El Said History 60000 58583 Califieri History 62000 15151 Mozart Music 40000 22222 Einstein Physics 95000 33465 Gold Physics 87000 Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.7 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Dense Index Files (Cont.) Dense index on dept_name, with instructor file sorted on dept_name
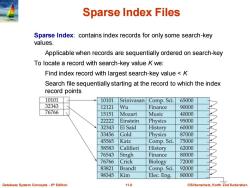
Sparse Index Files Sparse Index:contains index records for only some search-key values. Applicable when records are sequentially ordered on search-key To locate a record with search-key value K we: Find index record with largest search-key value <K Search file sequentially starting at the record to which the index record points 10101 10101 Srinivasan Comp.Sci. 65000 32343 12121 Wu Finance 90000 76766 15151 Mozart Music 40000 22222 Einstein Physics 95000 32343 El Said History 60000 33456 Gold Physics 87000 45565 Katz Comp.Sci. 75000 58583 Califieri History 62000 76543 Singh Finance 80000 76766 Crick Biology 72000 83821 Brandt Comp.Sci. 92000 98345 Kim Elec.Eng. 80000 Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.8 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Sparse Index Files Sparse Index: contains index records for only some search-key values. Applicable when records are sequentially ordered on search-key To locate a record with search-key value K we: Find index record with largest search-key value < K Search file sequentially starting at the record to which the index record points
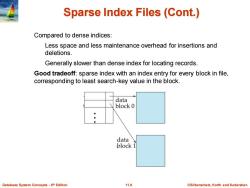
Sparse Index Files (Cont.) Compared to dense indices: Less space and less maintenance overhead for insertions and deletions. Generally slower than dense index for locating records. Good tradeoff:sparse index with an index entry for every block in file, corresponding to least search-key value in the block. data block 0 data block 1 Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.9 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Sparse Index Files (Cont.) Compared to dense indices: Less space and less maintenance overhead for insertions and deletions. Generally slower than dense index for locating records. Good tradeoff: sparse index with an index entry for every block in file, corresponding to least search-key value in the block
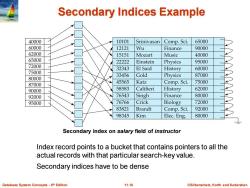
Secondary Indices Example 40000 10101 Srinivasan Comp.Sci. 65000 60000 12121 Wu Finance 90000 62000 15151 Mozart Music 40000 65000 22222 Einstein Physics 95000 72000 32343 El Said History 60000 75000 33456 Gold Physics 87000 80000 87000 45565 Katz Comp.Sci. 75000 90000 58583 Califieri History 62000 92000 76543 Singh Finance 80000 95000 76766 Crick Biology 72000 83821 Brandt Comp.Sci. 92000 98345 Kim Elec.Eng. 80000 Secondary index on salary field of instructor Index record points to a bucket that contains pointers to all the actual records with that particular search-key value. Secondary indices have to be dense Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.10 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Secondary Indices Example Index record points to a bucket that contains pointers to all the actual records with that particular search-key value. Secondary indices have to be dense Secondary index on salary field of instructor

Primary and Secondary Indices Indices offer substantial benefits when searching for records. BUT:Updating indices imposes overhead on database modification--when a file is modified,every index on the file must be updated, Sequential scan using primary index is efficient,but a sequential scan using a secondary index is expensive Each record access may fetch a new block from disk Block fetch requires about 5 to 10 milliseconds,versus about 100 nanoseconds for memory access Database System Concepts-6th Edition 11.11 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 6 11.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Primary and Secondary Indices Indices offer substantial benefits when searching for records. BUT: Updating indices imposes overhead on database modification --when a file is modified, every index on the file must be updated, Sequential scan using primary index is efficient, but a sequential scan using a secondary index is expensive Each record access may fetch a new block from disk Block fetch requires about 5 to 10 milliseconds, versus about 100 nanoseconds for memory access
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 Storage and File Structure.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 1 Introduction(Avi Silberschatz Henry F. Korth S. Sudarshan).ppt
- 电子科技大学:《大数据时代商业模式创新 Business model innovation》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,杜义飞).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《大数据时代商业模式创新 Business model innovation》研究生课程教学资源(讲座)换一个视角看清商业本质.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《大数据时代商业模式创新 Business Model Innovation in the Times of Big Data》研究生课程教学资源(教学大纲,杜义飞).pdf
- 《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)群智感知计算(清华大学:在后台操纵的同时,用户对于污染、扭曲文字的识 刘云浩).pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)基于位置服的务(架构与研究进展).pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)Wi-Fi雷达 - 从RSSI到CSI.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)Survey of Wireless Indoor Positioning Techniques and Systems.pdf
- 南京大学:《物联网技术导论 Introduction of Internet of Things》课程教学资源(参考文献)Location, Localization, and Localizability.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)ZOE - Fast Cardinality Estimation for Large-Scale RFID Systems.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)Every Bit Counts - Fast and Scalable RFID Estimation.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)Energy Efficient Algorithms for the RFID Estimation Problem.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)Counting RFID Tags Efficiently and Anonymously.pdf
- RFID标签数目估算机制研究(参考文献)An Efficient Protocol for RFID Multigroup Threshold-based Classification.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)Using Analog Network Coding to Improve the RFID Reading Throughput.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)Season Shelving Interference and Joint Identification in Large-scale RFID Systems.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)Probabilistic Optimal Tree Hopping for RFID Identification.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)P-MTI - Physical-layer Missing Tag Identification via Compressive Sensing.pdf
- RFID标签识别机制-冲突以及防冲突算法研究(参考文献)Efficient Tag Identification in Mobile RFID Systems.pdf
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Query Processing.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Query Optimization.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Transactions.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Concurrency Control.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Recovery System.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 Database System Architectures.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 Parallel Databases.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 19 Distributed Databases.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 2 Introduction to the Relational Model.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 Data Analysis.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 Information Retrieval.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 22 Object-Based Databases.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 23 XML.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 24 Advanced Application Development.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 25 Advanced Data Types and New Applications.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 26 Advanced Transaction Processing.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 3 Introduction to SQL.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 4 Intermediate SQL.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 5 Advanced SQL.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第六版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 6 Formal Relational Query Languages.ppt
