《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 3 SQL

Chapter 3:SQL Data Definition Basic Query Structure Set Operations Aggregate Functions Null Values Nested Subqueries Complex Queries Views Modification of the Database Joined Relations** Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.2 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Chapter 3: SQL Data Definition Basic Query Structure Set Operations Aggregate Functions Null Values Nested Subqueries Complex Queries Views Modification of the Database Joined Relations**

History IBM Sequel language developed as part of System R project at the IBM San Jose Research Laboratory Renamed Structured Query Language(SQL) ANSI and ISO standard SQL: SQL-86 SQL-89 SQL-92 SQL:1999(language name became Y2K compliant!) SQL:2003 Commercial systems offer most,if not all,SQL-92 features,plus varying feature sets from later standards and special proprietary features. Not all examples here may work on your particular system. Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.3 Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 History IBM Sequel language developed as part of System R project at the IBM San Jose Research Laboratory Renamed Structured Query Language (SQL) ANSI and ISO standard SQL: SQL-86 SQL-89 SQL-92 SQL:1999 (language name became Y2K compliant!) SQL:2003 Commercial systems offer most, if not all, SQL-92 features, plus varying feature sets from later standards and special proprietary features. Not all examples here may work on your particular system

Data Definition Language Allows the specification of not only a set of relations but also information about each relation,including: The schema for each relation. The domain of values associated with each attribute. Integrity constraints The set of indices to be maintained for each relations. Security and authorization information for each relation. The physical storage structure of each relation on disk. Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.4 Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Data Definition Language The schema for each relation. The domain of values associated with each attribute. Integrity constraints The set of indices to be maintained for each relations. Security and authorization information for each relation. The physical storage structure of each relation on disk. Allows the specification of not only a set of relations but also information about each relation, including:

Domain Types in SQL char(n).Fixed length character string,with user-specified length n. varchar(n).Variable length character strings,with user-specified maximum length n. int.Integer(a finite subset of the integers that is machine-dependent). smallint.Small integer(a machine-dependent subset of the integer domain type). numeric(p,d).Fixed point number,with user-specified precision of p digits with n digits to the right of decimal point. real,double precision.Floating point and double-precision floating point numbers,with machine-dependent precision. float(n).Floating point number,with user-specified precision of at least n digits. More are covered in Chapter 4. Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Domain Types in SQL char(n). Fixed length character string, with user-specified length n. varchar(n). Variable length character strings, with user-specified maximum length n. int. Integer (a finite subset of the integers that is machine-dependent). smallint. Small integer (a machine-dependent subset of the integer domain type). numeric(p,d). Fixed point number, with user-specified precision of p digits, with n digits to the right of decimal point. real, double precision. Floating point and double-precision floating point numbers, with machine-dependent precision. float(n). Floating point number, with user-specified precision of at least n digits. More are covered in Chapter 4

Create Table Construct An SQL relation is defined using the create table command: create table r(A1 D1,A2 D2,...,An Dn (integrity-constraint ) (integrity-constraintk)) r is the name of the relation each A,is an attribute name in the schema of relation r D,is the data type of values in the domain of attribute A, Example: create table branch (branch name char(15)not null, branch_city char(30), assets integer) Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Create Table Construct An SQL relation is defined using the create table command: create table r (A1 D1 , A2 D2 , ..., An Dn , (integrity-constraint1 ), ..., (integrity-constraintk )) r is the name of the relation each Ai is an attribute name in the schema of relation r Di is the data type of values in the domain of attribute Ai Example: create table branch (branch_name char(15) not null, branch_city char(30), assets integer)

Integrity Constraints in Create Table not null primary key(A1,,An) Example:Declare branch_name as the primary key for branch create table branch (branch name char(15), branch city char(30), assets integer, primary key(branch_name)) primary key declaration on an attribute automatically ensures not null in SQL-92 onwards,needs to be explicitly stated in SQL-89 Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.7 Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.7 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Integrity Constraints in Create Table not null primary key (A1 , ..., An ) Example: Declare branch_name as the primary key for branch . create table branch (branch_name char(15), branch_city char(30), assets integer, primary key (branch_name)) primary key declaration on an attribute automatically ensures not null in SQL-92 onwards, needs to be explicitly stated in SQL-89

Drop and Alter Table Constructs The drop table command deletes all information about the dropped relation from the database. The alter table command is used to add attributes to an existing relation: alter table r add A D where A is the name of the attribute to be added to relation r and D is the domain of A. All tuples in the relation are assigned null as the value for the new attribute. The alter table command can also be used to drop attributes of a relation: alter table r drop A where A is the name of an attribute of relation r Dropping of attributes not supported by many databases Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.8 Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Drop and Alter Table Constructs The drop table command deletes all information about the dropped relation from the database. The alter table command is used to add attributes to an existing relation: alter table r add A D where A is the name of the attribute to be added to relation r and D is the domain of A. All tuples in the relation are assigned null as the value for the new attribute. The alter table command can also be used to drop attributes of a relation: alter table r drop A where A is the name of an attribute of relation r Dropping of attributes not supported by many databases
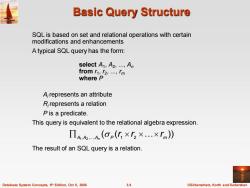
Basic Query Structure SQL is based on set and relational operations with certain modifications and enhancements A typical SQL query has the form: select A1,A2,..,An from r1,f2,,「m where P A,represents an attribute R,represents a relation P is a predicate. This query is equivalent to the relational algebra expression. Π4.A2A(o(化×r2×…×rm)》 The result of an SQL query is a relation. Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.9 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Basic Query Structure SQL is based on set and relational operations with certain modifications and enhancements A typical SQL query has the form: select A1 , A2 , ..., An from r1 , r2 , ..., rm where P Ai represents an attribute Ri represents a relation P is a predicate. This query is equivalent to the relational algebra expression. The result of an SQL query is a relation. ( ( )) A1 ,A2 , ,A P 1 2 m r r r n

The select Clause The select clause list the attributes desired in the result of a query corresponds to the projection operation of the relational algebra Example:find the names of all branches in the /oan relation: select branch name from loan In the relational algebra,the query would be: Ibranch_name(loan) NOTE:SQL names are case insensitive(i.e.,you may use upper-or lower-case letters.) E.g.Branch Name BRANCH NAME branch name Some people use upper case wherever we use bold font. Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.10 Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 The select Clause The select clause list the attributes desired in the result of a query corresponds to the projection operation of the relational algebra Example: find the names of all branches in the loan relation: select branch_name from loan In the relational algebra, the query would be: branch_name (loan) NOTE: SQL names are case insensitive (i.e., you may use upper- or lower-case letters.) E.g. Branch_Name ≡ BRANCH_NAME ≡ branch_name Some people use upper case wherever we use bold font

The select Clause(Cont.) SQL allows duplicates in relations as well as in query results. To force the elimination of duplicates,insert the keyword distinct after select. Find the names of all branches in the loan relations,and remove duplicates select distinct branch name from loan The keyword all specifies that duplicates not be removed. select all branch name from loan Database System Concepts,5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 3.11 ©ilberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 3.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 The select Clause (Cont.) SQL allows duplicates in relations as well as in query results. To force the elimination of duplicates, insert the keyword distinct after select. Find the names of all branches in the loan relations, and remove duplicates select distinct branch_name from loan The keyword all specifies that duplicates not be removed. select all branch_name from loan
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter Advanced Transaction Processing.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 24 Advanced Data Types.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 23 Advanced Application Development.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 22 Distributed Databases.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 Parallel Databases.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 Database System Architectures.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 2 Relational Model.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 19 Information Retrieval.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 Data Analysis and Mining.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 Recovery System.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Concurrency Control.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Transactions.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Query Optimization.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Query Processing.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Indexing and Hashing.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 Storage and File Structure.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 XML.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 1 Introduction(Avi Silberschatz Henry F. Korth S. Sudarshan).ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,附录,英文版)Appendix C Advanced Relational Database Design.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,附录,英文版)Chapter B Hierarchical Model.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 4 Advanced SQL.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 5 Other Relational Languages.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 6 Entity-Relationship Model.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 7 Relational Database Design.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 8 Application Design and Development.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第五版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 9 Object-Based Databases.ppt
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 01 Introduction(Avi Silberschatz Henry F. Korth S. Sudarshan).pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 10 Big Data.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 11 Data Analytics.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 12 Physical Storage Systems.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 13 Data Storage Structures.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 14 Indexing.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 15 Query Processing.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 16 Query Optimization.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 17 Transactions.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 18 Concurrency Control.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 19 Recovery System.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 02 Intro to Relational Model.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 20 Database System Architectures.pptx
- 《数据库系统概念 Database System Concepts》原书教学资源(第七版,PPT课件讲稿,英文版)Chapter 21 Parallel and Distributed Storage.pptx
