《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:An Analysis of the Law of Total Tricks

An Analysis of the Law of Total Tricks Matt Ginsberg,Eugene,OR In a recent"Bridge World"article(1996年9月号,On the Law of Total Tricks,Matt Ginsberg),I discussed the possibility of creating a computer bridge player based on the development of a fast double-dummy solver.Such a tool would have significant impact on bidding theory as well.Do you want to know if the Law of Total Tricks is valid when the two sides have 21 trumps between them?Generate 1,000 deals fitting that description,analyze them using the double-dummy solver,and you'‖know. This note gives the results of such an analysis.The Law says that the two sides,when playing in their longest suits,can take between them as many tricks as they have trumps.Thus if N/S have a nine-card fit and E/W have a ten-card fit,the two sides can take a total of 19 tricks in the two suits.Is this really a law,or just a vague rule of thumb Here is the answer, where we have selected randomly among trump suits of equal length but always assume that the contract is played from declarer's best side
An Analysis of the Law of Total Tricks Matt Ginsberg, Eugene, OR In a recent “Bridge World” article(1996 年 9 月号, On the Law of Total Tricks, Matt Ginsberg), I discussed the possibility of creating a computer bridge player based on the development of a fast double-dummy solver. Such a tool would have significant impact on bidding theory as well. Do you want to know if the Law of Total Tricks is valid when the two sides have 21 trumps between them? Generate 1,000 deals fitting that description, analyze them using the double-dummy solver, and you'll know. This note gives the results of such an analysis. The Law says that the two sides, when playing in their longest suits, can take between them as many tricks as they have trumps. Thus if N/S have a nine-card fit and E/W have a ten-card fit, the two sides can take a total of 19 tricks in the two suits. Is this really a law, or just a vague rule of thumb ? Here is the answer, where we have selected randomly among trump suits of equal length but always assume that the contract is played from declarer's best side

Length samples average error 14 46944 -0.15 0.63 The columns in the table mean the 15 47281 -0.14 0.64 following: 16 120525 0.10 0.70 17 102184 0.02 0.75 18 69792 -0.01 0.83 1.The left-hand column gives 19 37561 -0.22 0.87 the combined length in the 20 15845 -0.50 0.99 21 5041 -0.89 1.20 two suits. 22 1286 -1.31 1.48 2.The second figure is the 23 237 -1.78 1.83 24 45 -2.22 2.27 number of deals in the Total 446741 -0.05 0.75 sample that met the given conditions. 3.The third figure is the average difference between the number of tricks that can be taken by each side when playing in their longest suit(from the best side)and the combined lengths.Thus the -0.15 on the first line means that,on average,the two sides can take a total of 13.85 tricks (14-0.15).With a combined length of 16 cards,the two sides can take an average of 16.10 tricks. 4.The fourth figure is the average of the error in the Law.So even though the Law is off by only 0.15 tricks if the best fits are of 7 cards each,on any individual deal we can expect the Law to be off by a little more than half a
The columns in the table mean the following: 1. The left-hand column gives the combined length in the two suits. 2. The second figure is the number of deals in the sample that met the given conditions. 3. The third figure is the average difference between the number of tricks that can be taken by each side when playing in their longest suit (from the best side) and the combined lengths. Thus the −0.15 on the first line means that, on average, the two sides can take a total of 13.85 tricks (14 − 0.15). With a combined length of 16 cards, the two sides can take an average of 16.10 tricks. 4. The fourth figure is the average of the error in the Law. So even though the Law is off by only 0.15 tricks if the best fits are of 7 cards each, on any individual deal we can expect the Law to be off by a little more than half a Length samples average error 14 46944 −0.15 0.63 15 47281 −0.14 0.64 16 120525 0.10 0.70 17 102184 0.02 0.75 18 69792 −0.01 0.83 19 37561 −0.22 0.87 20 15845 −0.50 0.99 21 5041 −0.89 1.20 22 1286 −1.31 1.48 23 237 −1.78 1.83 24 45 −2.22 2.27 Total 446741 −0.05 0.75

trick--it just overestimates approximately as often as it underestimates. To evaluate the specific actions suggested by the Law,we need a bit more detail.Here it is: Error Length samples -4-3-2-1 0 +1 +2+3 +4 14 46,9440.10.64.827.046.618.22.40.20.0 15 47,2810.10.65.026.645.719.22.60.20.0 16 120,5250.10.53.820.742.426.35.50.70.1 17 102,1840.10.65.223.539.424.55.80.70.1 18 69,7920.10.87.125.036.022.86.91.20.1 19 37,5610.11.310.728.933.818.85.41.00.1 20 15,8450.23.116.431.529.913.74.40.70.0 21 5,0410.77.424.031.923.310.12.30.30.0 22 1,2862.713.728.630.217.75.41.60.10.0 23 2374.225.729.126.212.22.10.00.00.0 24 4511.133.328.922.22.22.20.00.00.0 Total446,7410.10.96.224.540.022.45.10.70.1 In this table,the figures give the probability that the Law is off by the given amount.Thus,with 16 cards in the two suits, there is a 42.4%chance that the Law is correct,a 26.3%chance that 17 tricks can be taken by the two sides,and so on. Do these results validate or invalidate the Law Something in between
trick -- it just overestimates approximately as often as it underestimates. To evaluate the specific actions suggested by the Law, we need a bit more detail. Here it is: Error Length samples −4 −3 −2 −1 0 +1 +2 +3 +4 14 46,944 0.1 0.6 4.8 27.0 46.6 18.2 2.4 0.2 0.0 15 47,281 0.1 0.6 5.0 26.6 45.7 19.2 2.6 0.2 0.0 16 120,525 0.1 0.5 3.8 20.7 42.4 26.3 5.5 0.7 0.1 17 102,184 0.1 0.6 5.2 23.5 39.4 24.5 5.8 0.7 0.1 18 69,792 0.1 0.8 7.1 25.0 36.0 22.8 6.9 1.2 0.1 19 37,561 0.1 1.3 10.7 28.9 33.8 18.8 5.4 1.0 0.1 20 15,845 0.2 3.1 16.4 31.5 29.9 13.7 4.4 0.7 0.0 21 5,041 0.7 7.4 24.0 31.9 23.3 10.1 2.3 0.3 0.0 22 1,286 2.7 13.7 28.6 30.2 17.7 5.4 1.6 0.1 0.0 23 237 4.2 25.7 29.1 26.2 12.2 2.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 24 45 11.1 33.3 28.9 22.2 2.2 2.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 Total 446,741 0.1 0.9 6.2 24.5 40.0 22.4 5.1 0.7 0.1 In this table, the figures give the probability that the Law is off by the given amount. Thus, with 16 cards in the two suits, there is a 42.4% chance that the Law is correct, a 26.3% chance that 17 tricks can be taken by the two sides, and so on. Do these results validate or invalidate the Law ? Something in between

Clearly as the number of trumps grows,the Law becomes less and less reliable,consistently overestimating the number of tricks that can be taken by the two sides. But let's look at a lower-level,competitive situation. Suppose that both you and your opponents appear to have 9-card fits,and your opponents have bid 3.Holding spades, do you compete further? It is a consequence of the Law that you should.Assuming that the opponents have not voluntarily missed a game,9 tricks will be their limit,leaving nine for you.If 18 tricks are available,competing is correct. The table shows that 18 tricks are available 67%of the time (the Law has to be either correct or conservative in estimating the number of tricks that can be taken).So if you follow the Law,you will make the correct decision 67%of the time. For better or worse,suppose you compete to 3.The opponents,if they make the decision suggested by the Law,will not bid on if vulnerable,and probably will bid on if not vulnerable, preferring the 100 penalty to going 140 defending spades.And if you would have gone down in 3,they will actually make 4,taking 10 of the presumed 18 tricks that are available
Clearly as the number of trumps grows, the Law becomes less and less reliable, consistently overestimating the number of tricks that can be taken by the two sides. But let's look at a lower-level, competitive situation. Suppose that both you and your opponents appear to have 9-card fits, and your opponents have bid 3 . Holding spades, do you compete further? It is a consequence of the Law that you should. Assuming that the opponents have not voluntarily missed a game, 9 tricks will be their limit, leaving nine for you. If 18 tricks are available, competing is correct. The table shows that 18 tricks are available 67% of the time (the Law has to be either correct or conservative in estimating the number of tricks that can be taken). So if you follow the Law, you will make the correct decision 67% of the time. For better or worse, suppose you compete to 3 . The opponents, if they make the decision suggested by the Law, will not bid on if vulnerable, and probably will bid on if not vulnerable, preferring the 100 penalty to going 140 defending spades. And if you would have gone down in 3 , they will actually make 4 , taking 10 of the presumed 18 tricks that are available

Are these decisions right? The decision to pass 3 vulnerable is right,provided that at most 18 tricks are available to the two sides.Looking at the table,this happens 69%of the time.The decision to bid on is right if at least 18 tricks are available,just as in the previous paragraph--so that Law leads you to the right decision 67%of the time in this case. In general,the Law will lead you to do the right thing when it's either exactly right or when it's wrong in the "right"direction. Bidding on is generally right if the Law is conservative;passing is right if the Law is overestimating the number of available tricks. Either way,the probabilities are similar whenever the suit lengths combine to 20 cards or fewer,which they will 99%of the time.So here's the straight story on the Law: Provided that the trump lengths combine to 20 cards or fewer,the Law of Total Tricks will lead you to correct decisions approximately 70%of the time. Does that mean you should follow it That depends, I suppose,on whether you can make competitive judgments correctly more or less than 70%of the time without it
Are these decisions right? The decision to pass 3 vulnerable is right, provided that at most 18 tricks are available to the two sides. Looking at the table, this happens 69% of the time. The decision to bid on is right if at least 18 tricks are available, just as in the previous paragraph -- so that Law leads you to the right decision 67% of the time in this case. In general, the Law will lead you to do the right thing when it's either exactly right or when it's wrong in the "right" direction. Bidding on is generally right if the Law is conservative; passing is right if the Law is overestimating the number of available tricks.Either way, the probabilities are similar whenever the suit lengths combine to 20 cards or fewer, which they will 99% of the time. So here's the straight story on the Law: Provided that the trump lengths combine to 20 cards or fewer, the Law of Total Tricks will lead you to correct decisions approximately 70% of the time. Does that mean you should follow it ? That depends, I suppose, on whether you can make competitive judgments correctly more or less than 70% of the time without it
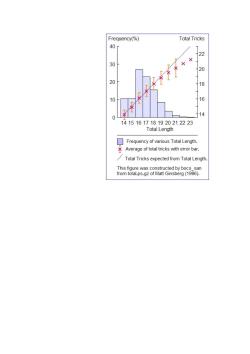
Frequency(%) Total Tricks 40r 22 + 30 20 20 18 10 16 14 0 14151617181920212223 Total Length Frequency of various Total Length. Average of total tricks with error bar. Total Tricks expected from Total Length. This figure was constructed by boco_san from total.ps.gz of Matt Ginsberg(1996)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:21世纪二盖——叫牌体系.doc
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)围棋基本知识.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)野外活动危险预测.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)篮球裁判理论与实践.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)排球运动技战术鉴赏 Volleyball technique and tactics appreciation.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)体育游戏课程简介.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)体育游戏的创编.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)足球文化与赛事欣赏.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)足球文化与赛事欣赏——足球比赛阵型.ppt
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(讲稿PPT课件)足球文化与赛事欣赏——德国国家队教练.pptx
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(教案讲义)FIFA 足球裁判规则 Laws of the Game 2012-2013.pdf
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(教案讲义)足球文化与赛事欣赏.doc
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(教案讲义)生命安全与救援.doc
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(教案讲义)桥牌教案.doc
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(教案讲义)排球运动技战术鉴赏.docx
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(教案讲义)体适能理论与实(体适能评定理论与方法).doc
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(教案讲义)体育游戏理论.doc
- 上海交通大学:《体育文化类通识核心课程》教学资源(教案讲义)体育游戏.doc
- 大学体育:《乒乓球》课程教学资源(精品教材,共四章,彩色版).pdf
- 西安石油大学:《世界极限飞盘运动》课程教学资源(书籍资料)极限飞盘术语大全.pdf
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:The Bridge World Magazine 1969——The Law of Total Tricks.docx
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:桥牌双人赛策略.pdf
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:第一堂课.pdf
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:《桥牌与博弈论》教学大纲.doc
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:标准美国黄卡.pdf
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:现代桥牌防守信号(王玉富).pdf
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:桥牌单套打法(单花色组合成功率打法一览表).pdf
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:桥牌牌型分布概率.pdf
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:桥牌约定卡——精确叫牌法.doc
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:桥牌实用战术《概率和安全》PDF电子书.pdf
- 《桥牌与博弈论》课程教学资源:美国标准黄卡约定卡.doc
- 《瑜伽与健康》课程教学资源(学术论文)Yoga and Mindfulness:Clinical Aspects of an Ancient Mind/Body Practice.pdf
- 《瑜伽与健康》课程教学资源(学术论文)Yoga clinical research review.pdf
- 《瑜伽与健康》课程教学资源(学术论文)Yoga for depressionThe research evidence.pdf
- 《瑜伽与健康》课程教学资源(学术论文)健身气功与现代瑜伽之比较研究(广州体育学院:魏开源).pdf
- 《瑜伽与健康》课程教学资源(学术论文)凯洛斯·几·缘起·瑜伽——对中西印文化中几个概念的会通(中国美术学院:朱文信).pdf
- 《瑜伽与健康》课程教学资源(学术论文)印度传统文化的哲学透视(黑龙江大学:姜玉洪).pdf
- 中央民族大学硕士学位论文:印度瑜伽的文化传承与教育研究.pdf
- 《柳州师专学报》:泰戈尔与老子之“和谐论”哲学美学观的阐释与比较(西南大学:王晓声).pdf
- 《中华物理医学与康复杂志》:瑜伽辅助应用于临床康复治疗的国外研究进展(王会儒).pdf
