南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)05_Operational Semantics

Syntax ot a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantcs Operational Semantics Operabonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Operational Semantics Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics A programming language o Syntax o Semantics Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics A programming language Syntax Semantics Operational Semantics

Syntax ot a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Formal semantics of a programming language o Operational semantics o Denotational semantics o Axiomatic semantics Operatonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Formal semantics of a programming language Operational semantics Denotational semantics Axiomatic semantics Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Operational semantics Operational semantics defines program executions: o Sequence of steps,formulated as transitions of an abstract machine Configurations of the abstract machine include: o Expression/statement being evaluated/executed o States:abstract description of registers,memory and other data structures involved in computation Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Operational semantics Operational semantics defines program executions: Sequence of steps, formulated as transitions of an abstract machine Configurations of the abstract machine include: Expression/statement being evaluated/executed States: abstract description of registers, memory and other data structures involved in computation Operational Semantics
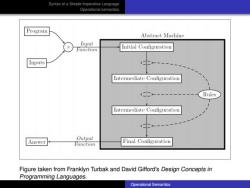
Syntax ot a Simple Imperative Language Cperational semantics Program Abstract Machine Input Function Initial Configuration Inputs Intermediate Configuration Rules Intermediate Configuration Auswer Output Function Final Configuration Figure taken from Franklyn Turbak and David Gifford's Design Concepts in Programming Languages. Operatonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Figure taken from Franklyn Turbak and David Gifford’s Design Concepts in Programming Languages. Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Different approaches of operational semantics oSmall-step semantics: Describe each single step of the execution o Big-step semantics: Describe the overall result of the execution We will explain both in detail by examples Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Different approaches of operational semantics Small-step semantics: Describe each single step of the execution Big-step semantics: Describe the overall result of the execution We will explain both in detail by examples. Operational Semantics

Syntax ot a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics After this class... You should be able to: o write down the evaluation/execution steps,if given the operational semantics rules o formulate the operational semantics rule,if given the informal meaning of an expression/statement Operatonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics After this class... You should be able to: write down the evaluation/execution steps, if given the operational semantics rules formulate the operational semantics rule, if given the informal meaning of an expression/statement Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Outline Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language 2 Operational semantics o Small-step operational semantics oStructural operational semantics(SOS) o Extensions:going wrong,local variable declaration,heap o Contextual semantics (a.k.a.reduction semantics) Big-step operational semantics Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Outline 1 Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language 2 Operational semantics Small-step operational semantics Structural operational semantics (SOS) Extensions: going wrong, local variable declaration, heap Contextual semantics (a.k.a. reduction semantics) Big-step operational semantics Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Syntax (IntExp)e ::n x I e+e l e-e l... (BoolExp)b ::true I false I e=elee b bAb lbvb l... (Comm)c ::skip |X:=e C;C if b then c else c I while b do c Operatonal Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Syntax (IntExp) e ::= n | x | e + e | e − e | . . . (BoolExp) b ::= true | false | e = e | e e | ¬b | b ∧ b | b ∨ b | . . . (Comm) c ::= skip | x := e | c ; c | if b then c else c | while b do c Operational Semantics

Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Syntax (IntExp)e ::n I x I e+e l e-e l... Here n ranges over the numerals 0,1,2,.... We distinguish between numerals,written n,0,1,2,...,and the natural numbers,written n,0,1,2,....The natural numbers are the normal numbers that we use in everyday life,while the numerals are just syntax for describing these numbers. We write Ln]to denote the meaning of n.We assume that Ln]=n, l0=0,l1J=1,.. The distinction is subtle,but important,because it is one manifestation of the difference between syntax and semantics. Operational Semantics
Syntax of a Simple Imperative Language Operational semantics Syntax (IntExp) e ::= n | x | e + e | e − e | . . . Here n ranges over the numerals 0, 1, 2, . . . . We distinguish between numerals, written n, 0, 1, 2, . . . , and the natural numbers, written n, 0, 1, 2, . . . . The natural numbers are the normal numbers that we use in everyday life, while the numerals are just syntax for describing these numbers. We write bnc to denote the meaning of n. We assume that bnc = n, b0c = 0, b1c = 1, . . . . The distinction is subtle, but important, because it is one manifestation of the difference between syntax and semantics. Operational Semantics
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)04_Lambda Calculus.pptx
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)03_Math.pdf
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)02_CoqOverview.pptx
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)01_Introduction(主讲:冯新宇)Formal Semantics of Programming Languages.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9章 CSS3高级应用.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 多媒体技术.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 表单的应用.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 浮动与定位.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 CSS盒子模型.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 CSS3选择器.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 CSS3入门.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 HTML5 页面元素及属性.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 初识HTML5.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(试卷习题)各章习题答案.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第9章 CSS3高级应用_习题.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第8章 多媒体嵌入_习题.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第7章 表单_习题.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第6章 浮动与定位_习题.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第5章 盒子模型_习题.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《html5》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第4章 CSS3选择器_习题.pdf
- 《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(文献资料)Lecture Notes on the Lambda Calculus.pdf
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)06_Denotational Semantics.pdf
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)07_Axiomatic Semantics and Hoare Logic.pdf
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Separation Logic(1/3).ppt
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)09_Shared-Variable Concurrency.pdf
- 《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(文献资料)An Introduction to Separation Logic(Preliminary Draft).pdf
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Separation Logic(2/3).ppt
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Separation Logic(3/3).ppt
- 南京大学:《程序设计语言的形式语义》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)10_Simply-Typed Lambda Calculus.pptx
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教学大纲.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)应用案例.pdf
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(教案讲义)课程标准(适用专业:物联网应用技术).pdf
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第一章 初识C语言(负责人:周鹏梅).ppt
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第三章 结构化程序设计.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第二章 数据类型与运算符.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第七章 结构体和共同体.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第五章 函数.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第八章 文件.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第六章 指针.ppt
- 私立华联学院:《C语言程序设计》课程电子教案(PPT课件)第四章 数组.ppt
